loading...

by Sadaqut | Jul 30, 2024 | Educational
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the demand for family therapy specialists is expected to grow by 15% from 2022 to 2032, which is faster than the average for all occupations.
As a family therapist, your commitment to continuous learning can greatly improve your practice’s effectiveness and quality. It equips you with the latest tools, techniques, and insights to address families’ diverse and complex issues.
Let’s dive into how ongoing education can transform your family therapy practice and let you provide the best possible care for your clients.
Staying Updated with the Latest Developments
Family dynamics are changing due to cultural shifts, technological advancements, and evolving social norms. For this reason, it’s crucial to stay abreast of these changes to provide relevant and effective interventions. Ongoing education allows you to keep up with the latest research, theories, and therapeutic approaches.
For example, recent studies have demonstrated the impact of social media on family relationships. You can better understand these influences and incorporate appropriate strategies into your practice by engaging in continuous learning.
This knowledge enhances your credibility and ensures that you provide the most current and effective care for your clients.

Upgrading Clinical Skills
Another benefit of ongoing education is that it sharpens your clinical skills. Family therapy requires a multifaceted approach, integrating various therapeutic models and techniques. Continuous education offers opportunities to learn and refine these skills.
Workshops, seminars, and online courses provide hands-on experience with new techniques, such as Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT), Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), or Structural Family Therapy. You can offer more tailored and effective interventions and address each family’s unique needs when you master these techniques.
For example, learning advanced approaches in EFT can help you navigate complex emotional landscapes within family dynamics. This can build deeper connections and resolutions. Similarly, gaining expertise in CBT can equip you with the tools to help families reframe negative thought patterns and develop healthier communication styles.
Building Confidence and Competence
The field of family therapy can be challenging, with each family presenting a unique set of issues and dynamics. Continuous education develops competence and confidence in your abilities as a therapist. You can approach each case with assurance when you have expert knowledge.
This confidence translates into better therapeutic outcomes. Clients can notice your expertise and confidence, which helps build trust and rapport. A well-informed and confident therapist can navigate difficult conversations, manage crises, and guide families toward healing and growth more effectively.
Expanding Your Professional Network
Engaging in ongoing education also provides valuable opportunities to expand your professional network. Conferences, workshops, and online courses bring together therapists from various backgrounds and specialties. These interactions can lead to fruitful collaborations, mentorship opportunities, and a broader support system.
Connecting with other professionals gives you access to diverse perspectives and innovative approaches you might not encounter in your daily practice. This exchange of ideas can inspire new ways of thinking and working, further enriching your therapeutic repertoire.
Meeting Licensing and Certification Requirements
In many states and countries, maintaining your license as a family therapist requires a certain number of continuing education hours. So ongoing education enables you to meet these requirements and remain in good standing with licensing boards.
This commitment to professional development shows your dedication to maintaining high standards of care and staying informed about the latest developments.
Also, additional family therapy certifications can improve your credentials and attract more clients. For example, becoming certified in Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT) or as a Gottman Method Couples Therapist can distinguish you in a competitive field. And it can signal to potential clients that you have advanced expertise in these areas.
Improving Client Outcomes
Ultimately, the goal of ongoing education is to improve client outcomes. Families seek therapy to address and resolve issues, and they rely on you to guide them through their challenges. You’re better equipped to provide effective interventions that lead to positive, lasting changes when you continually update your knowledge and skills
For example, understanding the latest findings in attachment theory can help you address issues related to bonding and relationship security. You can provide more targeted and effective support for families dealing with trauma-related issues if you’re well-versed in trauma’s impact on family dynamics.
Personal and Professional Growth
Continuous education is about improving your practice and personal and professional growth. The learning process keeps you engaged, curious, and passionate about your work. It prevents burnout by providing fresh perspectives and new challenges, keeping your practice dynamic and fulfilling.
Ongoing learning can also lead to career advancement opportunities. Whether you aspire to take on leadership roles, teach, or publish in your field, it provides the foundation for these pursuits. It positions you as a thought leader and an expert, opening doors to new opportunities and professional recognition.

Skyrocket Your Continuing Education With an Online Platform
As a family therapist, you have endless opportunities to outshine your peers and move the needle in your career through Internet programs. Online CE Credits offers high-quality online CEUs to counselors, therapists, social workers, and psychologists.
On-demand CE courses and completion certificates are available 24/7 from the comfort of your own home!
Give these courses on family therapy a shot:
In addition, dive more into counseling supervision training to learn how you can upgrade your supervision skills.
Leveraging Online Continuing Education (CE) Courses
In today’s digital age, accessing ongoing education has never been easier. Online continuing education (CE) courses are convenient and flexible to keep you updated with the latest family developments. These courses can fit into your busy schedule, allowing you to learn at your own pace and from the comfort of your home or office.
