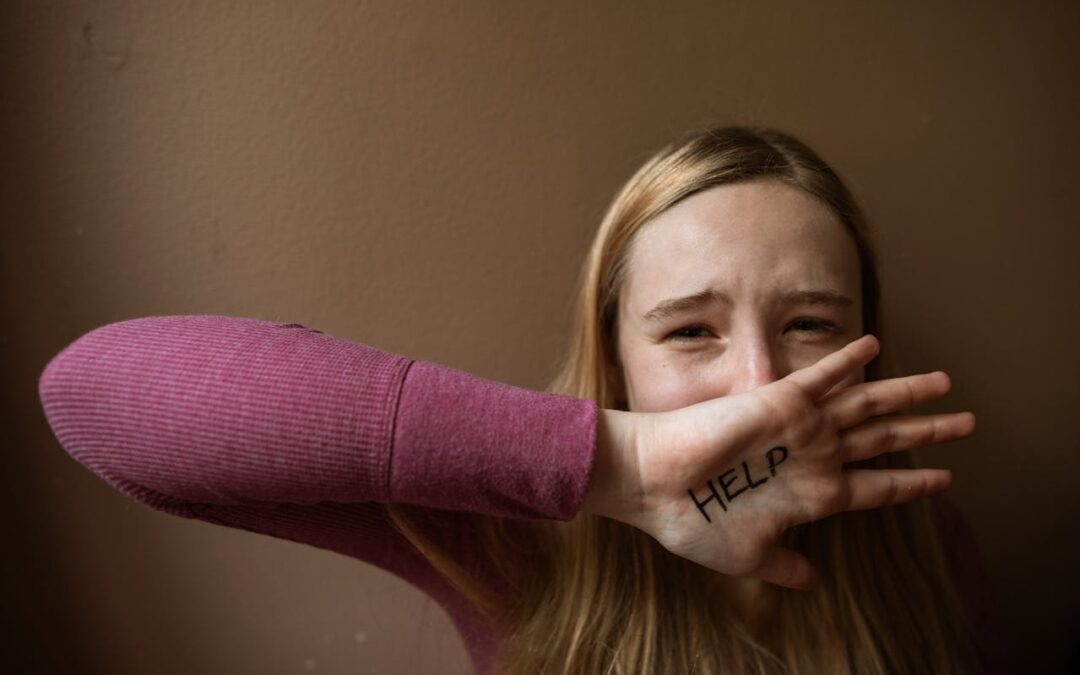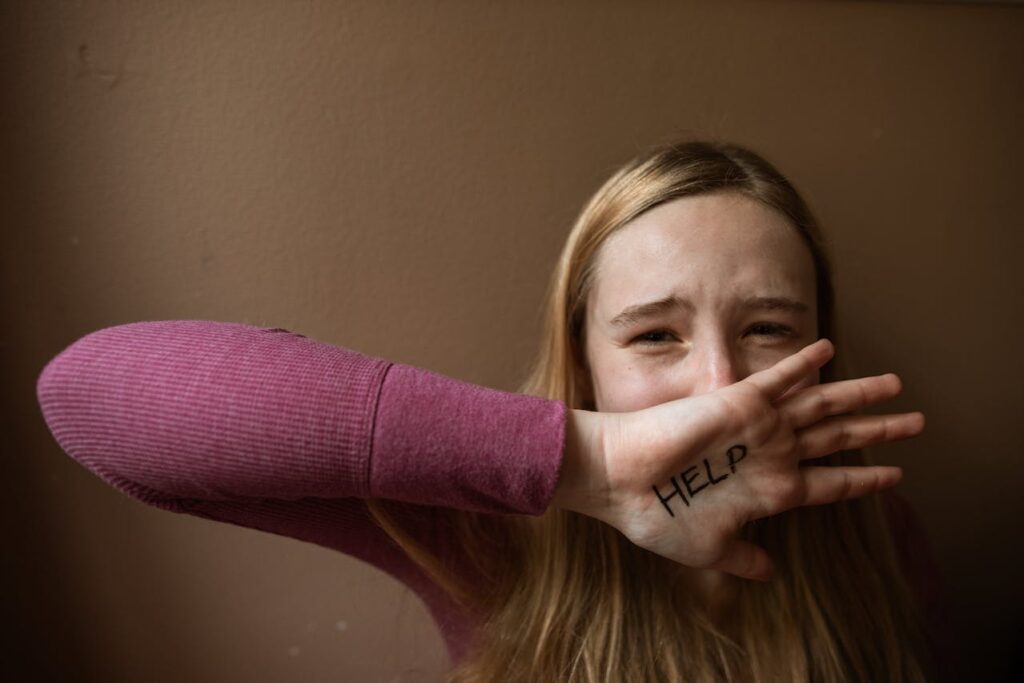loading...

by Sadaqut | Jul 19, 2024 | Educational
The Center for Disease Control and Prevention says suicide is a serious public health issue.
For this reason, mental health professionals should consider suicide intervention training to identify, assess, and manage individuals at risk. Advanced training can enhance patient outcomes and save lives.
And because suicide is not merely an impulsive act but often results from multiple interrelated factors, training in suicide prevention is essential.

Here’s what you need to know:
Key Highlights:
1. Mental health professionals need to undergo advanced suicide intervention training to identify, assess, and manage individuals at risk.
2. Advanced training programs focus on enhancing clinicians’ ability to conduct thorough risk assessments and develop tailored intervention plans for suicidal patients.
3. Effective suicide intervention involves developing a safety plan, which includes identifying warning signs, coping strategies, and sources of support for the patient during a crisis.
