loading...

by Sadaqut | Aug 6, 2024 | Educational
In the hustle and bustle of modern life, stress and anxiety often become unwelcome companions for many individuals. According to the Anxiety and Depression Association of America (ADAA), 6.8 million U.S. adults, or 3% of the population, suffer from generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
In this environment, integrating mindfulness into psychotherapy offers benefits and techniques that can enhance the therapeutic process and promote mental well-being.
But what exactly are the advantages of integrating mindfulness into psychotherapy, and how can you effectively utilize these techniques?
The Benefits of Mindfulness in Psychotherapy
Mindfulness is about being present in the moment, and it involves paying attention to one’s thoughts, feelings, and sensations without judgment. Practicing mindfulness in psychotherapy has many benefits for both the client and the therapist.
Building Self-awareness
Mindfulness helps clients develop greater self-awareness. They can understand the patterns and triggers that underlie their thoughts and behaviors by paying close attention to their internal experiences.
As a result, the heightened awareness allows patients to gain insights into their issues and take a more active role in their healing journey.
Reducing Anxiety and Depression Symptoms

Image Source
Also, mindfulness has been shown to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression. Research indicates that regular mindfulness practice can decrease the intensity and frequency of these symptoms, providing clients with much-needed relief. Individuals struggling with traditional forms of therapy or who aren’t finding success from medication alone can benefit from this approach.
Enhancing Emotional Regulation
Another great benefit is improving emotional regulation. Mindfulness encourages clients to observe their emotions without becoming overwhelmed by them. This can lead to a greater sense of control and stability, making it easier for patients to cope with stressors and challenges in their daily lives.
Upgrading Patient Care
Incorporating mindfulness into your practice can also be advantageous. It can enhance your self-awareness and emotional regulation. This reduces the risk of burnout and improves patient care.
Additionally, it can foster a deeper connection between you and the client, creating a more supportive and empathetic therapeutic environment.
How Do You Incorporate Mindfulness into Therapy?
Integrating mindfulness into psychotherapy involves combining several counseling techniques tailored to meet each client’s unique needs. Here are some effective strategies to consider:
Mindful Breathing
One of the simplest and most accessible mindfulness practices is mindful breathing. This technique involves paying close attention to the breath and noticing the sensations of inhaling and exhaling. Therapists can guide clients through this practice during sessions, encouraging them to focus on their breath whenever they feel overwhelmed or anxious.
Over time, patients can use mindful breathing as a tool to calm themselves in stressful situations.
Body Scan Meditation
Body scan meditation is another powerful technique in therapy. It involves guiding clients to focus their attention on their different body parts and noticing any sensations without judgment. The body scan enables patients to become more attuned to their physical experiences. And this is helpful for individuals struggling with dissociation or who have a trauma history.
Mindful Listening
Mindful listening can enhance the therapeutic relationship and improve communication between the therapist and the client. This technique involves listening to the client with full attention without interrupting or planning a response.
By modeling mindful listening, therapists can help clients feel heard and understood, fostering a sense of trust and safety in the therapeutic space.
Loving-Kindness Meditation
Loving-kindness Meditation, also known as metta meditation, is a practice that involves directing feelings of love and compassion towards oneself and others. This technique benefits clients who struggle with self-esteem or have difficulty connecting with others.
Therapists can guide clients through loving-kindness meditation, helping them to cultivate a sense of compassion and empathy.
Incorporating Mindfulness into Daily Activities
Encouraging clients to incorporate mindfulness into their daily activities can also be a valuable strategy. This might involve practicing mindfulness while eating, walking, or even during mundane tasks like washing dishes.
Patients can develop a greater sense of presence and reduce the impact of stressors by bringing mindfulness into everyday life.
4 Best Mindfulness Interventions for Therapists
Interventions based on mindfulness can help relieve stress symptoms, improve mental health, and alleviate physical pain.
Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT)
Mindfulness-Based Cognitive Therapy (MBCT) is an evidence-based approach that combines cognitive behavioral techniques with mindfulness practices. MBCT is effective in preventing the relapse of depression. You can use this approach to enable clients to identify negative thought patterns and develop healthier ways of thinking.
Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)
As a mindfulness-based behavioral therapy, ACT encourages clients to view their emotions, thoughts, and sensations as elements separate from the individual having them. For example, a client may be encouraged to notice that their anxiety is a sensation in the body rather than believing that it’s their anxiety.
Dialectical Behavior Therapy (DBT)
This therapy technique zeroes in on four skills: interpersonal effectiveness, emotional regulation, mindfulness, and distress tolerance. Studies show that DBT empowers a person to manage stress without harming themselves or others. Also, it’s an effective treatment for PTSD, eating disorders, depression, and anxiety.
Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR)
MBSR teaches people how to relax, focus, and be aware of their thoughts and feelings to manage stress and anxiety. It blends body awareness, mindfulness meditation, and yoga and encourages the client to explore their thinking, actions, feelings, and behavior.
Elevate Mindfulness Therapy with Relevant Interventions
Ongoing education allows you to revamp your mindfulness techniques and take your practice to the next level. Online CE Credits has a robust line-up of programs from dedicated and experienced therapists. Here are some courses to advance your professional development:
Also, take a look at mindfulness CEUs for mental health professionals.
Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of integrating mindfulness into psychotherapy are substantial, there are also challenges and considerations to keep in mind.
One potential challenge is client resistance. Some clients may be skeptical about mindfulness practices or may feel uncomfortable with the idea of meditation. So approach mindfulness with sensitivity, and be sure clients are ready. Also, introduce mindfulness gradually and provide clear explanations of its benefits to help ease any resistance.
Another consideration is proper training. While mindfulness techniques can be powerful, you need skill and expertise to implement them effectively. So training and continuing education opportunities can develop your proficiency.
Cultural sensitivity is also crucial when incorporating mindfulness into therapy. Mindfulness practices have roots in various cultural and spiritual traditions. As a result, be respectful and mindful of this heritage. Understand clients’ cultural backgrounds and be prepared to adapt mindfulness practices to fit their values and beliefs.
Incorporate Mindfulness into Your Psychotherapy

