loading...

by Tim Cassidy | Sep 17, 2024 | Certificate
Understanding criminal behavior has long fascinated psychologists, criminologists, social workers, and law enforcement professionals. Traditional criminology focuses on social, environmental, and economic factors influencing crime. However, neurocriminology is a more recent field that aims to understand criminal behavior by looking at the brain’s structure and function.
Neurocriminology blends neuroscience and criminology, examining how brain abnormalities, genetics, and neurological processes might contribute to criminal behavior. This field presents an innovative approach to understanding the criminal mind, with significant implications for predicting and preventing crime.
The Basics of Neurocriminology
Neurocriminology is based on the idea that certain brain structures and functions may predispose individuals to criminal behavior. It involves studying brain imaging, genetics, and neuropsychological tests to identify patterns that may be associated with violent or antisocial behavior.
Researchers in this field focus on areas such as the prefrontal cortex, the amygdala, and neurotransmitter systems. For example, the prefrontal cortex is involved in decision-making, impulse control, and social behavior. Abnormalities or dysfunctions in this area can be linked to aggressive and impulsive behavior.
The Dartmouth Undergraduate Journal of Science says a study found that there was a 4.3-fold increase in reoffending among parolees with diminished activity in the anterior cingulate cortex. It’s a brain region connected to executive function.

Also, genetic factors are also considered in neurocriminology. Studies have shown that some genes might influence traits such as aggression, impulsivity, and fearlessness. And these traits could increase the risk of criminal behavior when some environmental factors occur.
The “warrior gene,” also known as MAOA-L, is often highlighted in discussions about genetics and aggression. While having this gene does not guarantee criminal behavior, it may predispose individuals to violence when combined with adverse environments.
Master Effective Interventions in Neurocriminology
Want to advance your therapy in neurocriminology and fulfill your licensure requirements? Look no further! Onlince CE Credits has a treasure trove of practical and nationally approved certifications at fraction of the cost. Earn more than 10 credits by enrolling in the courses below:
The Role of Brain Imaging in Understanding Criminal Behavior
Advancements in brain imaging technology, such as functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET), have allowed researchers to explore the neural underpinnings of criminal behavior. These imaging techniques help visualize brain activity in real-time and examine how different brain regions communicate and respond to stimuli.
One landmark study used brain imaging to compare the brains of violent criminals with those of non-violent individuals. The study found that violent criminals often showed reduced activity in the prefrontal cortex, the part of the brain associated with impulse control and moral judgment. Such findings suggest a biological basis for impulsive and aggressive behavior, challenging the notion that criminal actions are purely a result of social or moral failing.
In another study, researchers used PET scans to study the amygdala, the brain’s emotional center responsible for processing fear and aggression. They discovered that criminals with a history of violent behavior had an overactive amygdala and an underactive prefrontal cortex. It could explain their inability to regulate emotions effectively.
These findings indicate that the structure and function of the brain can play a significant role in predisposing someone to criminal behavior.
The Implications for Early Intervention
One of the most promising aspects of neurocriminology is its potential for early intervention. If specific neurological markers can be identified that indicate a predisposition to violent behavior, there could be opportunities for early detection and intervention. This could include personalized treatment plans that focus on behavioral therapy, medication, or a combination of both to help mitigate these tendencies before they manifest as criminal behavior.
Research has suggested that children from high-risk environments displaying early signs of aggressive or antisocial behavior could benefit from interventions that focus on enhancing cognitive and emotional regulation skills. For instance, programs targeting impulse control, empathy development, and stress management have shown promise in reducing future criminal behavior.
Neurocriminology could inform these programs by identifying which children might benefit the most from certain types of interventions, making them more effective.
Neurocriminology in the Courtroom
The use of neurocriminology in legal settings is a growing area of interest. Some defense attorneys have started to use brain imaging and neurobiological evidence to argue for reduced sentences, claiming that their clients’ brains are “wired” for impulsivity and aggression, diminishing their culpability.
While this approach has led to reduced sentences in some cases, it also raises ethical concerns. If we start seeing criminal behavior as a consequence of brain structure, it challenges the traditional legal notion of free will and personal responsibility.
Forensic psychologists and mental health professionals need to navigate this complex landscape carefully. They must balance understanding the neurobiological factors contributing to criminal behavior with the ethical and legal implications of using such information in court.
The potential to identify neurobiological risk factors for crime should not overshadow the importance of social and environmental factors, nor should it absolve individuals of their actions.
Treatment and Rehabilitation: A Neuro-criminological Approach
Neurocriminology offers new avenues for treating and rehabilitating offenders. Traditional rehabilitation programs often focus on behavioral modification, education, and social skills training. However, if certain criminal behaviors are linked to brain abnormalities or dysfunctions, there must be tailored approaches that address these specific issues.
For instance, cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) has been shown to help modify neural pathways associated with negative thought patterns and behaviors. Neurofeedback is another promising area that uses real-time brain activity monitoring to teach self-regulation of brain function. By providing offenders with tools to regulate their brain activity, neurofeedback could help reduce impulsive and aggressive behavior.
Pharmacological interventions are also being explored. Some studies suggest that medications affecting neurotransmitter levels, such as selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), could help reduce aggression and impulsivity in individuals with certain neurobiological risk factors. However, the use of medication for managing criminal behavior is controversial. It must be approached with caution, keeping in mind ethical considerations and potential side effects.
Challenges and Controversies in Neurocriminology
While neurocriminology provides a new lens through which to view criminal behavior, it has some limitations. One major concern is the potential for neuro-criminological findings to be misused or misunderstood. For example, if a biological predisposition to criminal behavior is identified, individuals with certain genetic markers or brain abnormalities could be stigmatized or discriminated against.
This could lead to ethical and legal challenges regarding privacy, consent, and the potential for abuse of such information.

Another challenge is distinguishing correlation from causation. While certain brain patterns may be associated with criminal behavior, it does not necessarily mean they cause it. Environmental, social, and psychological factors may influence criminal behavior. So reducing criminal behavior to a purely neurological or genetic explanation oversimplifies a complex issue.