4. Communication skills are crucial in suicide intervention, emphasizing active listening, validation, and non-judgmental communication to build a strong therapeutic partnership.
5. Suicide prevention training provides strategies for self-care and professional support for clinicians, helping to prevent burnout and promote long-term sustainability in the profession.
With this in mind, let’s dive into how health practitioners can take advantage of suicide intervention strategies through specialized courses.
What Are the Intervention Strategies for Suicidal Clients?
According to the National Institute of Mental Health, suicide is the number one cause of death in the United States. And it affects everyone, regardless of gender, race, ethnicity, or age. Because suicidal causes are complex, interventions must include various approaches to get to the root of the problem.
Here are some issues to consider:
Advanced training programs
Advanced training programs enhance clinicians’ ability to conduct thorough risk assessments. Assessing suicide risk involves evaluating various factors, such as previous suicide attempts, mental health history, current stressors, and protective factors.
Training programs teach health professionals to ask the right questions and interpret the answers accurately, ensuring they don’t overlook any critical detail. This in-depth assessment creates a robust foundation for effective intervention. It enables you to develop a tailored intervention plan for suicidal patients.
Safety Plan
Developing a safety plan is a crucial component of suicide intervention. A well-structured safety plan involves identifying warning signs, coping strategies, and sources of support the patient can rely on during a crisis. Advanced training courses guide practitioners in producing effective, individualized, and practical safety plans.
They should serve as a vital resource for patients, providing them with a clear course of action when they feel overwhelmed.
Communication Skills
Communication skills are also a key focus in suicide prevention training. Therapists must create a safe and empathetic environment where patients feel comfortable sharing their thoughts and feelings.
Specialized training emphasizes active listening, validation, and non-judgmental communication. These skills help build a strong therapeutic partnership, which is essential for effective intervention.
Dealing with the Emotional Impact
Managing the emotional impact of working with suicidal patients is another important aspect of advanced training. Clinicians often experience significant stress and emotional burden in these cases.
Training courses provide strategies for self-care and professional support, helping counselors maintain their own well-being while providing the best possible care to their patients.
This aspect of training helps prevent burnout and promotes long-term sustainability in the profession.
Cultural factors
One of the critical elements of effective suicide intervention is to recognize and address cultural factors that influence suicidal behavior. Different cultures have varying beliefs, stigmas, and attitudes towards mental health and suicide.
Training at the highest level equips professionals with cultural competence, enabling them to understand and respect these differences. Ultimately, this results in culturally sensitive and appropriate communication and interventions.
Evidence-based practices
Evidence-based practices are central to advanced suicide intervention training. Therapists learn to apply effective, research-based interventions. For example, Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT), and other evidence-based approaches are part of these programs.
These therapies help patients develop coping mechanisms, challenge negative thought patterns, and build resilience. Incorporating these evidence-based practices into treatment plans leads to positive outcomes.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are also an integral part of suicide prevention training. Counselors must manage complex dilemmas, such as balancing patient confidentiality with protecting individuals from harm.
Advanced training guides how to approach these challenges, helping practitioners make informed and ethical decisions. Understanding the legal and ethical frameworks surrounding suicide intervention results in responsible and professional care.
Collaborations
Collaboration with other healthcare providers and community resources makes suicide intervention effective. Training programs focus on a multidisciplinary approach where suicide experts partner with psychiatrists, primary care providers, social workers, and other professionals.
This collaborative approach makes patient care comprehensive, addressing all aspects of their well-being. Program attendees also learn how to connect with patients through community resources such as crisis hotlines, support groups, and emergency services.
Ongoing education and training
Ongoing education and training are necessary to maintain proficiency in suicide treatment. This is because mental health is constantly evolving, with new research and best practices emerging regularly.
Specialized training courses encourage students to stay updated with the latest developments through continuous education. This commitment to lifelong learning equips clinicians with the most current and effective tools for suicide therapies.
Here are more benefits of continuing professional development:
- Training programs include opportunities for practical application through role-playing, simulations, and supervised practice. These hands-on experiences build confidence and competence in suicide intervention.
- Learners can apply their skills in a controlled environment, receive feedback, and refine their techniques. This practical aspect of training bridges the gap between theory and practice, preparing practitioners for real-world scenarios.
- Patients benefit from therapists with a wealth of experience through comprehensive, compassionate, and effective care. As a result, suicidal clients can feel understood, supported, and hopeful when they receive care.
- Also, specialized training can contribute to the goal of reducing suicide rates and improving mental health at a community and societal level.
Mental health organizations
Mental health organizations and institutions also support advanced suicide intervention training. Providing access to high-quality training programs, resources, and ongoing professional development opportunities is essential. Institutions that prioritize training demonstrate a commitment to excellence in patient care and advance the mental health profession.
If you want advanced training in suicide intervention, several reputable programs and organizations offer expert-driven courses. The American Association of Suicidology (AAS), the Suicide Prevention Resource Center (SPRC), and the National Suicide Prevention Lifeline (NSPL) are excellent starting points.
These bodies provide widely recognized resources, training programs, and certification opportunities.
Make Headway into Effective Suicide Interventions
Ready to jumpstart your knowledge about suicide therapies? Online CE Credits provides one of the most up-to-date certifications from experienced instructors. Learning the lessons is a breeze since you can complete them at your own pace, anywhere, anytime.

Select your relevant course from the programs below:
- Suicide and Parasuicide in BPD: Evidence-Based Strategies
- Suicide Assessment and Documentation: Using the L-RAMP
- At the Intersections: Suicide Prevention for BIPOC & 2SLGBTQIA+ Youth
Take a Leading Role in Suicidal Intervention
Ultimately, the goal of advanced suicide prevention training is to save lives.
