loading...

by Tim Cassidy | Oct 11, 2024 | Certificate
Prolonged Exposure Therapy (PE) is an established, research-backed method for treating Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). As a mental health professional, gaining expertise in this approach can be transformative for client outcomes, especially for individuals dealing with trauma-related symptoms.
This article will explore essential techniques, practical insights, and key training elements of PE therapy to enable you to offer effective care to your clients.
The Basics of Prolonged Exposure Therapy

Dr. Edna Foa developed PE therapy, and it’s grounded in cognitive behavioural principles. The method is based on the idea that avoidance maintains PTSD symptoms. When individuals avoid trauma reminders or memories, their fears remain unprocessed. PE works by encouraging clients to gradually confront these fears, allowing them to process the traumatic memory and reduce their emotional response.
In PE, clients are encouraged to relive their trauma memory in a controlled environment through a process called “imaginal exposure” and to face real-life situations they’ve been avoiding, referred to as “in vivo exposure.” Both forms of exposure allow the brain to reprocess the traumatic memory in a way that reduces its power over time.
Importance of PE Training
For mental health professionals, having proper PE training is crucial. Without the right understanding of its structure and techniques, it’s easy to misapply the treatment, leading to negative experiences for clients. It’s also essential for therapists to know how to manage the emotional intensity that arises during sessions.
Training in PE not only sharpens clinical skills but also ensures that clients are safely and effectively guided through their recovery process.
Core Techniques of Prolonged Exposure Therapy
Prolonged Exposure Therapy consists of several key techniques that therapists must become familiar with during their training:
Imaginal Exposure

Imaginal exposure is perhaps the most important element of PE. This involves asking clients to recount their trauma memory in detail, in the present tense, as if they are reliving the event. The therapist guides this process in a way that helps the client stay in the experience long enough for emotional processing to occur.
Clients typically do this exercise in session, and the therapist will ask them to revisit the memory multiple times, with the goal of reducing emotional arousal. Sessions are recorded, and clients are asked to listen to the recordings between sessions to further desensitize themselves to the trauma memory.
Training therapists in this technique involves learning how to structure imaginary exposure sessions, guiding clients through difficult emotions, and assessing when it’s appropriate to push further or pull back. The practitioner’s tone, pacing, and ability to create a supportive space are key components in this process.
In Vivo Exposure
In vivo exposure involves confronting real-life situations that the client has been avoiding due to trauma. For example, someone who experienced a car accident might avoid driving. The therapist and client will work together to create a list of situations called a “fear hierarchy,” ranging from mildly distressing to highly distressing.
Clients are encouraged to face these situations gradually, moving up the hierarchy as their anxiety diminishes. Mental health professionals need to help clients identify these situations and ensure that they are approached with appropriate pacing. PE training equips therapists with strategies to balance challenge and safety, helping clients face their fears without becoming overwhelmed.
Processing and Reflection
After each exposure exercise, whether imaginary or in vivo, the practitioner engages the client in processing what happened during the exposure. This involves asking open-ended questions that help clients reflect on their emotional and physical reactions. It’s not uncommon for clients to experience new insights about their trauma, which allows them to reinterpret their experience in a way that’s less threatening.
PE training focuses heavily on helping clinicians learn how to guide these post-exposure discussions. It’s important for therapists to understand the emotional arc of the exposure and enable clients to recognize the progress they’re making, even if it feels uncomfortable in the moment.
PE Training: What To Expect

For those interested in becoming proficient in PE, there are a variety of training programs available. These range from basic workshops to intensive certifications, often provided by institutions specializing in trauma treatment or cognitive-behavioral therapy.
Training typically involves a mix of didactic instruction, role-playing, and supervised practice. Trainees are expected to practice the techniques in controlled environments. In some cases, they might be asked to treat actual clients under supervision. Learning how to handle client anxiety and discomfort is a big part of the training. You can learn how to manage sessions in which clients become emotionally dysregulated or resistant to the process.
One valuable aspect of PE training is the emphasis on self-awareness. Health professionals are encouraged to monitor their own emotional reactions during sessions. This is because working with trauma can be intense and triggering for therapists, too. Developing skills for self-care and emotional regulation is a vital part of any good PE training program.
Research Supporting PE’s Effectiveness
Prolonged Exposure Therapy’s effectiveness has been well documented through numerous studies and clinical trials. Research has consistently shown that PE can significantly reduce PTSD symptoms in a variety of populations, including combat veterans, survivors of sexual assault, and individuals affected by natural disasters.
One of the most compelling aspects of PE is its versatility. It has been adapted for use with different cultural groups. It can be delivered in individual, group, or even virtual formats. For therapists, this adaptability means that training in PE opens doors to serving a broad range of clients, making it a highly practical and impactful treatment modality to add to one’s skill set.
Practical Applications in a Clinical Setting
When implementing PE in practice, you need to strike a balance between structure and flexibility. Although PE is structured therapy with specific protocols, you should be attuned to the individual needs of each client. For instance, some clients might progress quickly through their fear hierarchy, while others may need more time. Likewise, certain trauma memories may be harder to engage with than others.
The PE therapist is prepared to handle these nuances, tailoring the treatment to meet the client where they are. This requires not only mastery of the techniques but also a strong therapeutic alliance, which is critical for clients to feel safe enough to engage in the emotionally intense work of trauma processing.
Another key to successful PE implementation is regular assessment. Clinicians must continually evaluate client progress to ensure the exposure exercises have the desired effect of reducing trauma-related distress.
If the client’s symptoms are not improving, you may need to adjust the treatment plan. PE training teaches therapists how to assess progress effectively and how to modify the therapy if it’s not producing the expected results.
Why Pursue PE Training?