Integrating mindfulness into psychotherapy offers a wealth of benefits for both clients and therapists. You can enhance the therapeutic process and support clients in their healing journeys. From mindful breathing and body scan meditation to loving-kindness meditation, DBT, ACT, MBSR, and MBCT, you have numerous strategies to promote mindfulness in therapy.
Take Advantage of Continuing Education To Hone Your Skills
Ready to jumpstart your knowledge about mindfulness therapy interventions? You’re on the right platform. Online Credits offers affordable, exclusive mental health CEU certifications from home, risk-free. No due dates. No deadlines. You can complete the courses anytime, anywhere. Master your field with ease. Fulfill CE requirements and supercharge your clinical skills.

by Sadaqut | Jul 30, 2024 | Educational
The National Institutes of Health states that the healthcare system must take measures to address cultural competence to serve the needs of a diverse population. It explains that this can “alleviate healthcare disparities and improve healthcare outcomes in these patient populations.”
As the world becomes more globalized, cultural competency becomes a fundamental necessity. Therapists need knowledge, skills, and sensitivity to effectively deal with diverse clients.
In this post, we shall explore how developing cultural competence in therapy practices can improve therapeutic relationships and treatment outcomes.
What Is the Meaning of Cultural Competence?
Cultural competency refers to the ability of therapists to understand, communicate with, and effectively interact with clients across diverse cultures and backgrounds.
Several definitions from different health organizations shed more light on the essence of cultural competence. One example from the American Association for Health Education says:
“Cultural competence is the ability of an individual to understand and respect values, attitudes, beliefs, and morals that differ across cultures and to consider and respond appropriately to these differences in planning, implementing, and evaluating health education and promotion programs and interventions.”
In summary, if you’re culturally competent, it means you:
- recognize and respect the cultural influences that shape a client’s worldview, behaviors, and experiences.
- engage in an ongoing commitment to self-awareness, education, and adapting therapeutic approaches to meet the client’s uniqueness.
- understand how cultural identities impact a person’s mental health and coping mechanisms, and seek and deliver appropriate therapy.
Ultimately, it enables you to provide more tailored and effective treatment.