Training courses equip you with the skills, knowledge, and confidence to intervene effectively and make a significant impact. Also, you can create a long-lasting difference in individuals’ lives at risk of suicide as you give them hope and support during their darkest moments.
Ongoing education is a great investment in the patient’s well-being and the broader community.
Now Is the Time to Boost Your Credentials and Skills:
Advanced training in suicide intervention is a vital part of your professional development. It improves your ability to assess risk, develop safety plans, communicate effectively, manage your own well-being, and apply evidence-based practices.
Additionally, specialized courses put you on the right path to prevent suicide and promote mental health for clients. And Online CE Credits has affordable courses to help you kickstart your journey without breaking the bank. Stop feeling stuck at your current skill level. Get advanced training and certifications to level up your career today!

by Sadaqut | Jul 19, 2024 | Certificate
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) therapy has proven to be a groundbreaking approach in trauma treatment and other psychological disorders.
And negative cognitions are central to this method. These are the deeply ingrained, often unconscious beliefs individuals hold about themselves. As a result, they can prolong distress and hinder healing.
Understanding and using negative biases within the EMDR framework allows therapists to improve therapeutic outcomes.

Read on to dig deeper into EMDR therapy and how you can harness it to provide better patient care.
What Is EMDR Trauma Therapy?
EMDR is a treatment that uses psychotherapy to enable individuals to recover from distressing, traumatic events. According to the American Psychology Association (APA), the therapy encourages the patient to concentrate on the trauma memory to let them move past their stressful situation.
What Are Negative Cognitions?
Negative cognitions are self-referential, negative beliefs individuals develop, usually as a result of traumatic experiences. These cognitions can manifest in various forms, such as “I am worthless,” “I am powerless,” or “I am unlovable.”
They reflect the individual’s internalized response to trauma and are often irrational and overly generalized. Despite their irrationality, these beliefs can have a powerful hold on a person’s psyche, affecting their emotions, behaviors, and overall mental health.
EMDR Counseling Associates identifies the feelings below as negative beliefs:
- I don’t deserve love.
- I am a bad person.
- I am terrible.
- I am worthless (inadequate).
- I am shameful.
- I am not lovable.
- I am not good enough.
- I deserve only bad things.
What’s the Role of Negative Cognitions in EMDR Therapy?
In EMDR therapy, identifying and addressing negative distortions is a critical step. This is because you need to help the patient reprocess them, guiding them through the therapeutic process.
Also, therapists can allow clients to confront traumatic memories and replace negative thinking with more adaptive, positive beliefs.
How To Identify Negative Biases
The therapist and the client should work together to identify negative cognitions. For example, you can use various techniques to uncover these beliefs, such as direct questioning, exploring the client’s narrative, and examining their emotional responses to specific memories or situations.
You should also create a safe and supportive environment to let the clients explore their thoughts and feelings without judgment. For example, if the clients are feeling uncomfortable discussing a particular issue, you can give them time to pause and take a break before continuing the conversation.
How to Uncover Negative Cognitions: 3 Techniques?
Discovering negative biases can be challenging, as they are often deeply ingrained and unconscious. However, several techniques can be helpful in this process:
The Float Back Technique
The Float Back Technique is a powerful tool to identify negative cognitions linked to specific traumatic memories. This method involves asking the client to focus on a current distressing situation and then “floating back” to earlier memories that elicit similar feelings.
This approach helps therapists find out about the original traumas and the negative beliefs that stem from them.
Cognitive Interweave
Cognitive interweave involves integrating cognitive restructuring into the EMDR process. Therapists can introduce alternative, more adaptive thoughts during the reprocessing phases to challenge and change negative thinking. This technique allows clients to develop new perspectives and weaken the hold of irrational beliefs.
Mindfulness and Body Awareness
Encouraging clients to practice mindfulness and body awareness can also reveal negative distortions. They can become more aware of the underlying beliefs driving their distress by paying attention to bodily sensations and emotional responses.
How To Address Negative Cognitions in EMDR Therapy
Once you have identified negative cognitions, the next step is to address and reprocess them. EMDR therapy involves eight phases, each helping resolve traumatic memories and change negative beliefs.

History Taking and Treatment Planning
During the initial phase, therapists gather detailed information about the client’s history, including traumatic experiences and presenting issues. This stage also involves identifying the negative beliefs and developing a treatment plan tailored to the client’s needs.
Preparation
For this step, practitioners educate clients about the EMDR process, establish a therapeutic alliance, and teach self-soothing techniques to manage distress. It ensures patients feel safe and ready for the reprocessing work.
Assessment
In the assessment phase, clinicians identify the specific traumatic memory to target and the associated negative cognition. They also establish a positive perception that the client would prefer to believe. For example, if the negative cognition is “I am powerless,” the positive belief might be “I am in control.”
Some more examples include:
RESPONSIBILITY/ I DID SOMETHING “WRONG”
| Negative Thinking |
Positive Thinking |
| I should have done something. |
I did the best I could. |
| I did something wrong. |
I learned (can learn) from it. |
| I should have known better |
I do the best I can (I can learn). |
Source
Desensitization
Desensitization involves processing the traumatic memory while simultaneously focusing on bilateral stimulation (BLS), such as eye movements, taps, or tones. This reduces the emotional intensity of the memory and weakens negative cognition.
Installation
Installation strengthens the positive cognition identified in the assessment phase. Clients focus on positive beliefs while engaging in BLS. It allows the new thinking to become more deeply ingrained.
Body Scan
During the body scan phase, clients are asked to focus on their physical sensations while thinking about their traumatic memory and positive cognition. This step helps identify any residual distress and reinforces the integration of the new belief.