Online CE courses cover a wide range of topics, from specific therapeutic techniques to broader issues like ethics and cultural competency. They include interactive components, such as case studies, quizzes, and discussion forums, to enhance the learning experience
You can keep your knowledge and skills current without disrupting your practice by leveraging these online resources
A Commitment to Excellence
As a family therapist, your dedication to continuous learning reflects a commitment to excellence and a deep care for the families you serve. As a result, your practice remains dynamic, relevant, and impactful, making a lasting difference in your patients’ lives.
Have You Registered With Online CE Credits?
Unlimited CEs for the cost of a copay! All resources for all asynchronous courses are immediately available on your dashboard. Registration for all live CE events and webinars is free. There are no course due dates. Asynchronous courses allow for an unlimited number of post-test attempts. Signed PDF certificates are supplied promptly to your dashboard and via email. Earn 15 essential CE credits in just 2 weeks.

by Sadaqut | Jul 23, 2024 | Educational
The World Health Organization (WHO) reports that nearly 70% of people worldwide will experience severe trauma during their lifetime. This makes trauma a pervasive issue affecting anyone, regardless of age, gender, or socioeconomic status.
As a result, social workers often find themselves dealing with individuals and families with various forms of trauma. That’s why specialized trauma training is necessary to equip social assistants with the skills and knowledge to support their clients.
What Is Trauma Training?
A trauma training program focuses on what trauma is and how it impacts people. It explores levels, types, and examples of trauma and how to use a trauma-informed approach in different settings.
What Is Trauma-Informed Care in Social Work?
According to Florida State University, a trauma-informed clinical practice provides a supportive environment for individuals with a history of trauma. It’s not a therapeutic intervention. So it lets social workers recognize the effect of trauma on a person’s life.
And the UK government defines it this way:
Trauma-informed practice is an approach to health and care interventions that is grounded in the understanding that trauma exposure can impact an individual’s neurological, biological, psychological, and social development.
What’s the Role of Social Workers in Trauma-Informed Care?
Counselors play a crucial role in the healing process for trauma survivors. Their work involves addressing the client’s immediate needs and understanding the underlying trauma that impacts their lives.
Trauma-informed care is an approach that emphasizes safety, trustworthiness, choice, collaboration, and empowerment. Welfare workers can create a supportive environment that fosters healing and resilience by adopting a trauma-informed approach
What Are the Key Elements of Trauma Training?
Specialized trauma training includes several key components, each vital for effective practice. They include:
Trauma Theory and Types of Trauma:
Understanding the different types of trauma, including acute, chronic, and complex trauma, and how they affect individuals differently
Neurobiological Impact of Trauma:
Knowledge of how trauma affects the brain and body, influencing behavior, emotions, and physical health
Assessment and Diagnosis:
Skills for accurately assessing and diagnosing trauma-related conditions such as PTSD, depression, and anxiety
Evidence-Based Interventions:
Training in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR), and Somatic Experiencing
Cultural Competence:
Understanding how cultural factors influence the experience and expression of trauma and ensuring culturally sensitive care
Self-Care and Vicarious Trauma:
Strategies for social workers to maintain their well-being and prevent burnout
Trauma Theory and Types of Trauma
An in-depth understanding of trauma theory is the foundation of effective trauma training. Trauma can be acute, chronic, or complex. Acute trauma results from a single distressing event, such as a car accident or a natural disaster.
Chronic trauma involves repeated and prolonged exposure to stressful events, such as ongoing abuse or domestic violence. Complex trauma refers to exposure to multiple traumatic events, often of an invasive, interpersonal nature.
The Neurobiological Impact of Trauma
Trauma has a far-reaching effect on the brain and body. Knowledge of neurobiology helps social workers understand how trauma impacts their clients’ behavior and health.
Trauma can disrupt normal brain development, leading to changes in brain structure and function. This disruption can result in difficulties with emotional regulation, memory, and executive functioning.
Training that includes the neurobiological aspects of trauma provides guidance counselors with insights into the physical and psychological symptoms their clients may experience.
Assessment and Diagnosis of Trauma
Accurate assessment and diagnosis are an integral part of trauma-informed care. Social assistants must identify trauma-related symptoms and differentiate them from other mental health conditions.
Extensive trauma training includes education on standardized assessment tools and diagnostic criteria for conditions like PTSD, depression, and anxiety. This knowledge allows social workers to develop appropriate treatment plans tailored to their client’s needs.
Evidence-Based Interventions for Trauma
Implementing evidence-based interventions is essential to treating trauma effectively. Training programs should cover various therapeutic approaches, including:
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT):
Focuses on changing negative thought patterns and behaviors associated with trauma
Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR):
Uses bilateral stimulation to help clients process and integrate traumatic memories
Somatic Experiencing:
Emphasizes the connection between mind and body, helping clients release trauma stored in the body
Trauma-Focused Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (TF-CBT):
Specifically designed for children and adolescents, addressing both cognitive and emotional aspects of trauma
Cultural Competence in Trauma Care
Cultural competence is a vital aspect of a trauma-informed clinical practice. Social workers must understand how cultural factors influence the experience and expression of trauma.