Why Is Cultural Competence Important?
Cultural competence in healthcare has several benefits for practitioners. Let’s explore some below:
Enhancing the Therapeutic Relationship
The therapeutic relationship is the cornerstone of effective therapy. Trust, rapport, and mutual respect between therapist and client are essential for successful treatment. Cultural competency plays a vital role in building and maintaining this relationship.
When you demonstrate cultural sensitivity and understanding, clients are more likely to feel respected, valued, and understood. This fosters a safe and supportive environment where clients can openly share their thoughts and feelings without fear of judgment or misunderstanding.
For instance, consider a therapist working with a client in a collectivist culture where family and community ties are highly valued. You can help a client feel more understood and supported if you recognize these connections and integrate them into your therapeutic process.
Conversely, a lack of cultural awareness can lead to misunderstandings, miscommunication, and a breakdown in the therapeutic relationship. This hinders the client’s progress.
Improving Treatment Outcomes
Cultural competency is directly linked to improved treatment outcomes. Practitioners with culturally competent skills can more accurately assess, diagnose, and treat mental health issues within the context of the client’s cultural background. This leads to more personalized and effective treatment plans that consider cultural influences on mental health.
For example, certain cultural groups may have specific beliefs about mental health and illness, which can influence how they perceive and respond to treatment. Psychotherapists can develop strategies that resonate with the values and practices of their clients by understanding their beliefs. This removes potential barriers to treatment, such as stigma or mistrust of mental health services.
In addition, you’re better equipped to recognize and address culturally specific manifestations of mental health issues. Symptoms of depression, anxiety, or trauma can vary significantly across cultures. You can avoid misdiagnosis and provide more accurate and effective interventions by being attuned to these differences.
Fostering Inclusivity and Respect
Cultural competency also promotes inclusivity and respect within therapy practices. An inclusive approach ensures all clients, regardless of their cultural background, feel welcome and valued. This is particularly important in mental health care, where clients are vulnerable and seeking support during challenging times.
It’s also possible to create an environment that respects and honors diversity if you prioritize cultural competency. This involves using inclusive language, being aware of cultural customs and practices, and continuously educating yourself about different cultural perspectives. As a result, you can create a more equitable and supportive therapeutic space for all clients.
Addressing Power Dynamics and Bias

Image Source
Cultural competency requires therapists to acknowledge and address power dynamics and biases that may impact the therapeutic process. Therapists hold a position of power and influence, so you should be mindful of how this dynamic can affect clients from marginalized or minority backgrounds.
Therapists must engage in ongoing self-reflection to recognize their own biases and how these may impact their interactions with clients. This includes examining how personal beliefs, values, and assumptions about different cultures can influence the therapeutic process. By actively working to mitigate these biases, health professionals can provide more objective and equitable care.
For example, if you hold unconscious biases about a particular cultural group, you may inadvertently impose these biases on your client. This leads to a skewed understanding of the client’s experiences and needs. You can work to challenge and overcome these biases to provide patients with unbiased and respectful care through self-awareness and cultural education.
Widen Your Knowledge in Cultural Competence Online
You might think continuing education is time-consuming. Here’s the solution. Online CE Credits dishes out therapist-managed courses online without due dates and deadlines. So you can master your skills and outshine your peers in cultural competence anytime, anywhere. And you can complete the programs easier than you think without sacrificing your job or family time.
Dip your toes into the courses below:
The Role of Education and Training
Education and training enable you to develop and maintain cultural competency in therapy. Therapists must commit to lifelong learning and professional development to stay informed about cultural issues and best practices. This can involve participating in cultural competency training programs, attending workshops and seminars, and engaging with cultural literature and research.
Also, you can benefit from seeking supervision or consultation with experienced colleagues in cultural competency. This collaborative approach allows you to gain insights, receive feedback, and refine your skills in working with diverse clients.

Client-Centered Care and Empowerment
Cultural competency aligns with the principles of client-centered care and empowerment. You can empower clients to take an active role in their treatment by recognizing and valuing their cultural identities. This collaborative approach encourages them to share their cultural perspectives, preferences, and values, which can inform and fine-tune the therapeutic process.
Empowering clients fosters a sense of agency and autonomy, which is crucial for their overall well-being and recovery. Clients who feel heard and respected are more likely to engage in therapy, adhere to treatment plans, and experience positive outcomes.
Aim for Cultural Competence
Cultural competency is crucial for modern therapy practices. It enhances the therapeutic relationship, and treatment outcomes, fosters inclusivity and respect, and addresses power dynamics and bias. As the world becomes increasingly diverse, the need for culturally competent therapists will continue to grow.
You can offer more effective, respectful, and inclusive care to clients if you commit to cultural competency. Build a strong foundation for professional growth with our comprehensive programs. Create an account to get started!