Closure
Closure ensures clients leave each session feeling stable and safe. Practitioners guide patients through self-soothing techniques and grounding exercises and review progress during the session.
Reevaluation
Reevaluation occurs at the beginning of each subsequent session. Clinicians assess the client’s progress, determine if the targeted memory has been fully processed, and decide on the next steps in treatment.
Empower Yourself with Evidence-Based EMDR Therapy
If you want to advance your career in EMDR, Online CE Credits is a gold mine of on-demand CEU courses available online 24/7. The training programs, instructed by seasoned therapists, offer actionable insights from decades of experience. Here are examples of EMDR therapy certifications:
- Advanced EMDR Skills for Complex Trauma
- EMDR for Anxiety: Basic EMDR Skills and Anxiety Modifications
- EMDR Skills: Practical Modifications for Children & Other Populations
- Integrative Advanced Workshop: EMDR, Ego States, IFS
- Must-Have EMDR Skills for Online Therapy (even if you aren’t trained in EMDR!)
How to Improve EMDR Therapy Through Creative Interventions
While the standard EMDR principles are effective, incorporating creative interventions can boost the therapeutic process. These strategies help patients engage more deeply with their negative perceptions and simplify the reprocessing work.
Art Therapy Techniques
Art therapy techniques provide clients with alternative ways to express and explore their negative cognitions. Through drawing, painting, or sculpting, clients can externalize their beliefs and gain new insights. Art therapy can also be integrated into the desensitization phase, using creative activities as a form of bilateral stimulation.
Narrative Therapy Approaches
Narrative therapy approaches can complement EMDR by helping clients re-author their stories. They can create new, empowering stories about their lives by identifying and challenging the dominant narratives driven by negative cognitions.
This process is effective in the installation phase, reinforcing positive beliefs through the re-authoring of personal narratives.
Somatic Experiencing
Somatic experiencing focuses on the body’s response to trauma and can be used alongside EMDR to address negative cognitions. Counselors can encourage the release of trauma stored in the body by helping clients become more attuned to their bodily sensations This approach strengthens the body scan phase and promotes holistic healing.
Why Therapist Competence and Client Readiness Are Important?
The success of EMDR therapy in addressing negative cognitions relies heavily on the therapist’s competence and the client’s readiness. Health professionals must be well-versed in EMDR techniques and understand trauma and its impact on cognition. They should also possess strong skills in creating a safe, empathetic therapeutic environment.
Client readiness is equally crucial. Patients should be emotionally stable and familiarize themselves with coping resources before engaging in EMDR therapy. For example, pre-treatment preparation may involve stabilization techniques, psychoeducation, and supportive therapies.
Unearth Negative Distortions in EMDR Therapy
Understanding and using negative biases within EMDR therapy is a powerful approach to healing trauma and promoting psychological well-being. Practitioners can help clients transform their self-perception and lead healthier, more fulfilling lives by identifying, addressing, and reprocessing deeply ingrained beliefs.
Dominate Your EMDR Therapy Field with Online CEUs
Whether a beginner or an expert in EMDR Therapy, Online CE Credits offers expert-driven training programs to meet your needs. You can select from over 250 accredited certifications. The best part? You can finish the lessons at affordable rates and at your own pace. Stop losing clients to clinicians with specialized skills. Get cutting-edge training to expand your service offerings.

by Sadaqut | Jul 19, 2024 | Certificate
Mental health specialists should earn continuing education units (CEUs) to provide clients with the best possible care. Also, therapists must stay abreast of new methodologies, theories, and practices to advance their careers.
For these reasons, mindful CEUs offer a unique approach to professional growth. Integrating mindfulness practices can improve therapeutic skills while promoting self-care.

Here’s what you need to know:
What Is Mindfulness in Therapy?
Mindfulness, or mindfulness-based cognitive therapy (MBCT), is the practice of being present and fully engaged in the moment without judgment.
Also, ScienceDirect.com says:
Mindfulness-based therapies use meditation, relaxation, and awareness exercises to help focus on the present moment, aiming over time to experience day to day situations and stressors in nonjudgmental and non-reactionary ways.
Why Is Mindfulness Important for Therapists?
Incorporating mindfulness into CEUs deepens your therapeutic skills. Here’s how:
Enhancing Therapeutic Process
Emotion regulation describes a person’s ability to effectively manage and respond to an emotional experience. So mindfulness training can help you manage your own emotions more effectively.
You can maintain a calm and centered presence during sessions by cultivating an awareness of your emotional states and reactions. Emotional regulation provides a stable and supportive environment when dealing with clients’ intense emotions.
Enhanced Empathy and Attunement
Mindfulness practices encourage you to tune into your clients more deeply. This understanding allows therapists to pick up on subtle cues and non-verbal communication. As a result, it fosters a strong therapeutic partnership.
Clients feel more understood and valued, which can significantly improve therapeutic outcomes.
Increased Focus and Presence
Effective therapy depends on a therapist’s ability to stay present. Mindful CEUs train you to sustain your focus and stay fully engaged with your clients. This presence lets you better grasp the client’s issues and models mindfulness for patients, encouraging them to develop similar skills.
Promoting Self-Care and Preventing Burnout
The Society for the Advancement of Psychotherapy says practitioners often face high levels of stress and emotional exhaustion, which can lead to burnout. Mindful CEUs place a strong emphasis on self-care, equipping therapists with tools to manage stress and maintain their well-being.
Stress Reduction
Mindfulness practices, such as meditation and deep-breathing exercises, are effective tools for stress reduction. Regular practice enables you to lower your stress levels, which can improve your overall quality of life and professional performance.
