loading...

by Sadaqut | Aug 20, 2024 | Certificate
As a social worker in Michigan, staying current with your continuing education (CE) requirements is essential to maintaining your license and providing the best care to your clients. The social work landscape is ever-evolving, with new research, techniques, and ethical considerations continually emerging. As a result, Michigan’s requirements for Continuing Education Units (CEUs) enable practitioners to remain competent and up-to-date in their field.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about meeting your Michigan Social Work CEU requirements, from understanding the basics to finding the best courses to meet your needs.

Understanding Michigan Social Work CEU Requirements
What Are CEUs?
Continuing Education Units (CEUs) are a standardized measure used to quantify the time spent on professional development and learning activities. In Michigan, 1 CEU is equivalent to 10 contact hours of participation in an organized continuing education experience under responsible sponsorship, capable direction, and qualified instruction.
Michigan Social Work Licensure Levels
Michigan offers three levels of social work licensure:
CEU Requirements by License Type
LBSW and LMSW:
- Total CEUs Required: 45 CEUs every three years.
- Ethics Requirement: At least 5 of these hours must be in social work ethics.
- Pain and Symptom Management: At least 2 hours must focus on pain and symptom management.
- Human Trafficking: A one-time, one-hour training on human trafficking must be completed.
RSST:
- Total CEUs Required: 20 CEUs every three years.
- Ethics Requirement: At least 5 of these hours must be in social work ethics.
- Human Trafficking: A one-time, one-hour training on human trafficking must be completed.
Newly Licensed Social Workers
If you’re newly licensed, your CEU requirements are prorated based on when you received your license within three years. For example, if you’re licensed within the first year of the cycle, you would need to complete the full 45 CEUs (or 20 for RSST). If licensed in the second year, you would need 30 CEUs, and in the third year, 15 CEUs.
Meeting the Ethics Requirement
Ethical practice is the cornerstone of social work. Michigan mandates that all licensed social workers complete at least 5 hours of continuing education in ethics. This is crucial, as ethical dilemmas can arise in various aspects of social work, including confidentiality, dual relationships, and informed consent.
Recommended Topics for Ethics CEUs
- Boundaries in Social Work: Understanding the importance of boundaries to maintain professional relationships.
- Ethical Decision-Making Models: Learning different approaches to making ethical decisions.
- Cultural Competence and Ethics: Addressing ethical considerations in working with diverse populations.
- Technology and Ethics: Navigating ethical issues related to the use of technology and social media in social work.
Finding Ethics CEU Courses
Many organizations offer ethics-specific CEUs, both online and in-person. Make sure the content is relevant and applicable to your practice by looking for courses tailored to the unique challenges that social workers face.
Pain and Symptom Management CEUs
Michigan requires that all licensed social workers complete at least 2 hours of CEUs focused on pain and symptom management. The program teaches you how to help clients manage physical pain, which is especially relevant if you’re working in healthcare settings, hospice, or with populations experiencing chronic pain.
Topics Covered in Pain and Symptom Management CEUs
Understanding Pain:
Types of pain (acute vs. chronic) and their impacts on mental health.
Pain Assessment Tools:
Learning how to assess pain levels accurately.
Intervention Strategies:
Techniques for managing pain, including psychological approaches such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for pain management.
Multidisciplinary Approaches:
Collaborating with other healthcare providers to offer comprehensive pain management.
Future-Proof Your Social Work With Current CEUs
Need to ensure your license renewal and professional development are on track? Stay ahead of the curve with our comprehensive range of CE courses designed to develop your professional growth. Don’t let license renewal deadlines stress you out. Explore essential topics for social work professionals, including
The Human Trafficking Requirement
As a relatively new mandate, all social workers in Michigan must complete a one-time, one-hour training on human trafficking. This training aims to equip social workers with the knowledge to identify and intervene in cases of human trafficking.
What the Training Covers
- Understanding Human Trafficking: Definitions, types, and the scope of the problem
- Signs of Human Trafficking: How to Identify potential victims
- Intervention Strategies: What to do if you suspect someone is a victim of human trafficking
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: Understanding the laws surrounding human trafficking and your ethical obligations as a social worker
Where to Find Human Trafficking Training
The Michigan Department of Licensing and Regulatory Affairs (LARA) provides a list of approved human trafficking training programs. You can complete them online and usually fulfill the requirement in about an hour.
Choosing CEU Courses
When selecting CEU courses, it’s essential to consider the state’s requirements and your professional development goals. Here are some tips for selecting the best programs:
Accredited Providers
Always choose CEU courses from accredited providers. In Michigan, CEUs must be approved by the Michigan Social Work Continuing Education Collaborative. Courses from universities, professional associations, and recognized training organizations typically meet this standard.