by Sadaqut | Jul 30, 2024 | Educational
Staying current with the latest developments in the field is crucial for any professional and for counselors. This is because mental health is continually changing, with new research, techniques, and best practices emerging regularly. However, continuing education costs can add up, making it challenging for some practitioners to keep up. Fortunately, you can find free resources to keep up-to-date without breaking the bank.
Here’s a complete guide on how to stay relevant with free and paid continuing education resources as a counselor.
Understanding the Importance of Continuing Education (CE)
Before diving into the resources, learn why CE is vital for counselors.
First and foremost, it makes you competent in your field. Mental health practices and theories evolve, and staying current with these changes helps counselors provide the most effective care.
Additionally, many states require certain continuing education hours for license renewal to ensure you grow professionally and personally. Continuing education also enables counselors to specialize in new areas, expand their knowledge base, and enhance their career prospects.
Professional Organizations and Associations
Joining professional organizations provides several benefits, including access to free continuing education resources. They have extensive libraries of webinars, articles, and courses available to their members.
Online CE Credits
If you’re looking for a hassle-free learning environment for CE courses, Online CE Credits is the real deal. It’s a therapist-managed platform with over 250 accredited and nationally approved programs delivered 24/7 online. Instructors with decades of experience and practical insights take you through the latest research and evidence-based practices in psychotherapy treatments.
Here are some courses to consider as a counselor:
Also, learn more about trauma training for social workers to hone your clinical skills.
American Counseling Association (ACA):
The ACA offers numerous free resources to its members, including webinars, articles, and access to their extensive library. Membership also provides networking opportunities and access to conferences and workshops.
National Board for Certified Counselors (NBCC):
The NBCC provides free continuing education opportunities to its certified counselors. They offer webinars and resources to help counselors stay updated on the latest practices and research in their field.
American Psychological Association (APA):
While primarily for psychologists, the APA offers numerous resources for counselors as well. They provide free webinars and articles on a range of topics. And their membership benefits include access to an extensive library of research and educational materials.
Local and Community Resources

Don’t overlook local resources when seeking continuing education opportunities. Many community organizations, universities, and local health departments offer free or low-cost seminars and workshops.
Local Universities and Colleges:
Many universities and colleges offer free seminars and workshops on mental health topics. These can be a great way to learn about the latest research and techniques in the field.
Community Health Organizations:
Local health organizations often provide free training and workshops for mental health professionals. These can be a great way to learn about issues specific to your community and network with other local professionals.
Public Libraries:
Many public libraries offer free access to educational resources, including online courses and webinars. They may also host events and workshops on mental health topics.
Leveraging Technology for Continuous Learning
Technology has revolutionized the way we access information and learn new skills. Leveraging these tools can help counselors stay updated with minimal cost and effort.
Podcasts and Webinars:
You can also find free podcasts and webinars with a wide range of topics relevant to counselors. Podcasts such as “The Trauma Therapist Podcast” and “Shrink Rap Radio” provide valuable insights and discussions with experts.
YouTube Channels:
Platforms like YouTube have a wealth of free educational content available. Channels like “Therapist Aid” and “The School of Life” have videos on various counseling techniques and mental health topics.
Social Media Groups and Forums:
Joining professional groups on platforms like LinkedIn and Facebook can provide access to a community of peers who share resources and information about free continuing education opportunities. These groups post about upcoming webinars, free courses, and useful articles.
Staying Informed Through Journals and Publications
Professional journals and publications are essential resources for staying updated on the latest research and developments. Many organizations provide free access to certain articles or editions, making it easier to stay informed.
PubMed and Google Scholar:
These platforms offer access to a vast array of research articles and journals. While some articles require a subscription, many are available for free, particularly older publications.
Professional Organization Journals:
Journals published by organizations such as the ACA, APA, and NBCC grant free access to certain articles for members. In these journals, you’ll find the most recent developments and research on counseling.
Open Access Journals:
High-quality research articles are freely available online through open-access journals.
Journals such as the “Journal of Counseling & Development” and “Frontiers in Psychology” offer free access to many of their publications.
Building a Personal Learning Network
Creating a personal learning network is a powerful way to stay updated and engaged with the latest developments. This network can include mentors, colleagues, and other professionals who share your passion for learning and professional growth.
Networking Events:
Attending free or low-cost conferences, workshops, and seminars can help you connect with other professionals. These connections can provide valuable insights and resources for continuing education.
Online Communities:
Joining online communities and forums can help you stay connected with other professionals and stay informed about free continuing education opportunities. Platforms like Reddit, LinkedIn, and professional association forums are great places to start.
Mentorship:
Finding a mentor can provide guidance and support as you navigate your career and continue your education. A mentor can help you identify valuable resources and provide insights based on their own experiences.