Mental health professionals working in forensic settings need to be cautious about interpreting and applying neuro-criminological research. It is crucial to integrate neuro-criminological findings with insights from psychology, sociology, and criminology to create a more comprehensive understanding of criminal behavior.
The Future of Neurocriminology: Where Do We Go from Here?
As technology advances, the field of neurocriminology is likely to grow, providing deeper insights into the biological causes of criminal behavior. The potential to use neurobiological data to predict criminal behavior is both exciting and daunting. While early detection and targeted interventions could help reduce crime rates, but there is also the risk of infringing on civil liberties and privacy.
For mental health professionals, understanding neurocriminology’s role in criminal behavior offers a valuable perspective when working with at-risk individuals or those in the criminal justice system. This knowledge can inform more effective assessment, treatment, and rehabilitation approaches. However, it is essential to approach this field with a critical mind, acknowledging its limitations and ethical challenges.
Take Advantage of Neurocriminology
Ultimately, neurocriminology represents a new frontier in understanding crime, one that could reshape our approaches to prevention, intervention, and rehabilitation. By blending neuroscience with psychology and criminology, this field has the potential to revolutionize how we think about and address criminal behavior—offering new pathways for both research and practice. Take a bold step in your therapy and create an account with Online CE Credits.

by Tim Cassidy | Sep 3, 2024 | Certificate
Emotional eating presents a significant challenge for many individuals, deeply affecting their ability to manage their weight effectively. Traditional weight loss programs often emphasize diet and exercise, yet many overlook the emotional and psychological factors driving unhealthy eating habits. Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) therapy offers a unique and promising approach to addressing these underlying emotional triggers, thereby supporting sustainable weight loss.
Understanding Emotional Eating
Emotional eating occurs when individuals use food as a coping mechanism for handling emotional distress rather than addressing hunger. Common triggers include stress, sadness, anger, and even positive emotions. This habit can lead to the consumption of high-calorie comfort foods, which may provide temporary relief but often result in feelings of guilt and further emotional distress. This cycle is difficult to break and can undermine efforts at weight management.
The roots of emotional eating are often embedded in past experiences and unresolved emotional issues. For some, these issues may stem from childhood traumas, such as neglect or bullying, while others may have developed a negative body image or experienced the harmful effects of restrictive dieting. Over time, food becomes a source of comfort, security, or even self-punishment. Addressing these underlying emotional drivers is crucial for changing eating behaviors and achieving lasting weight loss.
How EMDR Can Help
EMDR is a psychotherapy technique originally developed to treat trauma, particularly post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It involves recalling distressing memories while simultaneously engaging in bilateral stimulation, typically through guided eye movements. This process helps the brain reprocess traumatic memories, reducing their emotional intensity and enabling individuals to move past them.
In the context of emotional eating, EMDR can be used to identify and reprocess the traumatic or distressing experiences that contribute to an unhealthy relationship with food. It’s possible to alter eating habits and emotional responses by addressing these root causes.
Here are examples of eating disorders in more detail:
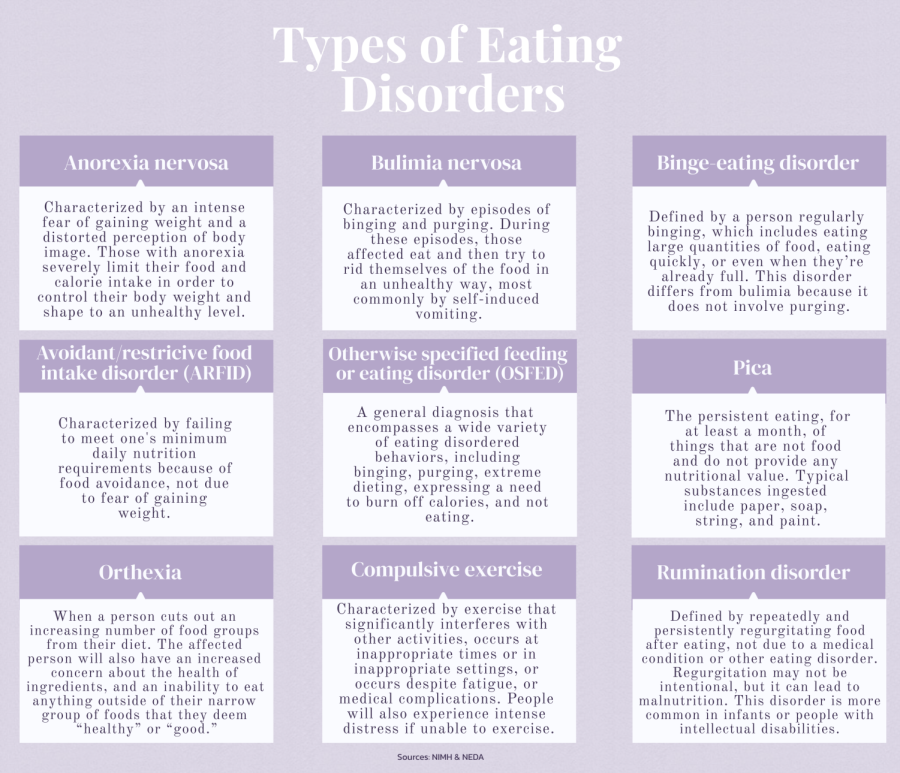
Image Source
Building Healthy Habits Through EMDR
In addition to addressing the root causes of emotional eating, EMDR can support the development of healthier eating habits. Many individuals hold negative beliefs or memories related to food that can sabotage their efforts to make positive changes. For instance, someone who associates dieting with feelings of deprivation or failure may find it challenging to stick to a healthy eating plan.
EMDR can help reframe these negative associations, making it easier for individuals to adopt and maintain new habits. With EMDR, healthier choices become more accessible and sustainable by reducing the emotional intensity of food-related memories.