This understanding develops a respectful and sensitive response to clients’ diverse backgrounds. Training should include cultural humility, awareness of one’s biases, and strategies to engage with patients from various cultural backgrounds.
Self-Care and Managing Vicarious Trauma
Working with trauma survivors can be emotionally taxing for welfare workers. Vicarious trauma, also known as secondary traumatic stress, can occur when social workers are repeatedly exposed to their clients’ traumatic experiences.
Specialized trauma training zeroes in on self-care and provides techniques to cope with vicarious trauma. Methods such as mindfulness, regular supervision, peer support, and professional development can maintain the social worker’s well-being.
Enhance Your Skills In Trauma-Informed Practice
Want to kickstart your knowledge of trauma? Online CE Credits offers a range of training programs in continuing education at a fraction of the cost. You can complete the certifications anytime, anywhere. No due dates. No deadlines.
And you can gain valuable insights from leading experts in trauma-informed certificate programs. Here are some courses to upskill yourself and boost your confidence:
What Are the Benefits of Trauma Training for Social Workers?
Investing in advanced trauma training offers many benefits for social assistants and their clients. They include:
Enhanced Professional Competence:
You’re better prepared to handle complex cases and provide high-quality care.
Improved Client Outcomes:
Clients receive more effective and targeted interventions, leading to better mental health and overall well-being.
Increased Job Satisfaction:
Because you feel competent and confident in your role, you can experience job satisfaction and remain longer in your work.
Reduction in Burnout:
Proper training and self-care strategies help prevent burnout and promote longevity in the profession.
How To Implement Trauma Training in Your Practice
Integrating comprehensive trauma training into your practice involves several steps. Start by identifying reputable training programs that offer an extensive curriculum. It must cover the essentials of trauma-informed care.
Secondly, look for programs that provide certification or continuing education credits and meet professional standards.
How To Choose the Right Training Program
When selecting a trauma training program, consider the following factors:
Accreditation and Credibility:
Ensure the program is accredited by a recognized professional organization
Experienced Instructors:
Choose programs taught by experts with extensive experience in trauma-informed practice
Practical Application:
Select courses with practical exercises, case studies, and role-playing to improve learning
Flexibility:
Consider online or hybrid programs with flexibility for busy professionals
Embrace Continuing Education and Professional Development
Trauma training should be an ongoing process. Continuing education and professional development help you stay current with the latest research and best practices in trauma care.
Be sure to attend workshops, conferences, and webinars to expand your knowledge and skills. Also, join professional organizations, such as the National Association of Social Workers (NASW), to get more resources, networking opportunities, and additional training.
Trauma training is a vital investment for social workers dedicated to providing the best possible care for their clients. Trauma theory, understanding trauma’s neurobiological impact, and using evidence-based interventions can advance your practice and support your clients’ healing journeys.
Have You Selected a Trauma-Informed Practice Training Approach?
Online CE Credits offers nationally approved trauma training programs to enable you to fulfill licensure requirements. You can choose from more than 250 certifications from experienced therapists. You don’t need to attend a physical venue to complete the courses since you can do them wherever and whenever.
And it’s as easy as ABC to get started with your CEU credits. Online CE Credits provides flexible payment plans. Stop putting your dream career on hold. Get the credentials you need to excel in your niche.
FAQ
What is trauma training?
Trauma-informed practice is a framework for understanding, responding to, and preventing the effects of all types of trauma.
How do you deal with trauma as a social worker?
Trauma-informed care focuses on recognizing signs of trauma in the client and responding with empathy and understanding. It also involves providing the client with resources and support to help them heal from their trauma.
What are the 5 principles of trauma-informed practice?
The five principles of trauma-informed practice are safety, trustworthiness, choice, collaboration, and empowerment. The four C’s of trauma-informed care are calm, contain, care, and cope.

by Sadaqut | Jul 23, 2024 | Educational
Training in counseling supervision can be a game-changer for your career, whether you’re an experienced practitioner looking to enhance your supervisory skills or a budding therapist becoming a supervisor.
Counseling supervision upgrades your clinical skills, helps colleagues understand their strengths and weaknesses, and helps identify performance issues before they become problems.
In this post, we look at the role of supervision in counseling, why you need specialized training, and the subjects under this program.
What Is Counseling Supervision?
Counseling supervision is when a therapist uses the services of another psychotherapy professional trained in supervision to review their work with clients and their professional and personal development. The supervisor offers professional service as a consultant, not as a boss.