Maximizing Free Resources for Your Continuing Education
To make the most of the free resources available, approach your continuing education with a strategic plan. Here are some tips to help you stay organized and take advantage of these opportunities:
Set Clear Goals:
Define what you want to achieve with your continuing education. Whether it’s meeting licensing requirements, learning a new technique, or staying updated on the latest research, having clear goals will help you focus your efforts.
Create a Schedule:
Dedicate regular time to your continuing education activities. Setting aside time each week to watch webinars, read articles, or participate in online discussions can help you stay on track.
Keep a Learning Journal:
Document what you learn and how it applies to your practice. Keeping a journal can help you reflect on your learning and identify areas for further study.
Engage with the Material:
Actively participate in webinars, discussions, and workshops. Asking questions and engaging with the material will help you retain the information and apply it in your practice.
Evaluate Your Progress:
Regularly assess your progress toward your continuing education goals. Adjust your plan as needed to ensure you are meeting your objectives and making the most of the resources available to you.
Embrace CE To Grow Professionally
Continuing education keeps you competent, knowledgeable, and effective in your practice. While the cost of continuing education can be a barrier, there are free resources to help you stay updated without breaking the bank. Leverage online platforms, professional organizations, local resources, and technology, and build a personal learning network to stay informed and grow professionally.
Also, approach your continuing education with a strategic plan, set clear goals, and engage actively with the material to make the most of these opportunities. As a result, you can be well-equipped to provide the best care for your clients and advance your career.
Climb the Ranks in CE with Online CE Credits
You might think CE is out of your reach. Think again! Our flexible payment plans are designed with your budget in mind. Invest in your career without breaking the bank. Unlock your potential with affordable, high-quality CE credits today.

by Sadaqut | Jul 30, 2024 | Educational
The National Association of Anorexia Nervosa and Associated Disorders (ANAD) says that 28.8 million Americans will suffer from an eating disorder during their lifetime. And this represents nearly 9% of the national population.
Eating disorders, including anorexia nervosa, bulimia nervosa, and binge eating disorders, present complex challenges that impact both the body and mind.
Understanding the latest approaches to treating these conditions allows you to refine your interventions and improve client outcomes. In this A-Z guide, we’ll dive into groundbreaking approaches to eating disorder therapies.
Understanding the Complexity of Eating Disorders

Image Source
Eating disorders are more than just food issues. They’re serious mental health conditions that stem from a combination of genetic, biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors. The consequences of eating disorders can be severe, affecting physical health, emotional well-being, and overall quality of life.
Traditional treatments have included a blend of medical intervention, nutritional counseling, and psychotherapy. However, innovative approaches are expanding the toolkit for practitioners, offering new hope for those struggling with these disorders.
The Role of Technology in Treatment
One of the most exciting advancements in eating disorder treatment is the integration of technology. For example, telehealth has become an invaluable resource, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic. It allows you to reach clients without access to specialized care in their geographic area. This remote approach can also reduce the stigma associated with seeking treatment, as patients can engage in therapy in the privacy of their homes.
Also, you can use specific apps and online programs to support eating disorder recovery. These tools can provide meal planning assistance, mindfulness exercises, and daily logs to track progress. They can also offer immediate access to coping strategies and educational resources, making support more accessible and continuous.
Integrating Mindfulness and Meditation
Mindfulness and meditation have long been recognized for their benefits in managing stress and improving mental health. In the context of eating disorders, these practices can help clients develop a healthier relationship with food and their bodies.
For instance, Mindfulness-Based Eating Awareness Training (MB-EAT) combines mindfulness meditation with guided eating practices to help individuals recognize their body’s hunger and satiety cues. This method encourages a non-judgmental awareness of eating habits and promotes a more intuitive way of eating.
You can also integrate mindfulness into cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), which is a cornerstone of eating disorder treatment. As a result, you can help clients stay present and focused during the session. This enhances their ability to challenge and change negative thought patterns related to body image and food.
The Promise of Nutritional Psychiatry
Nutritional psychiatry is an emerging field that examines the impact of diet on mental health. Research has shown that certain nutrients can influence brain function and mood regulation, which is relevant for eating disorder treatment. Therapists can collaborate with dietitians in nutritional psychiatry to create comprehensive treatment plans to address both psychological and nutritional needs.
For example, omega-3 fatty acids, found in fish and flaxseeds, have been linked to improved mood and cognitive function. Probiotics, which support gut health, are also being studied for their potential role in mental health. You can offer a more holistic approach to treatment by integrating nutritional guidance with psychotherapy,
Family-Based Treatment and Support Systems
Family-based treatment (FBT) has been effective for adolescents with eating disorders. It involves the entire family in the treatment process, recognizing that the family system plays a crucial role in the recovery journey. FBT empowers parents to take an active role in their child’s nutrition and encourages open communication within the family.
Innovative approaches also recognize the importance of peer support. In-person and online support groups provide a sense of community and shared experience that can be incredibly valuable for individuals in recovery. They offer a space for clients to share their struggles and successes, reducing feelings of isolation and promoting a sense of belonging.
The Power of Art and Expressive Therapies
Art therapy and other expressive therapies, such as dance and music therapy, offer alternative ways for clients to express emotions and experiences that may be difficult to articulate verbally. They help people with eating disorders, as they often struggle with verbalizing their feelings and may have a disrupted sense of self.
Art therapy lets clients explore their body image and self-perception in a non-threatening way. Creating art can serve as a metaphor for the therapeutic process, helping clients visualize their progress and confront their fears. Similarly, dance and movement therapy can help individuals reconnect with their bodies in a positive and empowering manner.
Advancing Your Continuing Education in Eating Disorders
Want to make strides in eating disorder treatment? Online CE Credits provides high-quality online CEUs for counselors, therapists, social workers, and psychologists. Access on-demand CE courses and completion certificates 24/7 from the convenience of your home! Take a look at the programs below:
Also, discover more insightful tips on ADHD training to elevate your practice.