Relevance to Your Practice
Pick courses relevant to your area of practice. For example, if you work primarily in clinical social work, courses on the latest therapeutic techniques or mental health trends would be beneficial. If you’re in a macro practice, policy development or organizational leadership certifications might be more applicable.
Course Format
Consider the format that works best for you—whether it’s in-person workshops, live webinars, or self-paced online courses. Online courses offer flexibility, allowing you to complete your CEUs at your convenience. On the other hand, in-person workshops can provide valuable networking opportunities and hands-on experience.
Cost and Time Investment
Compare the cost of courses and the time required to complete them. Some courses offer more CEUs for less time, but it’s essential to balance quantity with quality. Don’t just choose the cheapest option—make sure the course content is valuable and applicable to your work.

Record Keeping and Reporting
Maintaining accurate records of your CEUs is crucial. You must keep documentation of your completed CEUs for at least four years after the end of the renewal period in case of an audit by the Michigan Board of Social Work.
What to Keep:
- Certificates of Completion: These should include the course title, date, number of CEUs earned, and the provider’s accreditation information.
- Course Descriptions and Objectives: Keep a copy of the course syllabus or description to show the relevance of the course content.
- Transcripts: If you completed CEUs as part of an academic course, maintain transcript copies.
Reporting Your CEUs
When it’s time to renew your license, you’ll report your CEUs through the Michigan Online License Application/Renewal Service (MiPLUS). You must attest to completing the required number of CEUs, including the specific hours in ethics, pain management, and human trafficking.
Renewal Process and Deadlines
Social work licenses in Michigan are renewed every three years. It’s important to keep track of your renewal deadline and ensure all CEUs are completed well before this date to avoid any last-minute stress.
Late Renewals
If you miss the renewal deadline, your license will lapse, and you may not legally practice until it is reinstated. Late renewals require you to pay additional fees and submit proof of CEU completion.
Stay Abreast With Michigan Social Work Laws
Meeting the Michigan Social Work CEU requirements is a regulatory necessity and a commitment to your professional growth and the well-being of your clients. Your social work practice will continue to be high-quality if you select appropriate CEU courses and keep careful records.
Staying on top of your continuing education requirements is essential, regardless of when you started your career or how much experience you have. This will let you maintain your license, enhance your skills, expand your knowledge, and ultimately improve your patients’ lives.
Try Battle-Tested Online CE To Meet Licensure Requirements
Relax, and don’t worry about your license renewal. With expert-approved Online CE, you can easily fulfill your continuing education requirements while staying up-to-date on the latest trends and best practices. Enroll today and experience the convenience and flexibility of our online courses.

by Sadaqut | Aug 20, 2024 | Educational
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects communication, behavior, and social interaction. There’s an increasing prevalence of autism, as current estimates suggest that about 1 in 36 children in the United States are diagnosed with the disorder. As a result, there is a growing demand for mental health professionals with relevant skills to work with this population.
As a therapist, expanding your expertise in autism through continuing education can enhance your therapeutic techniques and improve outcomes for your clients.
In this detailed blog, we’ll explore the importance of specialized autism training and key focus areas for therapists. Also, the post shows how continuing education empowers you to provide the best possible care for autistic individuals.
The Growing Need for Autism Expertise in Therapy
The Rising Prevalence of Autism
The prevalence of autism has been on the rise for several decades. This increase highlights the need for more professionals who can provide effective support to individuals on the spectrum.
Autism is not a one-size-fits-all diagnosis; it encompasses a wide range of symptoms and severity levels. For this reason, therapists should be well-versed in the nuances of the condition.
Why Specialized Training Matters
While many therapists receive general training in developmental disorders, autism requires a specialized approach. The unique characteristics of ASD—such as difficulties with social communication, repetitive behaviors, and sensory sensitivities—require targeted strategies that go beyond traditional therapy methods. Specialized autism training provides therapists with the tools and knowledge to develop individualized treatment plans to address each client’s specific needs.
Key Areas of Focus in Autism Training
Autism training for therapists covers a broad spectrum of topics, from understanding the neurobiological underpinnings of the disorder to implementing evidence-based interventions. Here are some vital aspects of effective autism therapy:
Understanding the Autism Spectrum
Autism is often referred to as a “spectrum” because it presents differently in each individual. Understanding the diversity within the spectrum is essential for providing personalized care. Training programs typically cover the following aspects:
Core Symptoms:
Learning to identify the core symptoms of autism, such as challenges in communication and social interaction, as well as restricted and repetitive behaviors
Subtypes and Comorbidities:
Understanding the different subtypes of autism (e.g., Asperger’s Syndrome, PDD-NOS) and how comorbid conditions like ADHD, anxiety, or intellectual disabilities can impact treatment
Developmental and Behavioral Approaches
Autism training often emphasizes developmental and behavioral approaches, which are among the most effective strategies for working with individuals on the spectrum. They include:
Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA):
ABA is one of the most widely used interventions for autism. Training in ABA helps therapists use reinforcement strategies to encourage positive behaviors and reduce challenging ones.