According to the American Counseling Association, a counselor supervisor should have the qualities below:
- Grounded in theoretical and pedagogical foundations for their work
- Understand supervision models
- Should conduct a fair, accurate, and honest assessment of the professional clinical work of counselors and counselors-in-training
What Are the Objectives of Supervision in Counseling?
Supervision in counseling serves multiple vital functions. It ensures clients receive the highest standard of care while simultaneously supporting the therapist’s professional development.
Supervision allows therapists to reflect on their practice, receive feedback, and explore complex cases collaboratively and safely. This process helps identify blind spots, improve therapeutic techniques, and maintain ethical standards.
Also, counseling supervision promotes self-care among mental health professionals. This is because therapy involves a lot of emotions that can lead to burnout if not managed properly. As a result, regular supervision lets practitioners express their professional concerns, process challenging emotions, and develop resilience.
Ultimately, it creates a supportive environment where clinicians can explore their feelings, creating a sustainable and healthy practice.
Why Specialized Training Matters
Formal training in counseling supervision equips practitioners with advanced techniques and expert knowledge. It focuses on the nuances of the supervisory relationship, ethical considerations, multicultural competence, and effective communication strategies.
Structured training programs can refine your skills, build confidence, and ultimately help you provide high-quality supervision.
Because formal training emphasizes evidence-based practices, it uses new research and theories to provide up-to-date information. As a result, it keeps supervisors aware of the latest developments, providing them with current knowledge. And this enhances the overall quality of care provided to clients.
What Are the Key Elements of Counseling Supervision Training?

Training programs under counseling supervision zero in on several essential topics. They include theoretical knowledge, ethical and legal considerations, multicultural competence, communication, and feedback.
Now let’s look at each of these in detail.
Theoretical Foundations
An effective supervisor must possess robust theoretical knowledge.
Counseling supervision training introduces various models and theories to guide the supervisory process. These frameworks provide a structured approach to supervision. They help supervisors navigate complex situations and tailor their approach to the supervisee’s needs.
Some common theories include developmental models, which focus on the supervisor’s growth and progression. And integrative models combine elements from different theoretical approaches to create a flexible and adaptive supervisory style.
Understanding these theories allows you to create a supportive and effective learning environment, promoting the supervisee’s professional growth.
Ethical and Legal Considerations
Ethical practice is the bedrock of effective supervision. Training programs emphasize ethical standards, confidentiality, dual relationships, and informed consent. Supervisors learn to manage ethical dilemmas to empower them to maintain the highest professional standards.
Additionally, understanding the legal aspects of supervision is crucial. Training covers relevant laws and regulations, equipping supervisors with the knowledge to handle legal issues that may arise in their practice.
Supervisors who understand ethical and legal considerations can provide safe and ethical supervision for both supervisees and clients.
Multicultural Competence
Cultural competence is essential for effective supervision in our diverse society. Counseling supervision training focuses on multicultural competence. It explores how cultural factors influence the supervisory relationship. Supervisors learn to recognize and address cultural differences, promoting an inclusive and respectful environment.
As a result, it helps supervisors understand the supervisee’s unique experiences and challenges. By developing cultural competence, you can provide more effective support. And this improves the quality of the supervisory relationship.
Communication and Feedback
Clear and constructive communication is a cornerstone of effective supervision. Training programs focus on developing advanced communication skills. They teach supervisors how to provide supportive and constructive feedback.
Effective communication produces a collaborative relationship and encourages a supervisee to engage openly and honestly in the supervisory process.
Training also covers techniques to deliver difficult feedback, helping you address performance issues to promote growth and development. You can create a positive and productive supervisory relationship by mastering effective communication skills.
What Are The Benefits of Online Counseling Supervision Training?

Online counseling supervision training offers a flexible and accessible option for busy professionals. Internet programs provide the same high-quality training as in-person courses, as you can study from anywhere. This flexibility allows you to fit training into your existing commitments.
Online training programs may incorporate interactive elements, such as live webinars, discussion forums, and virtual role-plays. This creates an engaging and dynamic learning experience. They also build a sense of community and support, letting you connect with peers and instructors worldwide.
Additionally, online training provides access to a wealth of resources. They include recorded lectures, reading materials, and practical exercises. This approach gives you the necessary tools to develop your supervisory skills, advancing your professional competence and confidence.
How To Choose the Right Training Program
When selecting a counseling supervision training program, consider several factors below:
Here are some key considerations:
Accreditation and Credentials
Choose an accredited program from a recognized professional body. Accreditation shows the training meets established quality standards and that the program is reputable.
In addition, look for courses offering credentials or certification upon completion, as these can boost your professional standing and credibility.
Curriculum and Content
Review the curriculum to ensure it covers all the key components of effective supervision. Consider programs that dive into theoretical foundations, ethical and legal considerations, multicultural competence, and communication skills.