Increased Self-Awareness
Self-awareness is an integral part of mindfulness. You can become more aware of your own needs, boundaries, and limits by engaging in mindfulness training. This self-awareness allows you to implement effective self-care strategies and prevent burnout.
Enhanced Resilience
Mindfulness cultivates resilience by helping therapists develop a balanced perspective on challenges and setbacks. You can learn to approach difficulties with a non-judgmental attitude. And this can reduce the stress’s impact and let you bounce back from adversity.
Improving Client Outcomes with Mindful Interventions
Clients benefit significantly when therapists integrate mindfulness into their practice. Mindful interventions can lead to improved client outcomes in various ways.

Reduction in Anxiety and Depression
The National Institute of Mental Health says mindfulness-based interventions (MBIs) have been shown to reduce anxiety and depression symptoms.
You can provide your patients with practical tools to manage their mental health if you teach mindfulness techniques. These approaches empower clients to regulate their emotions, reduce rumination, and cultivate a sense of inner peace.
Improved Emotional Regulation in Clients
Clients who practice mindfulness learn to observe their thoughts and emotions without getting overwhelmed by them. This improved emotional regulation can lead to healthier coping mechanisms and better overall mental health.
Enhanced Therapeutic Relationship
Successful therapy relies heavily on the therapeutic relationship. You can bring a heightened sense of presence and empathy into sessions when you practice mindfulness. Clients often feel more connected and understood, which strengthens the therapeutic alliance and promotes positive outcomes.
How To Introduce Mindfulness to a Client
Integrating mindfulness into therapy involves more than just teaching clients meditation techniques. It requires therapists to embody mindfulness in their professional practice.
Mindful Listening
Mindful listening involves giving full attention to the client without distractions or preconceived judgment. By practicing mindfulness, you can create a safe space for clients to express themselves honestly.
Psychology for Today recommends the following mindfulness listening tips:
- Listen beyond the words: Pay attention to nonverbal cues like body language, voice tone, and silence.
- Focus on the “here and now”: Gauge the client’s presence in the present moment.
- Be aware of your own reactions: Observe your own thoughts and feelings triggered by the client to ensure unconditional acceptance.
- Practice deep listening: Listen not just to the client’s words, but also to their unspoken feelings, beliefs, and assumptions.
Mindful Reflection
You can also use mindfulness to reflect on your practice and interactions with clients. This reflection helps identify areas for improvement and promotes continuous professional growth. It also enables you to align with your clients’ needs and goals.
Mindfulness-Based Therapies
Therapists can integrate mindfulness-based therapies, such as Mindfulness-Based Stress Reduction (MBSR) or Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT), into their practice. These evidence-based approaches combine traditional therapeutic techniques with mindfulness practices, offering clients comprehensive support.
How Do I Practice Mindfulness as a Therapist?
Incorporating mindfulness into daily routines can be transformative for clinicians. Here are several mindful techniques you can practice daily to enhance your professional and personal well-being.
Mindful Breathing
One of the simplest and most effective mindfulness techniques is mindful breathing. Take a few minutes each day to focus on your breath. Inhale deeply through your nose, hold for a few seconds, and exhale slowly through your mouth. This practice helps ground you in the present moment, reducing stress and promoting a sense of calm.
Body Scan Meditation
The body scan meditation involves paying attention to different parts of your body, starting from your toes and moving up to your head. Notice any sensations, tension, or discomfort without judgment. This approach enhances body awareness and helps release physical tension, promoting relaxation and mental clarity.
Mindful Walking
Transform your daily walk into a mindfulness practice. Pay attention to the sensation of your feet touching the ground, the rhythm of your steps, and the surrounding environment. Mindful walking helps clear your mind, reduce stress, and increase your connection with the present moment.
Gratitude Practice
Begin or end your day with a gratitude practice. Take a few moments to reflect on three things you are grateful for. This simple exercise shifts your focus from what’s lacking to what’s abundant in your life, developing a positive mindset and emotional well-being.
Mindful Eating
Mindful eating involves paying full attention to the experience of eating and drinking. Utah State University says it’s about wellness and how we eat, not what we eat. So notice the colors, smells, textures, and flavors of your food.
And the Harvard School of Public Health states that mindfulness eating can improve an individual’s psychological well-being. Eating mindfully can improve digestion, reduce overeating, and increase your enjoyment of meals, making it a valuable self-care practice.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Progressive muscle relaxation (PMR) is a technique where you tense and then slowly release different muscle groups in your body. Start with your feet and work your way up to your head. This practice reduces physical tension and promotes relaxation, making it an excellent tool for stress management.
Mindful Journaling
Spend a few minutes each day writing in a journal. Reflect on your thoughts, feelings, and experiences without judgment. Mindful journaling helps process emotions, gain insights, and track your progress, contributing to emotional regulation and self-awareness.
Loving-Kindness Meditation
Loving-kindness meditation involves silently repeating phrases of goodwill and compassion towards yourself and others. For example, “May I be happy, may I be healthy, may I live with ease.” Extend these wishes to loved ones, acquaintances, and even difficult individuals. This technique builds empathy, compassion, and emotional resilience.
Mindful Stretching
Incorporate mindful stretching into your daily routine. Pay attention to the sensations in your muscles as you stretch, breathe deeply, and move slowly. Mindful stretching increases flexibility, reduces tension, and promotes a sense of physical well-being.
Digital Detox
Set aside specific times each day to disconnect from digital devices. Use this time to engage in mindfulness practices, connect with loved ones, or spend time in nature. A digital detox reduces screen-induced stress and enhances your ability to be present.