Developmental, Individual-Difference, Relationship-Based (DIR/Floortime):
This approach focuses on building relationships and encouraging emotional and social development by meeting the child at their developmental level and promoting interaction naturally.
Social Skills Training:
Many individuals with autism struggle with social interactions. Training in social skills interventions can help therapists teach clients how to interpret social cues, engage in conversation, and develop meaningful relationships.
Sensory Integration Therapy
Many individuals with autism experience sensory processing issues, making it difficult for them to cope with certain sounds, textures, lights, or other sensory stimuli. Sensory Integration Therapy (SIT) aims to help individuals with autism manage sensory input in a more organized and effective way. Autism training provides therapists with the knowledge to:
Identify Sensory Processing Disorders:
Recognize signs of sensory processing challenges in clients and assess how these difficulties impact daily functioning.
Implement Sensory-Based Interventions:
Use specific techniques and activities that can help clients regulate their sensory experiences, such as swinging, deep pressure, or tactile play.
Communication Strategies
Communication difficulties are a hallmark of autism. Effective therapy often involves teaching alternative communication methods, especially for nonverbal clients. Autism training equips therapists to:
Use Augmentative and Alternative Communication (AAC):
Learn to implement tools such as picture exchange communication systems (PECS), speech-generating devices, or sign language to facilitate communication.
Enhance Verbal Communication:
For clients with limited speech, therapists can learn strategies to expand vocabulary, improve sentence structure, and encourage spontaneous verbal communication.
Family Involvement and Support
Therapy for autism is most effective when it involves the family. Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in the generalization of skills learned in therapy to the home environment. Autism training programs often cover:
Parent Training and Education:
Equipping parents with strategies to support their child’s development at home, including behavior management techniques and communication strategies.
Understanding the emotional impact of an autism diagnosis on the family and providing counseling and support to address these challenges.
Ethical and Cultural Considerations
Working with individuals with autism requires sensitivity to ethical and cultural issues. Autism training often includes:
Understanding the ethical considerations in autism therapy, such as respecting client autonomy, maintaining confidentiality, and obtaining informed consent.
Cultural Competence:
Recognizing how cultural background can influence the presentation of autism and the family’s approach to treatment. Training helps therapists develop culturally responsive interventions.
Dominate Your Autism Therapy Practice with Online CE
Seeking to deepen your understanding of autism spectrum disorders? You can’t go wrong with Online CE. Our comprehensive courses provide the latest evidence-based techniques and strategies.
Key Features:
- Experienced Instructors: Get expert advice on autism therapy from seasoned, passionate professionals.
- Approved and Accredited Programs: Ensure your continuing education credits meet industry standards.
- Affordable Packages: Access high-quality courses without breaking the bank.
Join our community of dedicated therapists and take your practice to new heights. Enroll today in the courses below and discover the transformative power of online CE.

The Benefits of Continuing Education in Autism
Continuing education in autism is not just beneficial—it’s essential for staying current with the latest research and interventions. Here’s how ongoing training can enhance your therapy techniques:
Staying Updated with Evidence-Based Practices
The field of autism research is constantly evolving, with new studies and interventions being developed regularly. Continuing education ensures you’re up-to-date with the latest evidence-based practices, allowing you to offer the most effective therapies to your clients.
Expanding Your Skill Set
Autism training lets you expand your therapeutic toolkit. Continuing education enables you to grow as a professional and offers a broader range of services to your clients. You can learn a new intervention technique or gain a deeper understanding of a specific area, such as sensory processing.
Enhancing Client Outcomes
Clients benefit most when their therapist is knowledgeable and skilled in the latest autism interventions. With continuous training, you can improve your client’s communication, social skills, behavior management, and overall quality of life.
Building Professional Credibility
Specialized training in autism upgrades your skills and boosts your professional credibility. It demonstrates your commitment to providing the highest level of care to autism patients to potential clients, employers, and colleagues. This can open up new career opportunities and increase your reputation as an expert in the field.
Meeting Licensing and Certification Requirements
Many licensing boards and professional organizations require continuing education in specific areas, including autism. You can meet these requirements and maintain your professional credentials by staying current with your training.
Choosing the Right Autism Training Program
When selecting an autism training program, consider several factors to ensure the course meets your professional needs and goals:
Accreditation and Certification
Choose a program that is accredited by a recognized professional organization, such as the Behavior Analyst Certification Board (BACB), for ABA training. Accreditation ensures that the training meets high standards of quality and rigor.