EMDR and Long-Term Success
Maintaining weight loss is often more difficult than achieving it initially, especially when emotional eating is involved. Without addressing the emotional roots, the risk of regaining weight is high. EMDR provides long-term benefits by helping individuals reprocess the underlying issues that drive emotional eating, equipping them with the tools necessary to sustain their progress.
People can support their weight loss goals in the long run by reducing the power of unresolved emotions.
Outperform Your Peers in Emotional Eating Treatment With Bargain Programs
We’ve all felt the regret of wishing we knew something sooner. Don’t let that happen with your professional development. Our continuing education courses can help you achieve your career goals faster than you ever thought possible. Invest in your future as a competent therapist by enrolling in the accredited courses below:
Practical Considerations for Therapists
Therapists interested in incorporating EMDR into their work with clients struggling with emotional eating should approach the issue with sensitivity and care. Emotional eating is often linked to deeply personal and painful experiences, and clients may need time to build trust before they are ready to explore these issues.
It can be beneficial to begin by educating clients about the connection between trauma and emotional eating and how EMDR can help. Encouraging clients to identify specific memories or experiences that trigger their eating behaviors can provide a starting point for EMDR therapy.
As with any therapeutic approach, it is essential to tailor EMDR to the individual needs of each client. Some may benefit from focusing on past traumas, while others may need to address current stressors or future anxieties. By adopting a personalized approach, therapists can help clients achieve lasting changes in their relationship with food and overall well-being.
Beat Emotional Eating With EMDR Therapy
EMDR offers a powerful tool for addressing the emotional roots of unhealthy eating behaviors, supporting individuals in their journey toward sustainable weight loss. EMDR can help clients break the cycle of using food as a coping mechanism by assisting them in reprocessing traumatic or distressing experiences that fuel emotional eating.
As clients’ emotional responses improve, they are better able to adopt and maintain positive eating habits. This results in long-term weight-loss success.
For those struggling with emotional eating, EMDR may provide the missing piece in their weight loss journey. This provides a pathway to both physical and emotional well-being. Begin your learning experience today.
by Tim Cassidy | Sep 3, 2024 | Certificate
Crafting effective EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) questions is a skill that can significantly enhance the therapeutic process. It can lead to deeper emotional processing and healing for clients. While the EMDR protocol provides a structured approach, the flexibility within this framework allows therapists to tailor their questions that resonate with each client’s unique experiences. Understanding the art of asking the right questions can make a profound difference in the success of the therapy.
Also, completing an accredited course in EMDR for professional development enables you to identify what triggers a patient’s emotions and where they come from. From there, you can help the person identify and process their emotions positively.
The Art of Tapping into the Client’s Narrative
At the heart of EMDR therapy is the client’s narrative—their personal story that is often intertwined with traumatic experiences. The way a therapist engages with this narrative can either open doors to new understanding or inadvertently close them. The initial phase of EMDR, known as History-Taking, is crucial for building rapport and understanding the client’s experiences. Here, therapists gather information about the client’s past, present, and desired future.
4 EMDR History-Taking Components (Infographic)
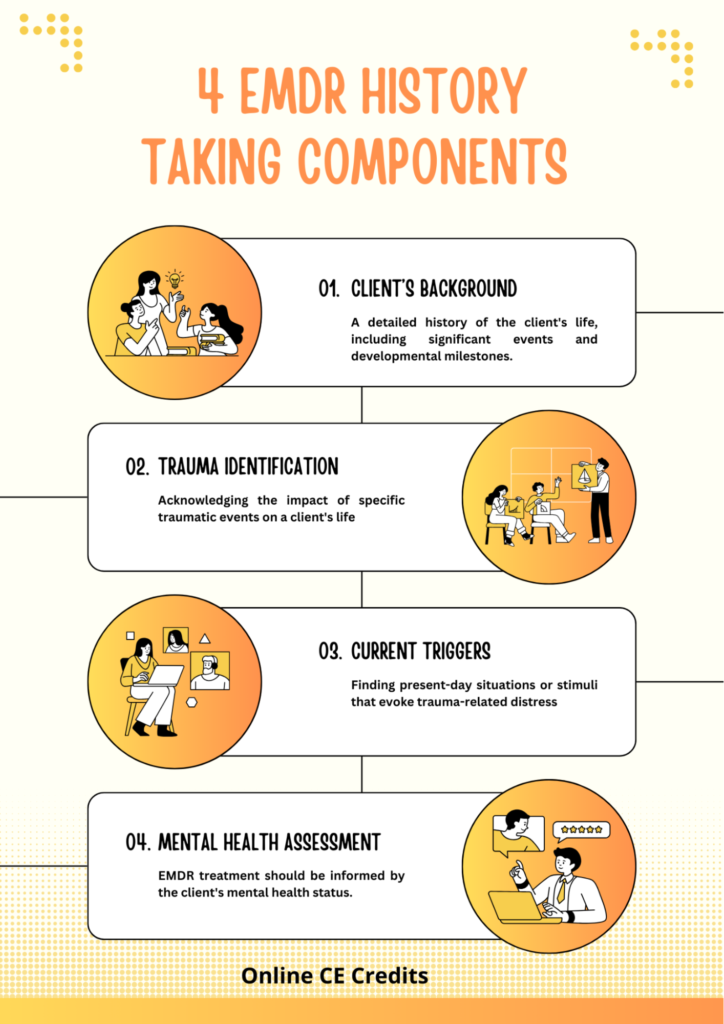
However, this phase goes beyond simple data collection. It’s about listening deeply to the way clients describe their memories, emotions, and beliefs.
For instance, when a client speaks about a traumatic event, it’s important to pay attention not just to the content but to the language they use. Are they using certain words repeatedly? Do they seem stuck on specific details? This language provides clues about where they might be emotionally or cognitively “stuck.” A therapist might then ask, “When you think of that moment, what image or thought stands out the most for you right now?” This type of question helps to hone in on the aspects of the memory that are most charged with emotion, setting the stage for effective EMDR processing.