You can cultivate a more mindful approach to life and work by integrating these mindful techniques into your daily routine.
How To Choose the Right Mindful CEU Program
Be sure to consider the following factors when selecting mindful CEUs to meet your professional and personal development needs:
Accreditation and Quality
Ensure the program is accredited and recognized by relevant professional bodies. Experts in mindfulness and mental health frequently design and teach high-quality programs.
Relevance to Practice
Choose a program that aligns with your therapeutic approach and the client’s needs. For example, opt for courses with practical techniques you can integrate into your practice effortlessly.
Support and Community
Support from like-minded professionals and ongoing support can enhance the learning experience. Peer support and collaboration can also provide additional insights and motivation.
Boost Your Credentials and Knowledge with Online CEUs
As you consider mindfulness in your professional practice, it’s a great idea to advance your skills in other areas. For example, Online CE Credits provides over 250 accredited programs, covering extensive topics in psychotherapy. Whether it’s a course on complex trauma, anxiety, depression, addiction, EMDR therapy, or Cognitive Processing therapy, you’re covered.
Wrapping Up: Embrace Mindfulness Techniques
Mindful CEUs offer a multifaceted approach to continuing education for therapists. They enhance your therapeutic skills, promote self-care, and improve client outcomes. Integrating mindfulness into your professional practice can let you achieve a balanced and fulfilling career while providing exceptional care to your clients.
Ready to upgrade your career and fulfill your licensure requirements? Online CE Credits is here to help you.
All our training programs are available online 24/7, and you can complete them anywhere, anytime. And the good news is that you can have direct access to seasoned therapists and up-to-date information. Stop settling for outdated mental health practices. Get evidence-based training to transform your clinical skills.
by Sadaqut | Jul 16, 2024 | Certificate
Studies show that domestic violence has a complex nature and far-reaching impact. It demands continuous learning and updated knowledge to ensure practitioners provide the most effective support and interventions.
For these reasons, continuing education units (CEUs) allow mental health specialists to stay current with legal requirements. They also help you maintain licensure, enhance skills, and keep abreast of the latest research and best practices in domestic abuse.
Here’s what you need to know:
What Is Domestic Violence?
According to the United Nations, domestic violence is “a pattern of behavior in any relationship that is used to gain or maintain power and control over an intimate partner.”
Also called domestic abuse or intimate partner violence, it’s a pervasive issue that affects individuals across all demographics. However, WHO reports that nearly 1 in 3 (30/%) of women worldwide have experienced some form of domestic abuse.
And intimate partner violence involves physical, emotional, psychological, sexual, and financial abuse within relationships. The U.S. Justice Department identifies the acts below as domestic violence:
- Physical abuse includes beatings, slappings, shovings, grabbings, pinchings, bites, hair pullings, and other types of harmful physical contact.
- Emotional abuse is attacking an individual’s value or self-esteem, like name-calling.
- Psychological abuse includes scaring the victim by intimidation, threatening to harm them, their partner, children, family, or friends, and permanently damaging their property and pets.
- Sexual abuse is any form of coercion or attempt to coerce sexual contact or behavior without consent.
- Financial abuse is restricting access to economic resources to which someone is entitled.
- Technological abuse is the act of harming, threatening, controlling, stalking, harassing, impersonating, exploiting, extorting, or monitoring another person through the use of technology.
Why Mental Health Professionals Need To Understand Domestic Violence
Domestic violence dynamics are complex as they involve power and control by one partner over another. This dominance has grave consequences that affect the immediate victim, the children, extended family members, and the broader community.
For mental health practitioners, grasping domestic violence complexity is essential. You need up-to-date knowledge about the patterns of abuse, the psychological impact on victims, and the most effective therapeutic interventions.
As a result, online CEU courses offer an invaluable resource for gaining this knowledge. They let you stay current with emerging trends and evidence-based practices.
What’s the Role of CEUs in Professional Development?
As a licensed mental health therapist, CEUs are a requirement for professional development. They enable you to maintain a high standard of practice and remain knowledgeable about the latest developments in your work.
And if you’re working with domestic violence survivors, CEUs can help you recognize signs of abuse, understand the legal and ethical considerations, and use appropriate therapeutic strategies.
Online CEU programs are flexible and convenient for busy professionals to fulfill their continuing education requirements. These courses can fit around your demanding schedules, allowing you to study at your own pace and from any location.
What Are the Benefits of Online CEU Courses for Domestic Violence?

Accessibility and Convenience
You can access online CEU training programs from anywhere, making it easier to balance your professional and personal commitments. And advancing your skills becomes a breeze if you’re working in rural or underserved areas, where there’s limited access to face-to-face training.
Diverse Learning Materials
Online certifications incorporate various learning materials, including videos, case studies, and interactive modules. This enhances the learning experience and helps practitioners engage with the content in different ways.
Expert Instruction
Leading experts teach online CEU courses on domestic abuse. Because of the instructors’ wealth of knowledge and experience, learners can gain valuable insights and practical techniques for their practice.
Up-to-Date Information
Research in domestic violence and intervention is continually evolving. Clinicians can remain relevant with current information and best practices since online CEU course providers regularly update their training to reflect the latest findings.
Continuing Certification
By completing online CEU certifications, therapists can meet their state’s licensure requirements. This enables you to maintain your professional status’ credibility and legitimacy.
What Topics Do Domestic Violence CEU Courses Cover?
Online CEU programs for domestic violence explore a range of topics, each crucial for providing comprehensive care to survivors. These courses dig deeper into the following areas:
Understanding the Dynamics of Abuse:
Courses explore different forms of domestic violence, including physical, emotional, psychological, and financial abuse. They examine the power and control tactics used by abusers and the effect they have on victims.