Course Content and Focus
Look for programs that offer comprehensive coverage of the topics that are most relevant to your practice. No matter what type of course you’re looking for, make sure it aligns with your learning goals.
Instructor Expertise
The instructor’s expertise influences the quality of the training. So choose programs from experienced professionals with a strong background in autism research and therapy.
Flexibility and Accessibility
Consider programs with flexible learning options, such as online courses or workshops, to accommodate your schedule. Accessibility to resources, such as course materials and peer support, is also crucial for a successful learning experience.
Take Advantage of Autism-Specialized Training
Empowering your therapy techniques with essential autism training is a vital step in providing the best possible care for individuals with Autism Spectrum Disorder. As the prevalence of autism continues to rise, the demand for skilled therapists who understand the condition’s complexities will only increase.
Investing in specialized training makes a profound difference in your client’s life and their families and advances your professional development.
Let Online CE Jumpstart Your Autism Therapy
Continuing education in autism equips you with the knowledge, skills, and confidence to address autism therapy’s unique challenges. Whether you’re just beginning your journey working with individuals on the spectrum or looking to deepen your expertise, there’s always more to learn. Choose the right training program, stay committed to your professional growth, and watch as your therapeutic techniques—and your clients’ outcomes—reach new heights. Expand your autism therapy knowledge. Explore our courses now.

by Sadaqut | Aug 6, 2024 | Educational
Grief is a universal experience yet profoundly personal and complex. For mental health professionals, providing effective grief counseling involves empathy and advanced techniques tailored to each individual’s unique journey through loss.
In this article, we’ll explore modern strategies that can enhance therapeutic effectiveness in grief counseling, aka bereavement therapy. We’ll also offer you deeper insights and practical tools for your practice.
Understanding Grief: A Multifaceted Process
Grief has a multifaceted nature. And traditional models, like the Kubler-Ross five stages of grief, provide a framework but often need to capture the full spectrum of grieving experiences.
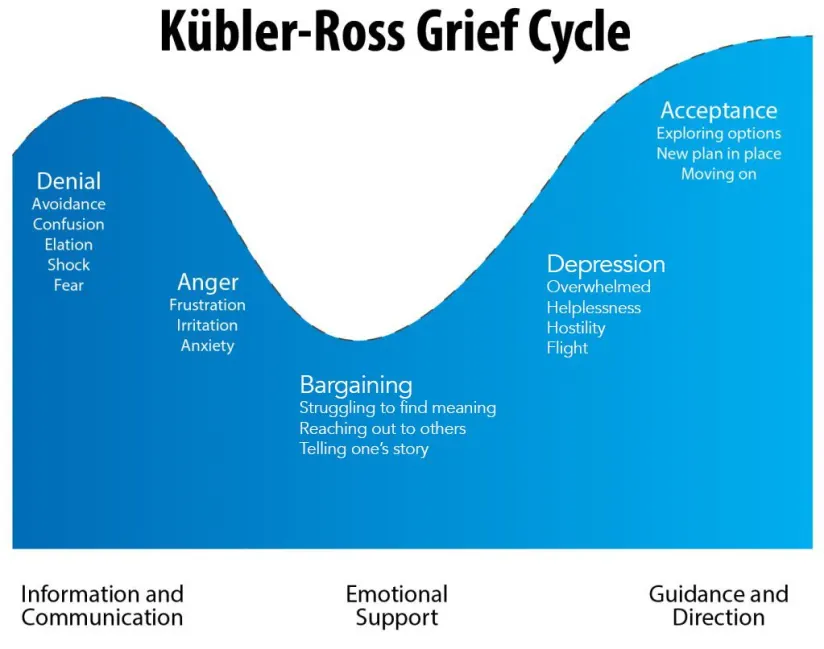
Image Source
Modern grief theories emphasize the non-linear, individualized, and often prolonged nature of grief. It’s an intricate and multifaceted experience that encompasses a range of emotions, thoughts, and physical sensations.
Death is the most common cause of grief. However, grief can include a variety of losses, like relationships, career opportunities, and health. As such, mental health professionals must adopt a flexible and client-centered approach to meet their clients’ diverse needs.
The Role of the Therapeutic Alliance
At the heart of effective grief counseling is the therapeutic alliance. Building a strong, trusting relationship between therapist and client is paramount. This bond is the foundation for exploring deeper emotional pain and fostering healing.
Therapists should prioritize active listening, empathy, and unconditional positive regard to create a safe space where clients feel understood and supported.