Balancing Structure With Flexibility
EMDR is often lauded for its structured approach, but within this structure, there’s a need for flexibility, especially when it comes to questioning. The Standard Protocol provides a series of steps and questions to follow, but each client’s journey through these steps is unique. This is where the therapist’s skill in crafting questions becomes particularly valuable.
For example, during the Assessment Phase, clients are asked to identify a negative cognition associated with a traumatic memory. The standard question might be, “What negative belief do you have about yourself when you think of that event?” While this is a good starting point, some clients may struggle to articulate clear negative cognition. In such cases, rather than pushing for an answer, a therapist might say, “If it’s hard to find the right words, can you share what feelings come up when you think about that event?” This invites the client to explore their internal experience without the pressure of finding the “right” answer, which can then naturally lead to identifying the underlying negative cognition.
Pacing and Timing: Knowing When To Ask
In EMDR, timing is everything. A question asked too soon can overwhelm a client, while a question asked too late might miss the emotional peak necessary for effective processing. This is particularly true during the Desensitization Phase, where clients process the traumatic memory through bilateral stimulation (e.g., eye movements).
Here, therapists must be attuned to the client’s responses—both verbal and non-verbal. If a client appears to be struggling with intense emotions, it might be tempting to jump in with a question to clarify or redirect. However, sometimes the best intervention is silence, giving the client space to process internally. When it does feel appropriate to ask a question, it should be one that helps the client stay with their experience without leading them away from it. A simple, “What do you notice now?” can be enough to keep the process moving forward without overwhelming the client.
Navigating Cognitive Interweaves: Gentle Nudging Towards Resolution
Cognitive interweaves are an advanced EMDR technique used when a client becomes stuck during processing. These are strategic interventions where the therapist introduces a piece of information or a perspective to help the client move past a block. The key to effective cognitive interweaves lies in how the therapist frames their questions or statements.
For example, if a client is stuck in a loop of self-blame, a cognitive interweave might involve gently challenging this belief. Instead of directly confronting the belief with a statement like, “It wasn’t your fault,” which might trigger resistance, a therapist might ask, “If someone else had experienced this, would you hold them responsible in the same way?” This type of question encourages the client to reflect and reconsider their belief from a different angle, without feeling confronted or judged.
The effectiveness of a cognitive interweave often hinges on the therapist’s ability to introduce new ideas subtly, allowing the client to come to their own conclusions. This requires a delicate balance—being supportive without leading and challenging without confronting.
Ignite Your Trauma Treatment With Core CEU Courses
Learn from experienced clinicians who specialize in trauma assessment, treatment, and prevention. Our online courses offer flexible learning at your own pace, allowing you to access valuable knowledge 24/7. Master techniques like clinically interviewing trauma clients without retraumatization, utilizing sensorimotor therapy for trauma recovery, and addressing personality and dissociative disorders stemming from trauma. Equip yourself to provide compassionate and effective care for clients navigating the complexities of trauma.
Fostering a Collaborative Relationship
EMDR is a collaborative process. The therapist and client work together, each bringing their expertise to the table—the therapist with their knowledge of the EMDR protocol and the client with their intimate understanding of their own experiences. Effective questioning in EMDR respects this collaboration, inviting the client’s input and feedback at every step.
For instance, after processing a memory, a therapist might ask, “How does that feel different now?” rather than assuming a shift has occurred. This open-ended question allows the client to express their experience without feeling pressured to report progress. It also reinforces the collaborative nature of the work, reminding the client that their experience is central to the process.
Additionally, therapists can invite clients to be active participants in setting the agenda for sessions. This might involve asking, “What would you like to focus on today?” at the start of a session, or “Is there something specific you’d like to explore further?” during the session. These questions empower the client, fostering a sense of agency that is crucial for effective therapy.

Reflecting on Progress and Reinforcing Positive Changes
As therapy progresses, it’s important to help clients recognize the changes they are making, both big and small. During the Reevaluation Phase, therapists review previously processed memories to assess the client’s progress and determine next steps. Here, the questions asked can help clients consolidate their gains and reinforce positive changes.
Rather than simply asking, “How do you feel about that memory now?” A more effective approach might be, “When you think about that event now, what’s different for you?” This question not only checks in on the client’s emotional state but also encourages them to reflect on the progress they have made. This reflection is a crucial part of the healing process, as it helps to solidify the new, more adaptive beliefs and feelings that have emerged through EMDR.
Use the Power of the Right Question
The questions asked in EMDR are more than just prompts for discussion—they are tools that guide the client’s journey through their memories, emotions, and beliefs. Crafting the right question at the right time can make the difference between a client feeling stuck or experiencing a breakthrough. It requires a blend of clinical knowledge, intuition, and a deep understanding of the client’s experience.
As therapists continue to refine their questioning techniques in EMDR, they not only deepen the therapeutic process but also enhance their clients’ ability to heal and grow. The power of EMDR lies in its ability to transform lives, one carefully crafted question at a time. Expand your expertise in trauma therapy with our expert-led CE courses.

by Tim Cassidy | Aug 27, 2024 | Certificate
When working with Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), selecting and applying the right cognitions is critical to the therapy’s success. As many therapists know, EMDR isn’t just about eye movements or tapping; it’s about carefully guiding the client through a process that helps them reprocess traumatic memories and replace negative beliefs with more adaptive ones.
EMDR therapy involves eight phases, but one of the most intricate aspects is the cognitive interweave—selecting and refining cognitions to ensure they resonate deeply with the client. This part of the therapy is essential because the success of EMDR often hinges on how well these cognitions are crafted and utilized.
Understanding the Core of EMDR Cognitions
Cognitions in EMDR can be broken down into two categories: Negative Cognitions (NCs) and Positive Cognitions (PCs). Negative Cognitions are the distorted beliefs clients hold about themselves due to traumatic experiences, while Positive Cognitions represent the more adaptive beliefs they aim to develop.
