Grief is a universal experience yet profoundly personal and complex. For mental health professionals, providing effective grief counseling involves empathy and advanced techniques tailored to each individual’s unique journey through loss.
In this article, we’ll explore modern strategies that can enhance therapeutic effectiveness in grief counseling, aka bereavement therapy. We’ll also offer you deeper insights and practical tools for your practice.
Understanding Grief: A Multifaceted Process
Grief has a multifaceted nature. And traditional models, like the Kubler-Ross five stages of grief, provide a framework but often need to capture the full spectrum of grieving experiences.
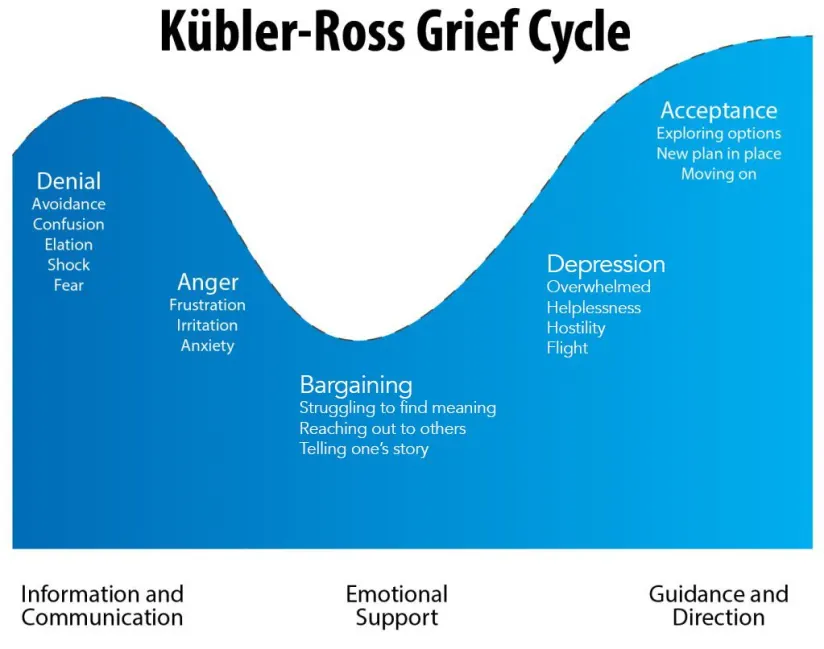
Modern grief theories emphasize the non-linear, individualized, and often prolonged nature of grief. It’s an intricate and multifaceted experience that encompasses a range of emotions, thoughts, and physical sensations.
Death is the most common cause of grief. However, grief can include a variety of losses, like relationships, career opportunities, and health. As such, mental health professionals must adopt a flexible and client-centered approach to meet their clients’ diverse needs.
The Role of the Therapeutic Alliance
At the heart of effective grief counseling is the therapeutic alliance. Building a strong, trusting relationship between therapist and client is paramount. This bond is the foundation for exploring deeper emotional pain and fostering healing.
Therapists should prioritize active listening, empathy, and unconditional positive regard to create a safe space where clients feel understood and supported.
Advanced Techniques in Grief Counseling
Meaning Reconstruction and Narrative Therapy
One of the most profound shifts in grief counseling in recent years is the focus on meaning reconstruction. Developed by Robert Neimeyer, this approach emphasizes helping clients reconstruct a sense of meaning and identity in the aftermath of loss.
Narrative therapy plays a crucial role here. Therapists can assist clients in integrating the loss into their lives to honor their past by encouraging them to tell their stories. This infuses a sense of hope for the future.
Narrative techniques involve exploring the client’s grief narrative, identifying themes of loss and resilience, and helping clients re-author their stories. This process allows the grieving to understand how the loss has shaped their identity and find new pathways to meaning and purpose.
Expressive Arts Therapy
Grief involves complex emotions that can be difficult to articulate. Expressive arts therapy offers an alternative means of expression. It encourages clients to process their grief through creative modalities such as art, music, dance, or writing. As a result, clients struggling with verbal expression or experiencing traumatic loss can cope with bereavement.
For example, art therapy enables clients to:
- Externalize their emotions through drawing, painting, or sculpting, providing a tangible representation of their inner experiences.
- Evoke powerful emotional responses and facilitate a deeper connection to memories of the deceased through music therapy.
- Release pent-up emotions and reconnect with their bodies via dance and movement therapy.
By engaging in these creative processes, clients can access and process their grief better than traditional talk therapy.
Integrating Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation practices have gained significant traction in grief counseling because they help clients stay present with their emotions without becoming overwhelmed.
Mindfulness involves paying attention to the present moment with non-judgmental awareness. This practice can help clients observe their grief with compassion and reduce the intensity of painful emotions.