Advanced Techniques in Grief Counseling
Meaning Reconstruction and Narrative Therapy
One of the most profound shifts in grief counseling in recent years is the focus on meaning reconstruction. Developed by Robert Neimeyer, this approach emphasizes helping clients reconstruct a sense of meaning and identity in the aftermath of loss.
Narrative therapy plays a crucial role here. Therapists can assist clients in integrating the loss into their lives to honor their past by encouraging them to tell their stories. This infuses a sense of hope for the future.
Narrative techniques involve exploring the client’s grief narrative, identifying themes of loss and resilience, and helping clients re-author their stories. This process allows the grieving to understand how the loss has shaped their identity and find new pathways to meaning and purpose.
Expressive Arts Therapy
Grief involves complex emotions that can be difficult to articulate. Expressive arts therapy offers an alternative means of expression. It encourages clients to process their grief through creative modalities such as art, music, dance, or writing. As a result, clients struggling with verbal expression or experiencing traumatic loss can cope with bereavement.
For example, art therapy enables clients to:
- Externalize their emotions through drawing, painting, or sculpting, providing a tangible representation of their inner experiences.
- Evoke powerful emotional responses and facilitate a deeper connection to memories of the deceased through music therapy.
- Release pent-up emotions and reconnect with their bodies via dance and movement therapy.
By engaging in these creative processes, clients can access and process their grief better than traditional talk therapy.
Integrating Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation practices have gained significant traction in grief counseling because they help clients stay present with their emotions without becoming overwhelmed.
Mindfulness involves paying attention to the present moment with non-judgmental awareness. This practice can help clients observe their grief with compassion and reduce the intensity of painful emotions.
Guided meditation, breathing exercises, and body scans are common mindfulness techniques used in grief counseling. They allow the grieving to develop a sense of inner calm, improve emotional regulation, and foster a greater acceptance of their grief. Eventually, clients can find moments of peace and cultivate resilience.
Continuing Bonds and Legacy Work
Traditional grief theories often emphasize the need to “let go” or “move on” from the deceased. However, contemporary approaches focus on continuing bonds. They let clients maintain a connection with the deceased as part of the grieving process. Therapists can help clients explore ways to honor and sustain their relationship with the deceased, providing comfort and a sense of continuity.
Legacy work is a powerful tool in this context. It involves activities that allow clients to create lasting tributes to their loved ones, such as writing letters, creating memory books, or engaging in commemorative rituals. These practices enable clients to preserve the memory of their loved ones and facilitate the integration of the loss into their ongoing lives.
Addressing Complicated Grief
While grief is a natural response to loss, some individuals may experience complicated grief, characterized by intense, prolonged, and debilitating symptoms that interfere with daily functioning. For these clients, specialized interventions are necessary.

Complicated Grief Therapy (CGT)
Developed by Dr. Katherine Shear, Complicated Grief Therapy (CGT) is a structured, evidence-based approach designed. It addresses the unique needs of individuals suffering from complicated grief. CGT combines elements of cognitive-behavioral therapy, attachment theory, and interpersonal therapy to help clients process their grief and restore a sense of meaning and purpose.
Also, the therapy involves several key components, including education about grief, exploration of the client’s relationship with the deceased, and exposure to avoided reminders of the loss. CGT empowers clients to move toward a healthier adaptation to their loss by addressing the specific challenges of complicated grief.
Trauma-Informed Grief Counseling
For clients who have experienced traumatic loss, integrating trauma-informed care into grief counseling is essential. Traumatic loss can include sudden, unexpected deaths, violent deaths, or losses that occur under distressing circumstances. These experiences can complicate the grieving process, leading to symptoms of post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Trauma-informed grief counseling involves creating a safe and supportive environment. It’s acknowledging the impact of trauma on the grieving process and using interventions that address grief and trauma symptoms. Techniques such as Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) and Somatic Experiencing can be effective in helping clients process traumatic memories and reduce the distress associated with their loss.
Reform Your Grief Counseling Techniques with CE Courses
Grief is a complicated experience so practitioners should be well-versed in trauma-based therapies. Thankfully, Online CE Credits has a treasure trove of continuing education (CE) courses to polish your skills. All programs are accredited and nationally approved to fulfill your licensure requirements.
Pick your relevant CE course below:
Also, discover how you can equip clients to manage anger by enrolling in an anger management course.
Cultural Sensitivity in Grief Counseling
Cultural and societal factors also influence grief. As such, effective grief counseling must be culturally sensitive and respectful of diverse mourning practices and beliefs. Therapists should strive to understand the cultural context of their clients’ grief, including rituals, traditions, and expressions of mourning.
Cultural competence involves being open to learning about different cultural perspectives on death and grief. It also means avoiding assumptions and engaging in ongoing education and self-reflection. By honoring the cultural dimensions of grief, you can provide more inclusive and effective support to your clients.