For instance, a client may come in with a Negative Cognition such as “I am powerless,” stemming from a childhood trauma.
The goal would be to replace the biased beliefs with a Positive Cognition, such as “I am in control now.” The challenge lies not just in identifying these cognitions but in making them resonate on a visceral level.
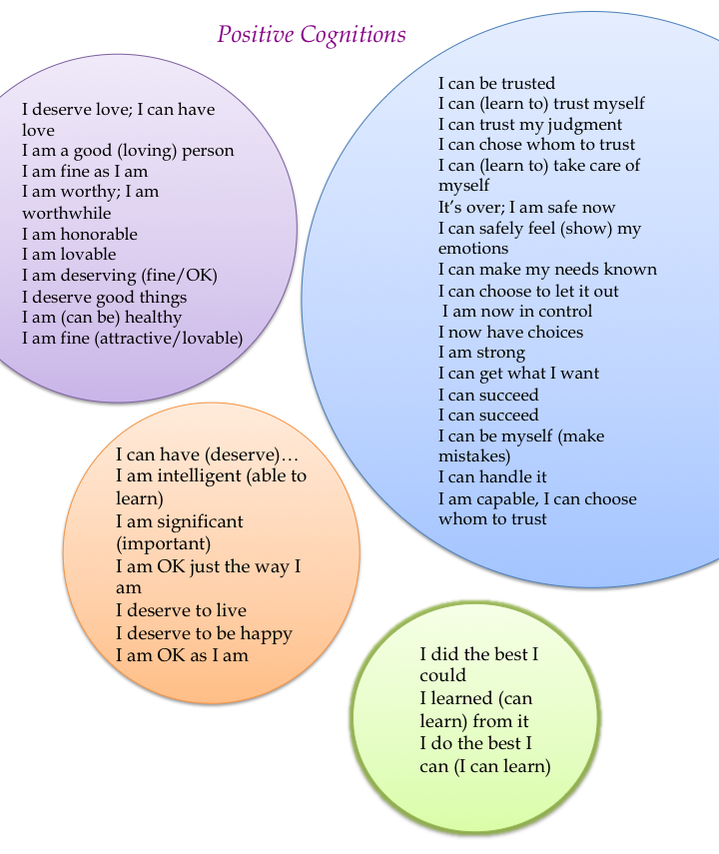
Image Source
The Art of Crafting Effective Cognitions
Effective cognitions are those that strike a chord with the client, facilitating the reprocessing of trauma. To do this, it’s important to consider the client’s language, values, and worldview. A cognition that feels generic or overly clinical may not have the same impact as one that aligns with the client’s personal experiences.
One practical approach is to engage the client in the process of identifying both Negative and Positive Cognitions. Instead of imposing a standard set of beliefs, involve the client in the exploration of their own thoughts and feelings. This collaboration not only ensures that the cognitions are meaningful but also empowers the client by giving them an active role in their healing process.
Another key aspect is specificity. A Positive Cognition that is too broad, such as “I am good enough,” may lack the personal relevance needed to be effective. On the other hand, a more specific cognition like “I did the best I could in that situation” might resonate more with a client who struggles with feelings of guilt or regret.
Tailoring Cognitions to the Client’s Developmental Stage
Clients often come into therapy at different developmental stages, and their capacity to engage with certain cognitions will vary accordingly. For example, a young adult client might still be in the process of forming their identity and could benefit from Positive Cognitions that reinforce self-worth, like “I am capable of making good decisions.” Meanwhile, an older client grappling with past regrets might need cognitions that focus on self-forgiveness or acceptance, such as “I accept my past and can learn from it.”
Understanding where a client is developmentally allows therapists to tailor cognitions that not only fit their current life stage but also encourage growth. This requires a deep awareness of human development and a keen ability to listen to the client’s needs and aspirations.
The Role of Cultural Sensitivity in Cognition Selection
Cultural sensitivity is another crucial factor when selecting cognitions in EMDR. A cognition that works well in one cultural context may not resonate in another. For instance, in some cultures, the concept of individualism is highly valued, and a cognition like “I am in control of my destiny” may be empowering. In contrast, in more collectivist cultures, where community and family are central, a cognition like “I contribute positively to my community” may be more appropriate.
To navigate this, it’s essential to have an ongoing dialogue with the client about their cultural background and how it influences their beliefs. By doing so, therapists can ensure that the Positive Cognitions not only promote healing but also respect and align with the client’s cultural identity.
Adjusting Cognitions During the EMDR Process
EMDR is not a linear process, and the same is true for the use of cognitions. As therapy progresses, the client’s understanding of their trauma and beliefs may evolve, necessitating adjustments to the cognitions being used. It’s important to remain flexible and open to revising Negative or Positive Cognitions as new insights emerge.
For example, a client might initially identify a Negative Cognition like “I am unsafe,” which, after several sessions, might shift to something more nuanced, such as “I can’t trust others.” In response, the therapist might adjust the Positive Cognition from “I am safe now” to something that addresses the trust issue more directly, like “I can choose who to trust.”
This ongoing refinement is a normal part of the EMDR process and should be embraced as a sign that the therapy is working. As the client’s understanding deepens, the cognitions must adapt to reflect their current state of mind and progress in therapy.
Overcoming Challenges in Cognition Selection
One of the most common challenges therapists face when working with EMDR cognitions is resistance from the client. Some clients may find it difficult to connect with Positive Cognitions, especially if they’ve held onto Negative Cognitions for a long time. This resistance can be addressed by validating the client’s experience and pacing the introduction of Positive Cognitions to avoid overwhelming them.
In some cases, it may be necessary to work on desensitizing the Negative Cognition before fully introducing a Positive Cognition. This can involve several sessions of processing the trauma without yet focusing on installing a Positive Cognition, allowing the client to come to terms with their experience gradually.
It’s also worth noting that not all clients will respond to Positive Cognitions in the same way. Some may require more time or a different approach to fully embrace these new beliefs. Patience and persistence are key, as is the willingness to explore alternative cognitions if the initial ones don’t seem to be effective.