Guided meditation, breathing exercises, and body scans are common mindfulness techniques used in grief counseling. They allow the grieving to develop a sense of inner calm, improve emotional regulation, and foster a greater acceptance of their grief. Eventually, clients can find moments of peace and cultivate resilience.
Continuing Bonds and Legacy Work
Traditional grief theories often emphasize the need to “let go” or “move on” from the deceased. However, contemporary approaches focus on continuing bonds. They let clients maintain a connection with the deceased as part of the grieving process. Therapists can help clients explore ways to honor and sustain their relationship with the deceased, providing comfort and a sense of continuity.
Legacy work is a powerful tool in this context. It involves activities that allow clients to create lasting tributes to their loved ones, such as writing letters, creating memory books, or engaging in commemorative rituals. These practices enable clients to preserve the memory of their loved ones and facilitate the integration of the loss into their ongoing lives.
Addressing Complicated Grief
While grief is a natural response to loss, some individuals may experience complicated grief, characterized by intense, prolonged, and debilitating symptoms that interfere with daily functioning. For these clients, specialized interventions are necessary.

Complicated Grief Therapy (CGT)
Developed by Dr. Katherine Shear, Complicated Grief Therapy (CGT) is a structured, evidence-based approach designed. It addresses the unique needs of individuals suffering from complicated grief. CGT combines elements of cognitive-behavioral therapy, attachment theory, and interpersonal therapy to help clients process their grief and restore a sense of meaning and purpose.
Also, the therapy involves several key components, including education about grief, exploration of the client’s relationship with the deceased, and exposure to avoided reminders of the loss. CGT empowers clients to move toward a healthier adaptation to their loss by addressing the specific challenges of complicated grief.
Trauma-Informed Grief Counseling
For clients who have experienced traumatic loss, integrating trauma-informed care into grief counseling is essential. Traumatic loss can include sudden, unexpected deaths, violent deaths, or losses that occur under distressing circumstances. These experiences can complicate the grieving process, leading to symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Trauma-informed grief counseling involves creating a safe and supportive environment. It’s acknowledging the impact of trauma on the grieving process and using interventions that address grief and trauma symptoms. Techniques such as Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) and Somatic Experiencing can be effective in helping clients process traumatic memories and reduce the distress associated with their loss.
Reform Your Grief Counseling Techniques with CE Courses
Grief is a complicated experience so practitioners should be well-versed in trauma-based therapies. Thankfully, Online CE Credits has a treasure trove of continuing education (CE) courses to polish your skills. All programs are accredited and nationally approved to fulfill your licensure requirements.
Pick your relevant CE course below:
- Treating Trauma Using Somatic Experiencing
- Complex Trauma: Screening, Treatment Considerations, and Common Concerns
- EMDR Comprehensive Foundations for Trauma Treatment
- Treating Grief-Stricken Clients: Culturally Sensitive Interventions
- Holiday Heartbreak: Clinical Tools to Manage Holiday Grief
- Brain-Based Trauma Treatment
Also, discover how you can equip clients to manage anger by enrolling in an anger management course.
Cultural Sensitivity in Grief Counseling
Cultural and societal factors also influence grief. As such, effective grief counseling must be culturally sensitive and respectful of diverse mourning practices and beliefs. Therapists should strive to understand the cultural context of their clients’ grief, including rituals, traditions, and expressions of mourning.
Cultural competence involves being open to learning about different cultural perspectives on death and grief. It also means avoiding assumptions and engaging in ongoing education and self-reflection. By honoring the cultural dimensions of grief, you can provide more inclusive and effective support to your clients.
The Importance of Self-Care for Therapists
Bereavement therapy can be emotionally taxing for therapists, given the deep pain and suffering they witness. So, self-care is crucial for maintaining therapeutic effectiveness and preventing burnout.
You should prioritize your well-being by engaging in regular self-care practices, seeking supervision or peer support, and setting healthy boundaries. Self-care can include activities that promote physical, emotional, and mental well-being, such as exercise, mindfulness, hobbies, and social connections. You can sustain your ability to provide compassionate and effective support to your clients by caring for yourself.
Adopt Different Grief Counseling Therapies
Advanced techniques in grief counseling offer mental health professionals a rich array of tools to improve therapeutic effectiveness and support clients through their unique grieving processes. Various approaches, such as meaning reconstruction, expressive arts therapy, mindfulness, and continuing bonds, can provide comprehensive and compassionate care.
Cultural sensitivity and self-care further enrich the therapeutic process. This enables clients and therapists to navigate the journey of grief with resilience and hope.
Kickstart Your Trauma-Based Care To Beat Grief
Get instant CE credit for individual courses completed along the way—recognize and recoup value before you even finish your certificate program! Pay one fee upfront or spread your payment out to 3 or 4 monthly installments—get instant program access with your first payment! Stay ahead of licensing board requirements effortlessly.