The Importance of Self-Care for Therapists
Bereavement therapy can be emotionally taxing for therapists, given the deep pain and suffering they witness. So, self-care is crucial for maintaining therapeutic effectiveness and preventing burnout.
You should prioritize your well-being by engaging in regular self-care practices, seeking supervision or peer support, and setting healthy boundaries. Self-care can include activities that promote physical, emotional, and mental well-being, such as exercise, mindfulness, hobbies, and social connections. You can sustain your ability to provide compassionate and effective support to your clients by caring for yourself.
Adopt Different Grief Counseling Therapies
Advanced techniques in grief counseling offer mental health professionals a rich array of tools to improve therapeutic effectiveness and support clients through their unique grieving processes. Various approaches, such as meaning reconstruction, expressive arts therapy, mindfulness, and continuing bonds, can provide comprehensive and compassionate care.
Cultural sensitivity and self-care further enrich the therapeutic process. This enables clients and therapists to navigate the journey of grief with resilience and hope.
Kickstart Your Trauma-Based Care To Beat Grief
Get instant CE credit for individual courses completed along the way—recognize and recoup value before you even finish your certificate program! Pay one fee upfront or spread your payment out to 3 or 4 monthly installments—get instant program access with your first payment! Stay ahead of licensing board requirements effortlessly.

by Sadaqut | Aug 6, 2024 | Certificate
Marriage and family therapy (MFT) is a specialized field that helps individuals, couples, and families navigate complex emotional and relational issues. As the demands on mental health professionals continue to evolve, obtaining certification in marriage and family therapy has become increasingly important.
This comprehensive guide will explore the benefits of certification and why it’s a valuable step to achieve excellence in this rewarding profession.
The Growing Need for Qualified Therapists
In today’s fast-paced and often stressful world, the need for skilled marriage and family therapists is more significant than ever. According to the American Association for Marriage and Family Therapy (AAMFT), nearly half of all marriages in the United States end in divorce.
And many families face challenges such as mental illness, substance abuse, and intergenerational conflicts. These issues can lead to significant emotional distress, making professional intervention crucial.
Certification in marriage and family therapy ensures that therapists are well-equipped to handle these complex issues. It shows you have met rigorous educational and professional standards and are competent and dedicated to your practice.
For clients seeking help, knowing their therapist is certified can provide an added layer of trust and confidence in the care they’ll receive.
The Path To Excellence
Achieving certification in marriage and family therapy involves several steps, each designed to ensure you possess the necessary knowledge and skills to provide effective treatment. The general process typically includes the following components, depending on your state:.
Educational Requirements:
Prospective therapists must complete a master’s or doctoral degree in marriage and family therapy or a related field. Accredited programs provide comprehensive training in areas such as human development, family dynamics, therapeutic techniques, and ethical practice.
Clinical Experience:
In addition to academic coursework, aspiring therapists must gain hands-on experience through supervised clinical practice. This typically involves completing a certain number of hours working directly with clients under the supervision of a licensed and experienced therapist.
Licensure Examination:
Upon completing their education and clinical training, candidates must pass a licensure examination. The examination tests their knowledge of marriage and family therapy principles, ethical standards, and clinical skills. Passing this exam is a critical step toward becoming a licensed marriage and family therapist.
Ongoing Professional Development:
Certification is not a one-time achievement. To maintain their credentials, certified therapists must engage in ongoing professional development. This includes continuing education through courses and workshops and staying current with the latest research and advancements in the field.
Revamp Your Marriage and Family Therapy Online
Current statistics say that 40% of families in the United States will seek family therapy at some point, according to AAMT. What better time to spruce up your therapy skills to provide clients with top-notch care? Online CE Credits makes this process a breeze by offering the latest courses on family therapy 24/7.
Choose your family therapy courses below:
In addition, this insightful article can expand your knowledge of reintegration therapy.
The Benefits of Certification
Enhanced Professional Credibility
One of the most significant benefits of certification is that it enhances your professional credibility. Clients, colleagues, and employers recognize certification as a mark of excellence and a commitment to high standards of practice. This recognition can open doors to career advancement opportunities, higher earning potential, and increased job satisfaction.
Improved Client Outcomes
Certified therapists are better equipped to deliver high-quality care, improving client outcomes. The rigorous training and clinical experience required for certification let you gain an in-depth understanding of the therapeutic process and how to use evidence-based techniques.
This expertise allows you to create effective treatment plans tailored to the client’s unique needs. This fosters better therapeutic relationships and more successful outcomes.