The Power of Collaboration in Cognition Development
Collaboration with the client in developing cognitions cannot be overstated. When clients are active participants in identifying and refining their cognitions, they’re more likely to feel invested in the process and experience greater benefits from the therapy. This collaborative approach fosters a sense of ownership and empowerment, which are crucial for lasting change.
Encouraging clients to voice their thoughts and feelings about the proposed cognitions can lead to a deeper understanding of what will be most effective for them. It also helps to build trust and rapport, as the client sees that the therapist is genuinely interested in their unique perspective.
Upgrade EMDR Techniques To Treat Negative Cognitions Effectively
Enhance your therapeutic practice with our affordable, accredited online EMDR courses. Learn from experienced therapists and gain the skills to address negative cognitions effectively. Our programs are designed to fit your busy schedule while providing you with the knowledge and tools you need to help clients overcome limiting beliefs and achieve lasting change.
Enroll in the programs below and unlock the power of EMDR today:
Practical Applications and Case Examples
Consider the case of a client who survived a serious car accident and developed the Negative Cognition “I am always in danger.”
Initially, the therapist might suggest a Positive Cognition like “I am safe now,” but the client might struggle to connect with this due to ongoing anxiety. Through collaboration, they might settle on a more nuanced cognition like “I can take steps to protect myself,” which acknowledges the client’s fear while empowering them to regain a sense of control.
Another example could be a client who grew up in a highly critical household and developed the Negative Cognition “I am not good enough.”
A broad Positive Cognition like “I am worthy” might feel too distant or abstract for the client to accept. Instead, a more specific cognition like “I have valuable skills and strengths” could be more impactful, as it ties directly to the client’s accomplishments and areas of competence.
These examples illustrate the importance of flexibility and creativity in developing cognitions that truly resonate with clients. By being attuned to the client’s needs and working collaboratively, therapists can help them move from a place of pain and negativity to one of healing and growth.
Understand EMDR Negative Thoughts
Mastering the art of selecting and refining EMDR cognitions is essential for effective therapy. During therapy, therapists can facilitate deep and lasting change by engaging clients in the process, tailoring cognitions to their developmental stage, and remaining flexible.
Each client’s journey is unique, and the key to success lies in the therapist’s ability to adapt and collaborate, ensuring that the cognitions used in EMDR are both meaningful and transformative for the individual. Take the next step in your professional journey.

by Tim Cassidy | Aug 6, 2024 | Certificate
Marriage and family therapy (MFT) is a specialized field that helps individuals, couples, and families navigate complex emotional and relational issues. As the demands on mental health professionals continue to evolve, obtaining certification in marriage and family therapy has become increasingly important.
This comprehensive guide will explore the benefits of certification and why it’s a valuable step to achieve excellence in this rewarding profession.
The Growing Need for Qualified Therapists
In today’s fast-paced and often stressful world, the need for skilled marriage and family therapists is more significant than ever. According to the American Association for Marriage and Family Therapy (AAMFT), nearly half of all marriages in the United States end in divorce.
And many families face challenges such as mental illness, substance abuse, and intergenerational conflicts. These issues can lead to significant emotional distress, making professional intervention crucial.
Certification in marriage and family therapy ensures that therapists are well-equipped to handle these complex issues. It shows you have met rigorous educational and professional standards and are competent and dedicated to your practice.
For clients seeking help, knowing their therapist is certified can provide an added layer of trust and confidence in the care they’ll receive.
The Path To Excellence
Achieving certification in marriage and family therapy involves several steps, each designed to ensure you possess the necessary knowledge and skills to provide effective treatment. The general process typically includes the following components, depending on your state:.
Educational Requirements:
Prospective therapists must complete a master’s or doctoral degree in marriage and family therapy or a related field. Accredited programs provide comprehensive training in areas such as human development, family dynamics, therapeutic techniques, and ethical practice.
Clinical Experience:
In addition to academic coursework, aspiring therapists must gain hands-on experience through supervised clinical practice. This typically involves completing a certain number of hours working directly with clients under the supervision of a licensed and experienced therapist.
Licensure Examination:
Upon completing their education and clinical training, candidates must pass a licensure examination. The examination tests their knowledge of marriage and family therapy principles, ethical standards, and clinical skills. Passing this exam is a critical step toward becoming a licensed marriage and family therapist.
Ongoing Professional Development:
Certification is not a one-time achievement. To maintain their credentials, certified therapists must engage in ongoing professional development. This includes continuing education through courses and workshops and staying current with the latest research and advancements in the field.
Revamp Your Marriage and Family Therapy Online
Current statistics say that 40% of families in the United States will seek family therapy at some point, according to AAMT. What better time to spruce up your therapy skills to provide clients with top-notch care? Online CE Credits makes this process a breeze by offering the latest courses on family therapy 24/7.
Choose your family therapy courses below:
In addition, this insightful article can expand your knowledge of reintegration therapy.
The Benefits of Certification
Enhanced Professional Credibility
One of the most significant benefits of certification is that it enhances your professional credibility. Clients, colleagues, and employers recognize certification as a mark of excellence and a commitment to high standards of practice. This recognition can open doors to career advancement opportunities, higher earning potential, and increased job satisfaction.
Improved Client Outcomes
Certified therapists are better equipped to deliver high-quality care, improving client outcomes. The rigorous training and clinical experience required for certification let you gain an in-depth understanding of the therapeutic process and how to use evidence-based techniques.
This expertise allows you to create effective treatment plans tailored to the client’s unique needs. This fosters better therapeutic relationships and more successful outcomes.
Professional Networking Opportunities
Joining professional organizations, such as the AAMFT, is a requirement for certification. These organizations provide valuable networking opportunities, allowing therapists to connect with peers, mentors, and leaders in the field. Networking can lead to collaborations, referrals, and access to resources to improve a therapist’s practice and professional development.