The curriculum should provide practical, hands-on learning experiences, enabling you to apply the skills and knowledge in real-world settings.
Instructor Expertise
The instructor’s expertise influences the quality of the training program. As a result, pick a program from experienced and knowledgeable professionals with a strong background in supervision. Instructors should provide practical insights and guidance from their own experiences to enhance learning.
Learning Format and Flexibility
Consider your own learning preferences and schedule when selecting a program. Online training offers flexibility and convenience, helping you study at your own pace and on your own schedule.
However, some individuals may prefer the structure and interaction of in-person training. Choose a format that aligns with your learning style and professional commitments.
Upskill Yourself in Emerging Trends in Counseling Courses
Statista reports that about 56 million adult Americans received therapy or counseling for their mental health in 2022. And anxiety and depression are the most common reasons to seek mental health treatment.
As a result, Online CE Credits provides the latest courses for continuing education in mental health treatment. The accredited and nationally approved online programs enable you to study at your own pace and interact with reputable practitioners. Also, they explore various treatments in psychotherapy to manage anxiety, depression, complex trauma, and more.
Here are examples of counseling courses:
Discover more insightful information on reintegration therapy for broken families.
Upgrade Your Profession in Counseling Provision
Counseling supervision training is a wise investment in your professional development. It provides the knowledge, skills, and confidence needed for effective supervision and quality care for clients.
Whether you’re an experienced supervisor or a beginner, specialized training offers the tools and insights to elevate your practice to new heights. Training in supervision lets you stay at the forefront of best practices. And it helps you provide the highest standard of support to your supervisors.
Partner with Online CE Credits for Continuing Education
Enrolling in continuing professional development is as easy as ABC with Online CE Credits. You have the option of paying once annually or taking on a cost-effective membership plan. And the certification is available to show your credits and progress to your employer or in your private practice.
Also, the learning platform has a refund and exchange policy, which you may not need because of the high-quality courses we offer. Stop feeling stuck at your current skill level. Get advanced training and certifications to level up your career.

by Sadaqut | Jul 23, 2024 | Certificate
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a common neurodevelopmental disorder among children and adults.
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, nearly 7 million U.S. children between the ages of 3-17 years have been diagnosed with ADHD.
Because of its prevalence, mental health professionals should stay updated with the latest research and treatment strategies.
And this is where ADHD continuing education becomes an invaluable asset. It equips you with relevant skills to offer the best care and empathy to those living with ADHD.
With this in mind, let’s dive deeper into the issues.
Understanding ADHD: A Brief Overview
ADHD is characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that interfere with functioning or development. These symptoms can manifest differently in each individual, making it a uniquely challenging disorder to treat.
Children with ADHD can’t sit still, follow instructions, or pay attention for long periods. On the other hand, adults with ADHD might struggle with time management, organizational skills, and maintaining focus on tasks.
Because the health disorder is complex, ADHD training for mental health professionals gives them a robust understanding of the condition. And it can also empower you to provide effective treatment and support strategies for your patients.
So ADHD certification and other CE programs offer you the latest research, tools, and techniques to develop a solid career and stay ahead of the curve.
Why ADHD Continuing Education Is Important
Continuing education in ADHD is crucial for several reasons:
Keeps You in the Loop With Emerging Trends
Firstly, it lets you stay current with the latest developments. ADHD research is changing, with new insights into its causes, manifestations, and treatments emerging regularly.
You can incorporate these new findings into your practice after completing ADHD continuing education courses. As a result, your clients can receive the most up-to-date care.
Gain a Better Understanding of the Ailment
Secondly, ADHD continuing education helps therapists understand the disorder. You can grasp its clinical aspects and the broader context in which it occurs.
For example, ADHD co-occurs with other mental health conditions such as anxiety, depression, and learning disabilities. Understanding these comorbidities helps you provide holistic care to clients.
Advances Your Career
Finally, continuing education fosters a sense of professional growth and development. It allows you to refine your skills, explore new treatment modalities, and stay engaged with your profession. This, in turn, can enhance job satisfaction and prevent burnout, a common issue in mental health.
What Are the Key Areas in ADHD Continuing Education?
ADHD training for professionals typically covers a range of subjects, each of which helps you understand the disorder and its treatment. Some specializations include:
Diagnosis and Assessment:
An accurate diagnosis of ADHD is the first step toward effective treatment. Continuing education courses often explore the latest diagnostic criteria, assessment tools, and evaluation techniques. This helps therapists identify ADHD in their clients and differentiate it from other conditions with similar symptoms.
Treatment Strategies:
There are various treatment approaches for ADHD, including behavioral therapy, medication, and lifestyle interventions. Continuing education provides therapists with a comprehensive overview of these treatments, including their benefits, limitations, and best practices for implementation.
Comorbid Conditions:
As mentioned earlier, ADHD often co-occurs with other mental health conditions. Continuing education helps therapists recognize and address these comorbidities to offer their clients holistic care.