Professional Networking Opportunities
Joining professional organizations, such as the AAMFT, is a requirement for certification. These organizations provide valuable networking opportunities, allowing therapists to connect with peers, mentors, and leaders in the field. Networking can lead to collaborations, referrals, and access to resources to improve a therapist’s practice and professional development.
Access to Specialized Training and Resources
Certified therapists have access to specialized training and resources that can further enhance their skills and knowledge. Many professional organizations offer exclusive workshops, conferences, and publications that cover the latest research and advancements in marriage and family therapy.
The resources can help practitioners stay current with best practices and emerging trends, resulting in the highest level of care for their clients.
Increased Job Opportunities
Certification can significantly increase job opportunities for marriage and family therapists. Many employers prefer certified candidates, as they demonstrate a commitment to professional excellence and a proven track record of competence.
Also, training makes you more competitive in the job market since it sets you apart from people without advanced qualifications.
Enhanced Ethical and Legal Awareness
Ethical and legal considerations are crucial in marriage and family therapy practice. Certification programs emphasize ethical practice and provide training on the therapist’s legal responsibilities. This training helps certified therapists navigate complex ethical dilemmas and adhere to professional standards, protecting both their clients and their professional integrity.
Real-Life Impact: Stories of Certified Therapists

The true value of certification in marriage and family therapy can be best understood through the stories of those who have achieved it.
Consider the case of Jane, a certified marriage and family therapist who has been practicing for over a decade. Jane credits her certification with giving her the confidence and skills needed to handle even the most challenging cases. She recalls working with a family struggling with multiple issues, including substance abuse and communication breakdowns.
Through her training and experience, Jane was able to develop a comprehensive treatment plan to address each family member’s needs. This led to significant improvements in their relationships and overall well-being.
Similarly, Tom, another certified therapist, shares how certification has opened doors to opportunities he never imagined. Tom works in a community mental health center and often collaborates with other professionals, including social workers and psychologists. His certification has earned him respect among his colleagues, leading to collaborative projects and an expanded professional network.
Tom believes that his certification enhances his credibility and continually motivates him to strive for excellence in his practice.
The Path to Excellence in Marriage and Family Therapy
Certification in marriage and family therapy is a valuable investment in professional development and a commitment to providing the best care to clients. The rigorous process prepares you to handle complex cases, leading to improved client outcomes and enhanced professional credibility.
Also, certification provides a structured pathway, enabling you to remain at the forefront of your profession. Whether you’re starting a journey in marriage and family therapy or advancing your career, it’s a step toward achieving excellence.
Sign Up for an Account To Kickstart Your Continuing Education
Therapy expertise can result in higher revenue and improved client outcomes! Our self-paced programs provide a targeted and complete learning experience to help you advance from generalist to specialist.
Keeping up with traditional certificates can be redundant, time-consuming, and costly! Our certifications provide a post-nominal credential and are designed to be completed in a single cycle for a one-time program fee (or in three or four equal installments). Earn 20 CE credits in 1 month without disrupting your busy schedule.

by Sadaqut | Aug 6, 2024 | Educational
Understanding psychopharmacology is vital for mental health professionals striving to provide effective therapy. This specialized knowledge equips therapists with insights into how medications can influence their clients’ mental health and behavior. This results in a more holistic and informed treatment approach.
In this blog post, we’ll unpack the role of psychopharmacology in therapy and how continuing education can help you update your knowledge in the field.
Why Psychopharmacology Matters?
News-Medical explains psychopharmacology as a practice that examines the effect of different medications on a patient’s mental health. Also, the field analyzes how various compounds change a patient’s behavior by altering the way the person feels or thinks.
For this reason, mental health professionals should understand how different drugs can affect the brain and behavior. This knowledge is critical for several reasons:
Comprehensive Understanding of Client Conditions:
Therapists with a solid grasp of psychopharmacology can better understand the full scope of their client’s conditions. As a result, they become aware of how medications affect clients’ mood, cognition, and behavior beyond recognizing symptoms.
For example, if a client is experiencing heightened anxiety or depressive symptoms, psychopharmacology awareness can help you discern whether these symptoms might be side effects of a new medication. And if that’s the case, the medication may need adjustment.
Enhanced Communication with Prescribers:
Effective therapy often involves collaboration with other healthcare providers who prescribe medications, such as psychiatrists or primary care physicians. With knowledge of psychopharmacology, you can engage in more meaningful and productive conversations with these prescribers. It enables you to advocate for your client’s needs more effectively.
Clients receive integrated mental health care that addresses all aspects of their condition through this collaborative approach.
Informed Treatment Planning:
Mental health practitioners who understand psychopharmacology can incorporate this knowledge into their treatment planning. For example, they can tailor their therapeutic approaches to account for the effects of medications.