Addressing Trauma and Co-occurring Disorders
Many individuals with eating disorders have a history of trauma or co-occurring mental health conditions, such as anxiety, depression, or obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
Innovative treatment approaches recognize the need to address these underlying issues to support lasting recovery.
Trauma-informed care also emphasizes safety, trustworthiness, and empowerment and creates a therapeutic environment where clients feel secure and understood.
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) is an evidence-based therapy that has shown promise in treating trauma and associated symptoms. It can help clients with eating disorders find relief from distressing thoughts and behaviors since it processes traumatic memories to reduce their emotional impact
The Importance of Cultural Competence
Eating disorders affect individuals from diverse backgrounds, and cultural factors can influence the presentation and treatment of these conditions. Cultural competence in therapy involves understanding and respecting the cultural contexts of clients’ lives. This includes being aware of cultural attitudes toward body image, food, and mental health.
You can brush up on your cultural competence by seeking training and education on working with diverse populations. A culturally sensitive therapeutic environment enables you to build stronger connections with your clients and provide more effective, individualized care.
The Future of Eating Disorder Treatment
The field of eating disorder treatment is changing, with new research and innovations paving the way for more effective interventions. As a therapist, stay informed about these developments to provide the highest quality care. For example, you can attend professional development workshops, participate in continuing education courses, and engage with the latest research.
Incorporating these innovative approaches into your practice improves your effectiveness as a therapist and offers hope and healing to those struggling with eating disorders.
Head On Over to Online CE Credits
Earning your CE credits doesn’t have to be hard. We offer asynchronous lessons on flexible payment options. You can either choose to pay once or take on a membership plan. And the good news is that if you’re unhappy with your program, you can claim a refund. Overcome CE challenges with our flexible and convenient options.