Legal and Ethical Considerations:
Clinicians learn about the legal frameworks surrounding domestic violence, including mandatory reporting laws, restraining orders, and the rights of victims. Ethical considerations, such as maintaining confidentiality and navigating dual relationships, are also part of this course.
Trauma-Informed Care:
Because domestic violence has a profound impact on mental health, courses emphasize trauma-informed care. The training empowers professionals to recognize the signs of trauma, employ trauma-sensitive interventions, and create a safe and supportive therapeutic environment.
Cultural Competency:
Domestic violence affects individuals from all cultural backgrounds. As a result, the training highlights cultural sensitivity and competency. This helps counselors consider cultural factors in their assessments and treatments.
Intervention Strategies:
Mental health specialists gain practical skills on how to work with domestic violence survivors, including safety planning, crisis intervention, and long-term therapeutic approaches. Certifications may also cover group therapy techniques and the role of support networks.
Impact on Children:
Domestic violence has significant implications for children who witness or experience abuse. Programs address the psychological and developmental impact on children and provide methods to support child survivors and their non-abusive parents.
How To Upskill Yourself in Domestic Violence Therapy?
Online CE Credits is your trusted companion if you want to upgrade your knowledge and expertise in domestic abuse and interventions. It provides an in-depth training program on trauma treatment skills for survivors of domestic abuse and intimate partner violence.
Taught by a therapist with decades of experience, the course aims to:
- Enhance your understanding of the domestic violence spectrum
- Highlight its impact and long-term effects on survivors
- Explore interventions such as Power Threat Meaning Framework and Trauma Informed Practice, psychoeducation, and stabilization
Ultimately, the training program enables you to restore control over trauma symptoms and emotional regulation to allow for effective processing of the DA experiences.
You can also check out another vital certification in teen dating violence.
Enhance Your Professional Competence and Confidence
One of the primary benefits of engaging in online CEU courses is that it improves your professional competence and confidence. As you deepen your understanding of domestic violence, you become more adept at identifying signs of abuse. As a result, you can provide appropriate interventions, and advocate for clients.
This competence boosts your confidence to support survivors and make a meaningful difference in their lives.
Additionally, the knowledge gained from CEU courses allows you to stay informed about the latest research and trends in domestic abuse. This ongoing education is vital to adjust to new challenges and ensure therapeutic practices remain effective and relevant.
Build a Supportive Professional Network
Online CEU programs also offer opportunities for practitioners to connect with peers and experts. Many programs include discussion forums, webinars, and networking events where you can share experiences, ask questions, and gain support.
Building a supportive professional network provides space for collaboration, resource sharing, and professional growth.
Commit To Lifelong Learning with Online CE Credits
Staying certified and informed through online CEU courses shows you’re committed to lifelong learning and professional excellence. The knowledge and skills you get from domestic abuse courses enable you to offer the highest standard of care to support healing. And you can contribute to the broader effort to end domestic violence.
Online CE Credits lets you remain relevant and equipped with the latest tools and insights in intimate partner violence. This ongoing education advances your practice and reinforces your dedication to the well-being and safety of those you serve. Begin your online CE course today!
Grab This Golden Opportunity To Upgrade Your Expertise
Want to dominate your space in domestic violence therapy? Online CE Credits has a treasure trove of information on the emerging trends in domestic abuse. All the training programs are from experienced instructors with actionable insights. You can complete the lessons at your own pace since there are no due dates or deadlines.
And the payment plans are so flexible that you can have instant access to online CEU certification after choosing your payment method. Stop stressing about CEUs! Get affordable, convenient online courses for licensure renewal.
FAQs
How long is a domestic abuse course?
You only need to dedicate a few hours to complete the domestic violence CE course with Online CE Credits. You can finish the program anytime, anywhere.
What skills do you need to be a domestic abuse worker?
A domestic abuse worker should recognize signs of abuse, provide emotional support, and refer victims to appropriate resources. They should also know the laws and policies related to domestic violence.
What are the objectives of studying domestic violence?
Studying domestic violence helps to identify risk factors, understand the underlying causes, and develop strategies to prevent and respond to it. It also provides insight into how to support victims and prevent further harm.

by Sadaqut | Jul 16, 2024 | Educational
Anger is a natural and often necessary emotion. However, it can lead to significant personal and professional issues when it’s overwhelming or uncontrollable.
For mental health professionals, becoming a Certified Anger Management Specialist (CAMS) presents a unique opportunity to help people with serious anger problems.
Also, an anger management certification course can enhance your skills, expand your practice, and let you change clients’ lives.

Here’s what you need to know:
What Is Anger Management?
Anger management is the process of learning to recognize signs of becoming angry and taking action to calm down and deal with the situation positively. It involves a series of therapeutic techniques and practices to help individuals manage their anger constructively.
Professionals trained in anger management have the relevant skills to teach these interventions. And they provide clients with tools to manage their emotions more effectively.
What Does a Certified Anger Management Specialist Do?
Certified specialists in anger management are professionals with specialized training and certification to provide anger management therapy. They work with individuals, groups, and organizations to help manage anger-related issues. Their role often involves:
- Conducting assessments to determine the severity and triggers of anger
- Developing personalized anger management plans
- Teaching coping strategies and techniques to manage anger
- Providing ongoing support and counseling
- Working with other professionals to address underlying issues contributing to anger
What Are the Anger Management Specialist Certification Benefits?
Enhanced Professional Skills
Pursuing certification as an anger management counselor improves your professional skills. The training enables you to understand anger’s psychological and physiological aspects. This equips you with advanced techniques to encourage clients to manage their anger effectively.