Access to Specialized Training and Resources
Certified therapists have access to specialized training and resources that can further enhance their skills and knowledge. Many professional organizations offer exclusive workshops, conferences, and publications that cover the latest research and advancements in marriage and family therapy.
The resources can help practitioners stay current with best practices and emerging trends, resulting in the highest level of care for their clients.
Increased Job Opportunities
Certification can significantly increase job opportunities for marriage and family therapists. Many employers prefer certified candidates, as they demonstrate a commitment to professional excellence and a proven track record of competence.
Also, training makes you more competitive in the job market since it sets you apart from people without advanced qualifications.
Enhanced Ethical and Legal Awareness
Ethical and legal considerations are crucial in marriage and family therapy practice. Certification programs emphasize ethical practice and provide training on the therapist’s legal responsibilities. This training helps certified therapists navigate complex ethical dilemmas and adhere to professional standards, protecting both their clients and their professional integrity.
Real-Life Impact: Stories of Certified Therapists

The true value of certification in marriage and family therapy can be best understood through the stories of those who have achieved it.
Consider the case of Jane, a certified marriage and family therapist who has been practicing for over a decade. Jane credits her certification with giving her the confidence and skills needed to handle even the most challenging cases. She recalls working with a family struggling with multiple issues, including substance abuse and communication breakdowns.
Through her training and experience, Jane was able to develop a comprehensive treatment plan to address each family member’s needs. This led to significant improvements in their relationships and overall well-being.
Similarly, Tom, another certified therapist, shares how certification has opened doors to opportunities he never imagined. Tom works in a community mental health center and often collaborates with other professionals, including social workers and psychologists. His certification has earned him respect among his colleagues, leading to collaborative projects and an expanded professional network.
Tom believes that his certification enhances his credibility and continually motivates him to strive for excellence in his practice.
The Path to Excellence in Marriage and Family Therapy
Certification in marriage and family therapy is a valuable investment in professional development and a commitment to providing the best care to clients. The rigorous process prepares you to handle complex cases, leading to improved client outcomes and enhanced professional credibility.
Also, certification provides a structured pathway, enabling you to remain at the forefront of your profession. Whether you’re starting a journey in marriage and family therapy or advancing your career, it’s a step toward achieving excellence.
Sign Up for an Account To Kickstart Your Continuing Education
Therapy expertise can result in higher revenue and improved client outcomes! Our self-paced programs provide a targeted and complete learning experience to help you advance from generalist to specialist.
Keeping up with traditional certificates can be redundant, time-consuming, and costly! Our certifications provide a post-nominal credential and are designed to be completed in a single cycle for a one-time program fee (or in three or four equal installments). Earn 20 CE credits in 1 month without disrupting your busy schedule.

by Tim Cassidy | Jul 23, 2024 | Certificate
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a common neurodevelopmental disorder among children and adults.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, nearly 7 million U.S. children between the ages of 3-17 years have been diagnosed with ADHD.
Because of its prevalence, mental health professionals should stay updated with the latest research and treatment strategies.
And this is where ADHD continuing education becomes an invaluable asset. It equips you with relevant skills to offer the best care and empathy to those living with ADHD.
With this in mind, let’s dive deeper into the issues.
Understanding ADHD: A Brief Overview
ADHD is characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that interfere with functioning or development. These symptoms can manifest differently in each individual, making it a uniquely challenging disorder to treat.
Children with ADHD can’t sit still, follow instructions, or pay attention for long periods. On the other hand, adults with ADHD might struggle with time management, organizational skills, and maintaining focus on tasks.
Because the health disorder is complex, ADHD training for mental health professionals gives them a robust understanding of the condition. And it can also empower you to provide effective treatment and support strategies for your patients.
So ADHD certification and other CE programs offer you the latest research, tools, and techniques to develop a solid career and stay ahead of the curve.
Why ADHD Continuing Education Is Important
Continuing education in ADHD is crucial for several reasons:
Keeps You in the Loop With Emerging Trends
Firstly, it lets you stay current with the latest developments. ADHD research is changing, with new insights into its causes, manifestations, and treatments emerging regularly.
You can incorporate these new findings into your practice after completing ADHD continuing education courses. As a result, your clients can receive the most up-to-date care.
Gain a Better Understanding of the Ailment
Secondly, ADHD continuing education helps therapists understand the disorder. You can grasp its clinical aspects and the broader context in which it occurs.
For example, ADHD co-occurs with other mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and learning disabilities. Understanding these comorbidities helps you provide holistic care to clients.
Advances Your Career
Finally, continuing education fosters a sense of professional growth and development. It allows you to refine your skills, explore new treatment modalities, and stay engaged with your profession. This, in turn, can enhance job satisfaction and prevent burnout, a common issue in mental health.
What Are the Key Areas in ADHD Continuing Education?
ADHD training for professionals typically covers a range of subjects, each of which helps you understand the disorder and its treatment. Some specializations include:
Diagnosis and Assessment:
An accurate diagnosis of ADHD is the first step toward effective treatment. Continuing education courses often explore the latest diagnostic criteria, assessment tools, and evaluation techniques. This helps therapists identify ADHD in their clients and differentiate it from other conditions with similar symptoms.
Treatment Strategies:
There are various treatment approaches for ADHD, including behavioral therapy, medication, and lifestyle interventions. Continuing education provides therapists with a comprehensive overview of these treatments, including their benefits, limitations, and best practices for implementation.
Comorbid Conditions:
As mentioned earlier, ADHD often co-occurs with other mental health conditions. Continuing education helps therapists recognize and address these comorbidities to offer their clients holistic care.