by Sadaqut | Jul 30, 2024 | Educational
The World Health Organization explains that death and disability due to Parkinson’s disease are increasing worldwide.
While medication and physical treatments are common in PD, therapy is equally vital to manage the disease’s emotional and psychological impacts. This blog post aims to explore the role of therapy in managing Parkinson’s disease and equip counselors with novel strategies.
What Is Parkinson’s Disease?
Parkinson’s disease is a chronic and progressive movement disorder, meaning that symptoms continue and worsen over time. Although genetics and environmental factors are thought to play a role in PD, its cause is unknown.
According to the American Association of Neurological Surgeons (ANNS), PD results from nerve cell degeneration in the movement-controlling part of the brain called the substantia nigra. An important chemical called dopamine is lost when these nerve cells die or become impaired.
Dopamine is a neurotransmitter that sends messages to the part of the brain that controls movement and coordination. The decrease in dopamine leads to the hallmark symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, including tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability.
The Emotional and Psychological Impact of Parkinson’s Disease
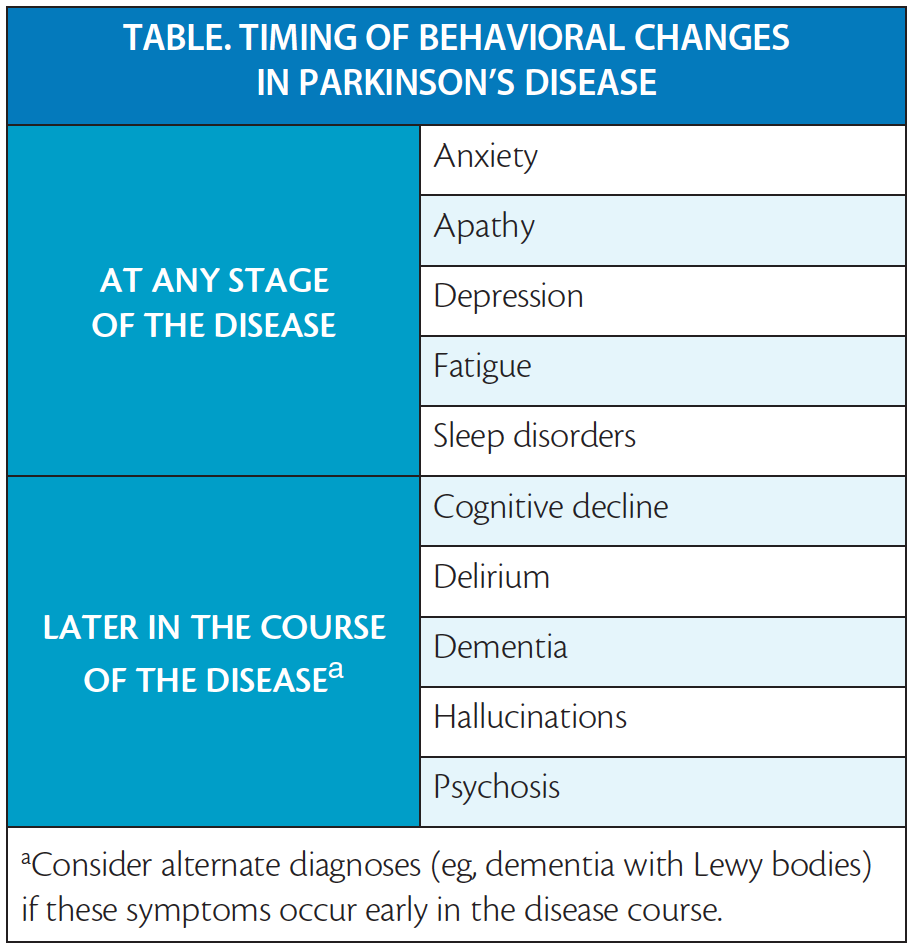
Image Source
The diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease can be devastating for individuals and their families. It often brings about significant emotional and psychological challenges, including anxiety, depression, and a sense of loss. Patients may struggle with the reality of a progressive illness, fear of disability, and changes in their roles and identities.
The physical symptoms, coupled with the emotional strain, can lead to social isolation, a reduced quality of life, and a diminished sense of well-being. This is where therapy plays a critical role.
The Role of Therapy in Managing Parkinson’s Disease
Therapy for Parkinson’s disease is multifaceted, addressing both the physical and psychological aspects of the condition.
Here, we’ll focus on the psychological and emotional support you can provide to help individuals with Parkinson’s disease and their families cope with their challenges.
Counseling and Psychotherapy
Counseling and psychotherapy enable individuals with Parkinson’s disease to manage the emotional and psychological impact of their condition.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is effective in addressing depression and anxiety, common comorbidities in PD patients. CBT helps individuals identify and challenge negative thought patterns and behaviors, promoting more positive ways of thinking and coping.
You can enhance your client’s quality of life by working with them to develop practical strategies for managing their symptoms and emotions
Support for Caregivers and Families
The impact of Parkinson’s disease extends beyond the individual to their caregivers and families. Providing support to caregivers is essential, as they experience high levels of stress, anxiety, and burnout.
Family therapy helps manage the dynamics and communication within the family unit, fostering a supportive environment for the patient and their loved ones. Educating families about the disease, its progression, and coping strategies can empower them to better support their loved ones while taking care of their own emotional needs.
Mindfulness and Stress Reduction Techniques
Mindfulness-based stress reduction (MBSR) and other mindfulness techniques can be highly effective in managing the stress and emotional turmoil associated with Parkinson’s disease.
They empower individuals to focus on the present moment, reducing feelings of anxiety and depression.
Techniques such as deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, and guided imagery can help patients manage stress and improve their emotional well-being. You can incorporate these techniques into your sessions, teaching clients how to use them in their daily lives.
Addressing Cognitive Changes
Cognitive changes are common in Parkinson’s disease, with some individuals experiencing difficulties with memory, attention, and executive function. Neuropsychological assessments can help identify specific cognitive deficits, allowing counselors to tailor their therapeutic approaches accordingly.
Cognitive rehabilitation therapy (CRT) revitalizes a patient’s cognitive functioning and develops compensatory strategies for managing daily tasks. Providing education and support to patients and their families about cognitive changes can also help reduce anxiety and improve coping.
Building a Support Network
Social support is crucial for individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Encouraging clients to build and maintain a strong support network can help alleviate feelings of isolation and improve their overall well-being.
Online and in-person support groups provide a platform for individuals to share their experiences, gain insights, and receive emotional support from others who understand their challenges. Counselors can help clients find appropriate support groups and encourage their participation.
Promoting Self-Efficacy and Resilience
Promoting self-efficacy and resilience is an important aspect of therapy for individuals with Parkinson’s disease. Helping clients set realistic goals, recognize their achievements, and develop problem-solving skills can fortify their sense of control and competence.
Clients can also improve their mood and overall quality of life by participating in activities they enjoy. By building resilience, individuals become more positive and develop better coping methods as they adapt to the conditions brought about by the disease.
Mastering Therapies for Depression and Anxiety
Parkinson’s disease poses a ton of challenges for practitioners since it’s associated with depression and anxiety. However, it’s possible to alleviate mental disorders through online CEU programs from Online CE Credits. The learning platform has in-depth certifications from specialists with decades of experience in treating anxiety and depression.
Dominate your practice with the courses below:
Want to explore more insights into continuing education? Take a look at ethics CEUs.
Physical and Occupational Therapy
Physical and occupational therapies are integral components of Parkinson’s disease management. Physical therapy focuses on improving mobility, balance, and strength, while occupational therapy helps patients maintain independence in their daily activities.
For example, physical therapy exercises can include elements of mindfulness and relaxation, reducing stress and promoting mental well-being. Occupational therapy can cover strategies to simplify daily tasks, minimize frustration, and increase the patient’s sense of autonomy.
As a result, you can collaborate with physical and occupational therapists to create a holistic treatment plan to deal with the disease’s physical and psychological aspects.