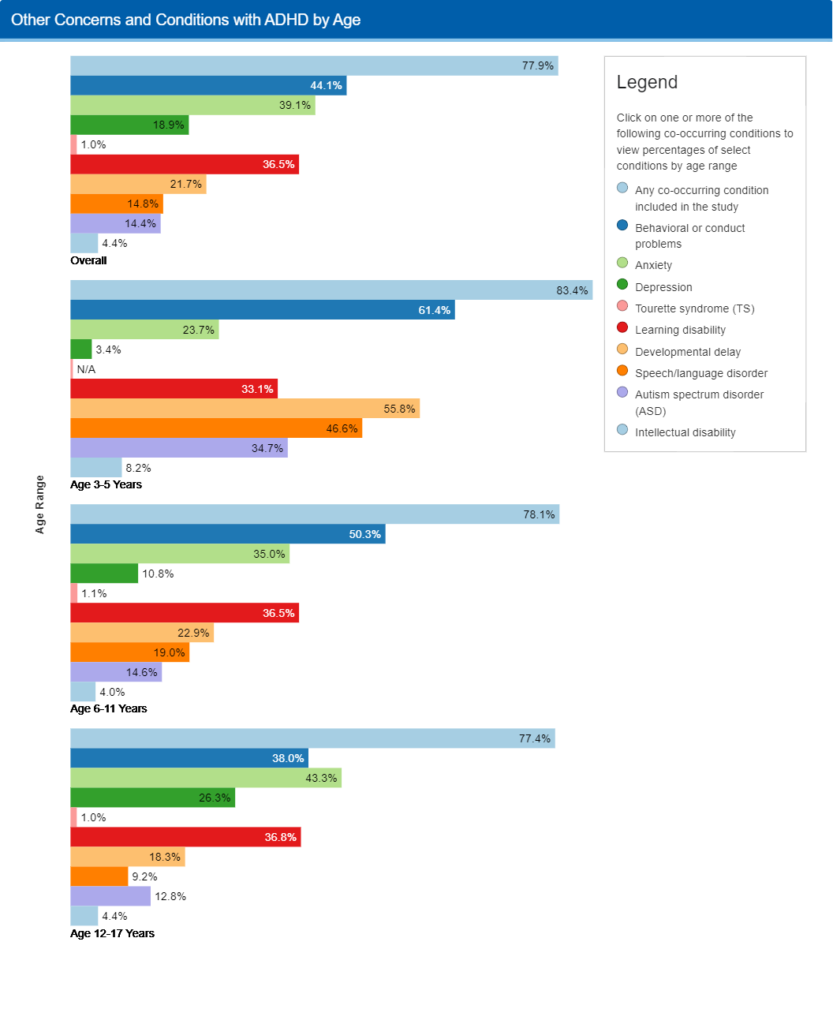
Image Source
Client and Family Education:
Educating clients and their families about ADHD is a crucial aspect of treatment. Continuing education equips therapists with the knowledge and resources to provide accurate, helpful information to their clients, fostering a supportive and informed environment.
Cultural Competency:
ADHD affects individuals from all cultural backgrounds, and understanding these cultural nuances is essential for effective treatment. Continuing education courses often explore the cultural aspects of ADHD, helping therapists provide culturally sensitive care.
What Are the Benefits of Online CE Courses in ADHD?
One of the advantages of ADHD continuing education is that the courses are available online.
Convenient and Flexible
Unlike traditional in-person training that requires a physical venue, online CEUs are flexible since you can attend them virtually anywhere.
As a busy mental health professional, you can develop yourself without sacrificing your practice or personal commitments. You can learn at your own pace, revisiting complex topics as needed and moving quickly through familiar material.
Internet programs also grant you access to a wealth of resources, including video lectures, interactive modules, and discussion forums. This improves the learning experience and caters to individual needs and learning styles.
In addition, online continuing education courses feature expert instructors and leaders in ADHD. They bring a wealth of knowledge and practical experience, offering insights and guidance to enhance a therapist’s practice.
Build a Supportive Community
Another benefit of online ADHD continuing education credits is connecting with a community of peers.
Discussion forums and online study groups allow therapists to share their experiences, ask questions, and support each other in their learning journey. They provide a network of support and encouragement.
Additionally, some online courses offer live interactions with instructors and fellow students through webinars and virtual office hours. These engagements deepen your understanding, clarify complex topics, and enhance your learning experience.
How To Select the Right Continuing Education Provider?
Be sure to consider the following factors when you choose a provider for ADHD continuing education:
Firstly, look for accredited and recognized providers within the mental health field. It enables you to take courses that meet high standards of quality and relevance.
Secondly, consider the expertise of the instructors. Opt for courses from professionals with extensive experience and knowledge of ADHD. Their insights and guidance can improve your learning experience.