These skills are invaluable in various therapeutic settings, allowing you to offer more comprehensive care.
Increased Employability and Career Advancement
The demand for anger management specialists is growing, as 75% of individuals who receive therapy improve. So the increased awareness of mental health issues and the importance of emotional regulation encourage people to seek help.
Employers across various sectors, including mental health clinics, schools, correctional facilities, and corporate settings, want professionals with this specialized skill set. As a result, certification can set you apart from other candidates, leading to increased job opportunities and career advancement.
Expanded Client Base
Specializing in anger management can attract a broader client base to your practice. According to one study, fewer than 13% of individuals sought help specifically for anger-related issues. And 58% of people had no idea where to seek help to resolve their anger challenges.
Through awareness, licensed anger management specialists can find people who want help by making their services accessible.
Because you’re trained, referrals from other mental health professionals and organizations can increase. And this can boost your practice’s growth.
Contribution to Public Health
Unmanaged anger can contribute to many health issues, including cardiovascular disease, depression, and substance abuse. As a Certified Anger Management Specialist, you can empower individuals to manage their anger, reducing the risk of these associated health problems.
Your work contributes to the overall well-being of your clients and the community.
Personal Fulfillment
Helping individuals control their anger and improve their lives can be incredibly rewarding. You can feel personally and professionally satisfied when you see the positive changes in your clients’ behavior, relationships, and overall quality of life.
This career path allows you to make a significant difference in the lives of your patients.
How Can A Certified Anger Management Specialist Practice?

Private Practice
Opening a private practice is a common path for many Certified Anger Management Specialists. This option is so flexible that you can set your schedule, choose your clients, and tailor your services to meet specific needs.
A private practice can be highly rewarding, both financially and personally, as it lets you build long-term relationships with your clients.
Working in Educational Settings
Schools and universities often seek professionals to address students’ emotional and behavioral issues. As a Certified Anger Management Specialist, you can work within educational settings to provide support to students struggling with anger.
This role may involve conducting workshops, individual counseling, and working with teachers and administrators to create a supportive environment.
Corporate Training and Workshops
Corporate environments are increasingly recognizing the importance of emotional intelligence and anger management in maintaining a productive workforce. Certified Anger Management Specialists can offer workshops and training sessions to employees
You can teach them how to manage stress and anger in the workplace. It enables you to work with a diverse group of individuals and organizations, expanding your professional network.
Correctional Facilities
Anger management is also part of rehabilitation programs in correctional facilities. Trained professionals can work within these settings to help inmates manage their anger, reduce recidivism, and prepare for reintegration into society. This work is challenging but can have a significant impact on individuals and the community.
Collaboration with Other Health Professionals
Many clients with anger issues also struggle with other mental health or substance abuse problems. Collaborating with other health professionals, such as psychologists, psychiatrists, and addiction counselors, can provide a more holistic approach to treatment.
This interdisciplinary collaboration can lead to more effective outcomes for patients and enrich your professional experience.
How To Become a Certified Anger Management Specialist
Educational Requirements
A background in mental health or a related field is typically required to pursue certification as an anger management specialist. This often includes degrees in psychology, counseling, social work, or psychiatry. Some programs may also accept professionals with degrees in education or criminal justice, depending on their experience and training.
Certification Programs
Various organizations offer certification programs for anger management specialists. These programs usually include comprehensive training covering the theoretical and practical aspects of anger management. Coursework may involve topics such as:
- Understanding the roots of anger.
- Techniques for managing and reducing anger.
- Strategies for teaching anger management skills.
- Ethical and legal considerations in anger management therapy.
Programs often require combining coursework, practical experience, and supervision to prepare candidates well enough to work with clients.
Continuing Education (CE)
Continuing education is crucial to maintaining certification and staying current with the latest research and techniques in anger management. Many certification programs contain ongoing education to enable specialists to develop their skills and knowledge.
This commitment to lifelong learning improves your credibility and effectiveness as a professional.
Level Up Your Skills in Anger Management with Online CE
Want to jumpstart your career in anger management? Online CE Credits provides extensive resources on therapies to treat anger. These courses from well-renowned psychotherapists are great for counselors who want to upgrade their skills in CE. Also, they’re rich with practical insights from years of experience in dealing with mental disorders.
Here are some emerging therapies:
Learn the Benefits of Certified Anger Management Specialist Training
Becoming a Certified Anger Management Specialist offers several benefits and opportunities for mental health professionals. This specialized certification advances your professional skills and career prospects. It also lets you make a meaningful impact on your clients’ lives.
Whether you choose to work in private practice, educational settings, corporate environments, or correctional facilities, the demand for anger management specialists is significant and growing.
You can use this certification to help individuals lead healthier, more balanced lives by providing them with the tools and knowledge they need.
Sign Up for an Account To Upgrade Your Knowledge
Busy mental health professionals like you don’t have enough time to develop your career to fulfill licensure requirements. And you have several financial obligations to meet. We understand. And that’s why the training programs are available online 24/7, and you can finish them without due dates or deadlines.
As for the payments, you can choose a membership plan or pay in installments. Or, better yet, enjoy special discounts when you enroll in one of the certification programs. Stop stressing about CEUs! Get affordable, hassle-free online courses for licensure renewal.
FAQs
Is DBT or CBT better for anger management?
DBT and CBT are both effective for anger management.
How can a counselor help with anger issues?
A counselor can help by providing strategies to help individuals recognize their triggers and develop strategies to manage their anger.
Does anger management fall under mental health?
Anger management falls under mental health because it involves understanding and managing emotions.