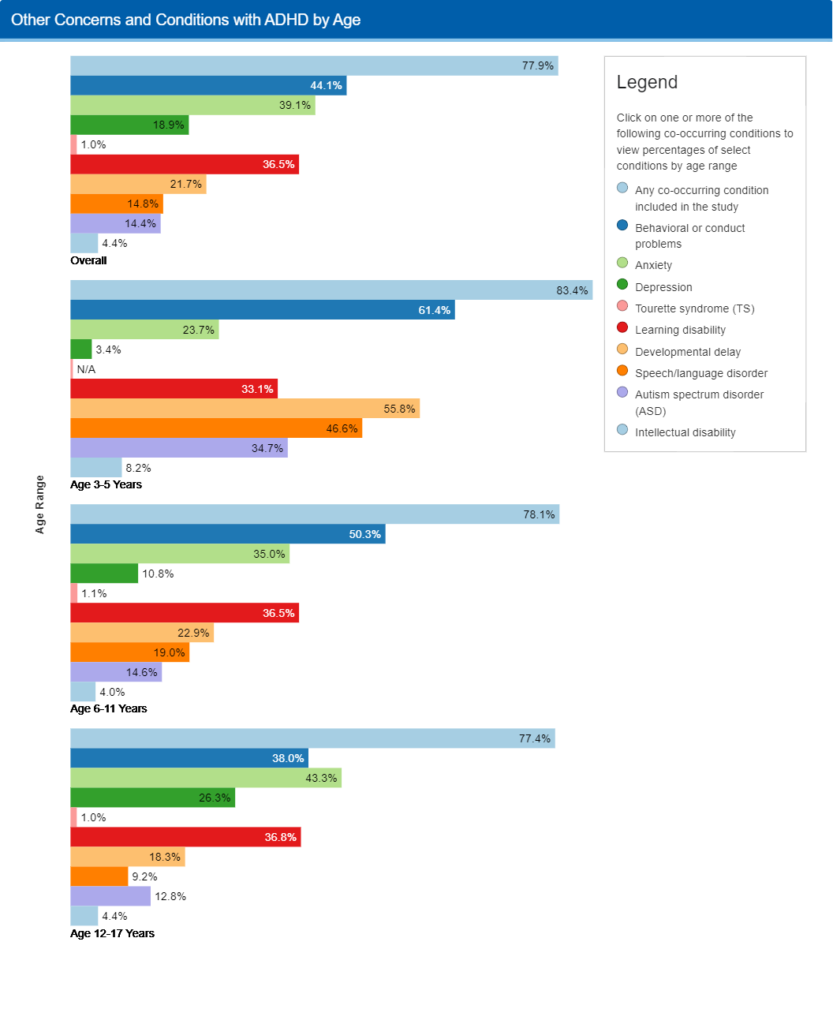
Image Source
Client and Family Education:
Educating clients and their families about ADHD is a crucial aspect of treatment. Continuing education equips therapists with the knowledge and resources to provide accurate, helpful information to their clients, fostering a supportive and informed environment.
Cultural Competency:
ADHD affects individuals from all cultural backgrounds, and understanding these cultural nuances is essential for effective treatment. Continuing education courses often explore the cultural aspects of ADHD, helping therapists provide culturally sensitive care.
What Are the Benefits of Online CE Courses in ADHD?
One of the advantages of ADHD continuing education is that the courses are available online.
Convenient and Flexible
Unlike traditional in-person training that requires a physical venue, online CEUs are flexible since you can attend them virtually anywhere.
As a busy mental health professional, you can develop yourself without sacrificing your practice or personal commitments. You can learn at your own pace, revisiting complex topics as needed and moving quickly through familiar material.
Internet programs also grant you access to a wealth of resources, including video lectures, interactive modules, and discussion forums. This improves the learning experience and caters to individual needs and learning styles.
In addition, online continuing education courses feature expert instructors and leaders in ADHD. They bring a wealth of knowledge and practical experience, offering insights and guidance to enhance a therapist’s practice.
Build a Supportive Community
Another benefit of online ADHD continuing education credits is connecting with a community of peers.
Discussion forums and online study groups allow therapists to share their experiences, ask questions, and support each other in their learning journey. They provide a network of support and encouragement.
Additionally, some online courses offer live interactions with instructors and fellow students through webinars and virtual office hours. These engagements deepen your understanding, clarify complex topics, and enhance your learning experience.
How To Select the Right Continuing Education Provider?
Be sure to consider the following factors when you choose a provider for ADHD continuing education:
Firstly, look for accredited and recognized providers within the mental health field. It enables you to take courses that meet high standards of quality and relevance.
Secondly, consider the expertise of the instructors. Opt for courses from professionals with extensive experience and knowledge of ADHD. Their insights and guidance can improve your learning experience.
Thirdly, evaluate the course offerings’ flexibility and convenience. Online courses should have different learning formats, including video lectures, interactive modules, and discussion forums.
Additionally, consider the support and resources available. Can the learning platform give you access to research articles and case studies? Does it have live interaction with instructors and peers?
Upgrade Your Skills in ADHD Continuing Education Courses
Want to jumpstart your knowledge of adult ADHD training for therapists hassle-free? You’re in luck. Online CE Credits offers flexible and convenient programs 24/7 without due dates or deadlines. You can benefit from reputable instructors with decades of experience in theory and practice.
Also, live webinars and direct engagements with the therapists make your learning enjoyable, memorable, and practical.
So, what are you waiting for? Choose your training program below!

Empower Yourself through ADHD Continuing Education
ADHD continuing education is a powerful tool that allows therapists to provide the best possible care to their clients. You can offer effective, compassionate, and holistic support to individuals living with ADHD when you keep tabs on the latest research and treatment strategies.
Convenient and flexible online courses make it a breeze for busy professionals to pursue continuing education. You can enhance your skills, deepen your understanding, and grow personally and professionally.
Ultimately, ADHD continuing education is about professional development.
Create an Account To Get Started with Online CE Credits
Looking for affordable online courses on ADHD? Online CE Credits offers flexible payment plans to set you up for success. As a result, it’s possible to earn your certifications without breaking the bank. And you can refer to the courses anytime, even after completing them. Stop feeling overwhelmed by the demands of being a clinician. Get practical strategies and support to thrive in your practice.