Thirdly, evaluate the course offerings’ flexibility and convenience. Online courses should have different learning formats, including video lectures, interactive modules, and discussion forums.
Additionally, consider the support and resources available. Can the learning platform give you access to research articles and case studies? Does it have live interaction with instructors and peers?
Upgrade Your Skills in ADHD Continuing Education Courses
Want to jumpstart your knowledge of adult ADHD training for therapists hassle-free? You’re in luck. Online CE Credits offers flexible and convenient programs 24/7 without due dates or deadlines. You can benefit from reputable instructors with decades of experience in theory and practice.
Also, live webinars and direct engagements with the therapists make your learning enjoyable, memorable, and practical.
So, what are you waiting for? Choose your training program below!

Empower Yourself through ADHD Continuing Education
ADHD continuing education is a powerful tool that allows therapists to provide the best possible care to their clients. You can offer effective, compassionate, and holistic support to individuals living with ADHD when you keep tabs on the latest research and treatment strategies.
Convenient and flexible online courses make it a breeze for busy professionals to pursue continuing education. You can enhance your skills, deepen your understanding, and grow personally and professionally.
Ultimately, ADHD continuing education is about professional development.
Create an Account To Get Started with Online CE Credits
Looking for affordable online courses on ADHD? Online CE Credits offers flexible payment plans to set you up for success. As a result, it’s possible to earn your certifications without breaking the bank. And you can refer to the courses anytime, even after completing them. Stop feeling overwhelmed by the demands of being a clinician. Get practical strategies and support to thrive in your practice.

by Sadaqut | Jul 23, 2024 | Educational
According to Jenner Law firm, the most common violations in therapy include sexual relations, breach of confidentiality, and engaging in dual relationships.
For this reason, continuing education in ethics for therapists enables them to protect their clients and profession. Also, ethics CEUs (Continuing Education Units) allow you to grow professionally and strengthen your practice’s integrity.
In this blog post, we’ll dive into the significance of CEUs in ethics, their impact on your career, and how they contribute to mental health practices.
What Are the Ethical Considerations for Therapists?
Ethical principles are a framework that helps therapists make decisions based on fairness, respect, and responsibility. They guide you on how to serve your clients best and protect yourself from potential legal or professional repercussions.
And they include confidentiality, dual relationships, informed consent, and professional boundaries.
For example, the American Psychological Association’s Ethical Principles of Psychologists and Code of Conduct provide guidelines for psychologists to consider when making decisions about their clients.

Image Source
Ethics for counselors enable you to navigate complex situations where the lines between right and wrong might blur. So adhering to ethical principles protects your clients, upholds the profession’s integrity, and maintains public trust.
Why Does Ethics Matter in Mental Health Practice?
Ethics form the backbone of any professional practice, and this is especially true in mental health. As a therapist, counselor, social worker, or psychologist, you have a delicate and significant responsibility to guide individuals through their most vulnerable moments.
Your decisions and actions can profoundly impact their lives. This is why understanding and adhering to ethical standards are non-negotiable.
What’s the Role of Ethics CEUs?
Ethics CEUs keep you updated on the latest ethical standards and practices in mental health. They’re not just a box to check off on your license renewal form, but a crucial aspect of your professional development. Ethics courses provide you with the tools and knowledge to handle ethical dilemmas with confidence and competence.
Continuing education in ethics helps you stay current with changes in laws and regulations affecting your practice. You learn about new ethical challenges that might arise due to technological advancements, changes in societal norms, or clinical practice developments.
For instance, the rise of telehealth and other therapeutic technologies has introduced new ethical considerations regarding confidentiality and client privacy. Ethics CEUs can help you manage these new terrains effectively.
Enhancing Professional Competence
One of the key benefits of ethics CEUs is that they enhance your professional competence. These courses involve case studies, real-life scenarios, and interactive discussions that challenge you to think critically about ethical issues.
Also, they encourage you to reflect on your own practices and identify areas where you need to improve. As a result, you understand ethical principles in-depth and learn how to apply them in your daily practice.
Ultimately, CEUs in ethics let you make better decisions and boost your confidence in handling complex ethical situations. It reassures your clients about your commitment to maintaining the highest standards of professional conduct.
Building Trust with Clients
Trust is the foundation of any therapeutic relationship. Clients must feel confident that you’re trustworthy, competent, and committed to their well-being. You demonstrate your dedication to ethical practice and professional growth when you engage in ethics CEUs.
The programs can boost your reputation and help you build stronger relationships with your clients.
In addition, patients can trust you with their personal and sensitive information when they know you’re continuously educating yourself on ethical issues.
They can get assurance that you’ll handle their cases with the utmost care and integrity. And this trust is vital for effective therapy and positive outcomes.