If a client is on a medication that causes drowsiness, the therapist might schedule sessions at a time of day when the client is most alert and capable of engaging in therapy. Similarly, understanding the timing of medication effects can help therapists align their interventions with periods when clients are most receptive.
Supporting Client Education and Advocacy:
Clients have questions and concerns about their medications, including potential side effects, the rationale behind their prescriptions, and how medications might interact with other treatments.
Therapists with psychopharmacology knowledge can provide accurate information, helping clients understand their treatment options. And this empowers them to advocate for themselves in conversations with prescribers. This support is vital for clients who feel overwhelmed or uncertain about their medications.
Building Psychopharmacology Knowledge
Because psychopharmacology is integral to therapy, mental health professionals should prioritize building and maintaining this knowledge. Here are some strategies to consider:
Continuing Education:
Participating in continuing education courses focused on psychopharmacology is one of the most effective ways to stay informed. These programs provide in-depth, up-to-date information about various medications, their mechanisms of action, potential side effects, and best practices for integrating this knowledge into therapeutic practice.
For example, several organizations offer online CE credits, making it convenient for busy professionals to enhance their expertise.
Reading Current Literature:
Keeping up with the latest research and publications in psychopharmacology can help therapists stay abreast of new developments and emerging trends. Journals such as the “Journal of Psychopharmacology” and “Psychiatric Times” feature articles on the latest studies, clinical trials, and expert opinions, providing valuable insights that can inform practice.
Collaborative Learning:
Discussions with colleagues, attending professional conferences, and joining professional organizations can provide opportunities for collaborative learning. These interactions allow therapists to share knowledge, ask questions, and learn from the experiences of others in the field.
Consultation and Supervision:
Seeking supervision or consultation from experienced colleagues with a background in psychopharmacology is also immensely beneficial. These mentors can offer guidance, share practical insights, and help therapists navigate complex cases involving medication management.
Grasp These Mental Health Disorders: Depression and Anxiety
Psychopharmacology is a science that analyzes drugs’ impact on mental health, so therapists also need to understand how to treat depression and anxiety. Online CE Credits is a therapist-managed platform with over 250 accredited and nationally approved programs to renew your clinical practice. Consider the courses below:
Also, explore other practical insights into trauma for social workers to elevate your continuing education.

Practical Applications in Therapy
Integrating psychopharmacology knowledge into therapeutic practice involves more than just understanding medications. It requires thoughtful application tailored to each client’s unique needs. Here are some practical ways therapists can apply this knowledge in their work:
Assessment and Diagnosis:
When assessing and diagnosing clients, therapists should consider the potential impact of medications on their symptoms. This holistic approach ensures the diagnosis accounts for all relevant factors, leading to more accurate and effective treatment planning.
A therapist might investigate whether depression symptoms are caused by a new medication or an existing prescription that is not working.
Treatment Planning:
In developing treatment plans, practitioners should consider how medications might interact with therapeutic interventions. This includes understanding the potential side effects that could impact the client’s ability to engage in therapy. Also, they need to recognize how medication changes might influence the client’s mood and behavior.
Mental health experts can enhance the overall effectiveness of the treatment by aligning therapeutic approaches with the client’s medication regimen.
Monitoring Progress:
Regularly monitoring clients’ progress and any changes in their symptoms is crucial when new medications are introduced or existing prescriptions are adjusted. Therapists should be vigilant in observing how these changes might affect the client’s mental health and well-being and adjust their therapeutic approaches accordingly.
This ongoing assessment helps ensure that the therapy remains responsive to the client’s evolving needs.
Client Education:
Educating clients about their medications, and their potential side effects, and following the drug’s directions is a key aspect of integrated care. This enables clients to make informed decisions about their treatment. And the education can also alleviate clients’ concerns and anxieties about their medications, promoting a more positive therapeutic experience.
Crisis Intervention:
Psychopharmacology knowledge helps therapists respond more effectively in situations where clients experience severe side effects or adverse reactions to medications. They can identify potential medication-related issues and collaborate with prescribers to address these concerns promptly, ensuring the client’s safety and well-being.
Consider the Impact of Psychopharmacology Knowledge
The essential role of psychopharmacology knowledge in effective therapy cannot be overstated. For mental health professionals, understanding the complex interplay between medications and mental health is crucial for providing comprehensive, informed, and effective care.
Modernize Your Clinical Practice with Online CE Credits
You can enhance your psychopharmacology knowledge and apply it thoughtfully in your practice by investing in continuing education, staying current with the latest research, and engaging in collaborative learning.
This integrated approach improves treatment outcomes and empowers clients to take an active role in their mental health journey, fostering a more collaborative and effective therapeutic experience. Earn 10 essential CE credits in just 2 weeks.