The Importance of Early Intervention
Early intervention is key to managing Parkinson’s disease effectively. Counselors should encourage patients and their families to seek help as soon as symptoms arise. Early diagnosis and treatment can slow the progression of the disease and improve the quality of life.
Educational sessions about Parkinson’s disease can benefit patients, families, and caregivers. Understanding the disease, its symptoms, and available treatment options enables individuals to make informed decisions and take an active role in their care.
You can also organize workshops or informational sessions to disseminate this vital information.
Continuing Education for Counselors
Because Parkinson’s disease is progressive in nature and complex, counselors must engage in ongoing education and training. The latest research, treatment options, and therapeutic techniques allow you to provide the best possible care for your clients.
Online continuing education courses are convenient for you as they let you stay updated on the latest developments. They cover a range of topics, including the psychological impact of Parkinson’s disease, effective therapeutic interventions, and strategies for supporting caregivers and families.
Consider Various Therapies for Treating Parkinson’s Disease
The multifaceted nature of the disease requires a comprehensive approach that addresses physical and emotional health. Psychological support, family counseling, cognitive rehabilitation, and collaboration with other healthcare professionals can enhance the well-being of people living with Parkinson’s disease.
Gain Ground with Online CE Credits
Wondering how you can hone your skills in treating mental disorders associated with PD at affordable rates? Online CE Credits makes learning and earning CE credits a breeze. Our premium video CE courses bring experienced mental health trainers to your living room, either on-demand or via live events/webinars! NOW INCLUDES access to Certificate Program enrollment and live consultation events! Advance your career in just 5 days with our flexible CE courses.
