Navigating Ethical Dilemmas
Ethical dilemmas are an inevitable part of mental health practice. Whether it’s maintaining confidentiality when a client poses a danger to themselves or others, managing dual relationships, or ensuring informed consent, ethical challenges can arise unexpectedly.
So ethics training programs can equip you with the knowledge and skills to cope with these dilemmas effectively.
Also, they present complex scenarios that require you to think critically and make tough decisions. The courses provide a safe space to explore different perspectives and outcomes, helping you prepare for real-life situations.
You can approach dilemmas with greater clarity and confidence by honing your ethical decision-making skills.
Staying Updated with Regulatory Changes
Mental health is evolving, with new research, technologies, and regulations emerging regularly. Keeping up with these changes allows you to maintain your license and provide the best possible care for your clients. CEUs in ethics let you stay informed about new laws and guidelines that impact your practice.
For example, changes in confidentiality laws, mandatory reporting requirements, or telehealth regulations can affect how you conduct your practice. Completing ethics CEUs keeps you updated on these changes, helping you remain compliant and avoid legal pitfalls.
Promoting a Culture of Ethical Practice
As a result of ethics CEUs, mental health experts can contribute to a culture of ethical practice throughout the profession.
When you prioritize ethical education, you can set a standard for your peers and colleagues. And this collective commitment to ethics enhances the profession’s reputation.
You can also become a role model for others in your career by going through ethics programs. This fosters a culture of continuous learning and ethical awareness, ultimately benefiting clients and the profession.
How To Choose the Right Ethics Programs
The next step is selecting the right courses to fulfill your continuing education requirements. Not all CEUs are created equal, so pick high-quality, reputable courses that provide valuable content and meet your state’s requirements.
Look for accredited courses from recognized organizations, such as the American Psychological Association (APA) or the National Association of Social Workers (NASW). The certifications enable you to meet the licensing boards’ standards and offer relevant, up-to-date information.
Consider the format of the courses as well. Online courses offer flexibility and convenience, allowing you to complete your CEUs at your own pace and from the comfort of your home or office. And they’re perfect for busy professionals who want to balance their education with their practice.
Protect Your Clients and Profession with Ethics Courses

Courses in ethics are like an insurance policy, which protects and empowers you to provide the best possible services to your clients. For this reason, Online CE Credits is a therapist-managed training platform with in-depth and on-demand ethics CEUs. It offers over 250 programs online from established therapists to allow you to study anytime, anywhere.
Ready to kickstart your ethics courses? Select from the accredited programs below:
How To Make the Most of Your Ethics CEUs
To get the most out of your CEUs in ethics, approach them with an open mind and a willingness to learn. Engage actively in the course material, participate in discussions, and reflect on how the concepts apply to your practice.
Also, consider keeping a journal to document your thoughts and insights, which’ll serve as a valuable resource for future reference.
Don’t hesitate to seek out additional resources or mentorship if you encounter ethical dilemmas that you find challenging. Discussing these issues with colleagues or supervisors can provide new perspectives and help you develop a more nuanced understanding.
Explore Ethics for Therapists
Remember, ethics CEUs are not just a requirement but an opportunity for growth. Embrace them to hone your professional skills, improve practice, and better serve your clients. Also, integrating ethics into your continuing education demonstrates your commitment to excellence and integrity.
In addition, ethics programs keep you updated on the latest ethical standards, advance your professional competence, and build trust with your clients. They equip you with the knowledge and skills to handle ethical dilemmas and maintain the highest standards of professional conduct.
Fuel Your Success with Nationally Approved Ethics Courses
If you’re looking for accredited programs in ethics for counselors, psychologists, social workers, or mental health professionals, you’re on the right platform. Online CE Credits provides nationally approved ethics CEUs to help you advance your career and fulfill licensure requirements. The best part? You can gain instant access to the lessons at affordable rates.
Don’t take our word for it. Stop just meeting the minimum requirements. Get the knowledge and skills to become a leader in ethics courses.
FAQS
What is the Universal Declaration of Ethics for psychologists?
The Universal Declaration of Ethics for Psychologists is a document that provides ethical guidelines for psychologists. It was developed by the American Psychological Association in 1953.
What happens if a psychologist breaks the code of ethics?
If a psychologist breaks the code of ethics, their professional organization may discipline them. This could include being fined, suspended, or having their license revoked. Additionally, they may be held liable for any damages caused to a client or the public.
What are the responsibilities of a psychologist in ethics?
A psychologist must follow the American Psychological Association’s code of ethics, which outlines their responsibilities to their patients, the public, and the profession. These responsibilities include providing competent and ethical care, maintaining confidentiality, and engaging in research that is in the public interest.
What are the violations of ethics in therapy?
Violations of ethics in therapy include engaging in sexual relationships with clients, providing inaccurate or misleading information, and exploiting clients for personal gain.