PE training offers a concrete way to help clients move forward in their healing process. Unlike some therapies that rely heavily on insight or discussion, PE is an active, results-driven approach that focuses on doing. This can be incredibly empowering for clients who have felt stuck in their trauma for years.
Also, the evidence base supporting PE means that clinicians can feel confident about using a treatment with a high success rate. The intervention stands out as a proven intervention in a field where some therapies lack strong research backing. Investing time in training is a step toward providing clients with the best possible care.
Consider Other PSTD Therapy Interventions
Since PE also deals with PTSD, you can brush up your skills in other relevant therapies to empower your clients to recover from their mental health condition. Here are some modern courses to consider:
- Diagnosing PTSD and Other Trauma or Stressor-Related Disorders
- Written Exposure Therapy: Evidence-Based Tools for Trauma & PTSD
- Certificate in Evidence-Based PTSD Treatment
- ACT for Trauma & PTSD: Integrative Neuroscience-Informed Applications
- Cognitive Therapy Techniques for Trauma, PTSD, & Co-Occurring Addiction
Take Advantage of PE To Manage PTSD
In summary, Prolonged Exposure Therapy offers an effective, evidence-based approach to treating PTSD. Training can equip you with powerful tools to help clients confront and process their trauma. Through the use of imaginal and in vivo exposures, you can guide clients toward significant improvements in their symptoms, providing hope for a brighter future. And you can partner with Online CE Credits to enhance your PE therapy skills today!

by Tim Cassidy | Aug 20, 2024 | Certificate
Because of the ever-changing social work landscape, the ability to effectively engage with diverse populations is not just an asset; it’s a necessity. Social workers should provide support and resources to individuals from a wide range of cultural backgrounds. As a result of increasing diversity in communities, mastering cultural competence has become more critical than ever.
This is where specialized Continuing Education Units (CEUs) come into play. These educational opportunities empower social workers to enhance their cultural competence, resulting in improved client care.
Understanding Cultural Competence in Social Work
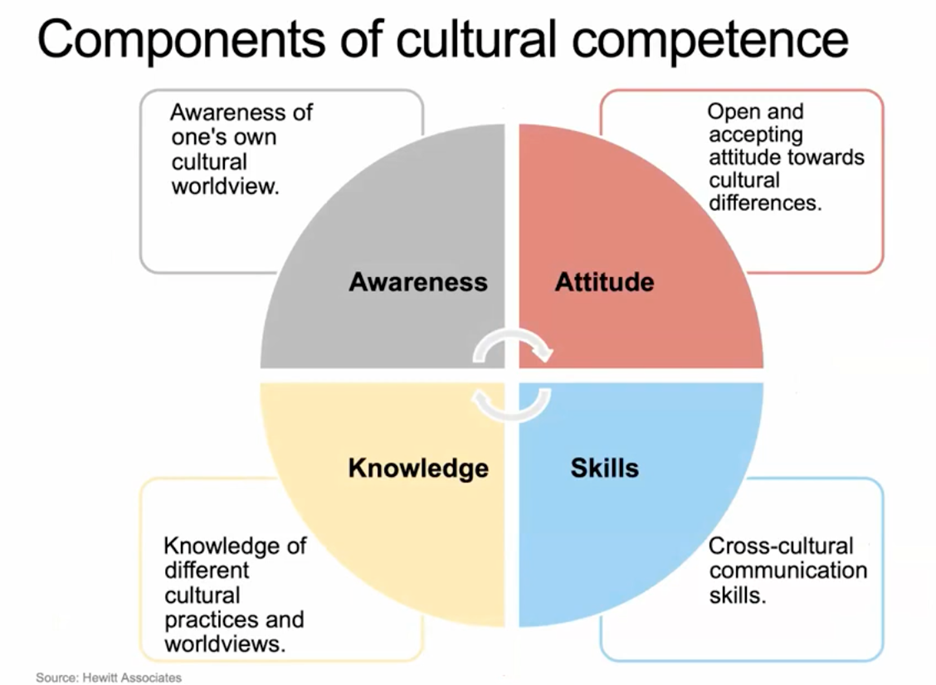
Cultural competence refers to the ability of social workers to understand, appreciate, and interact with individuals from cultures different from their own.
The National Association of Social Workers (NASW) defines social competence as “the process by which individuals and systems respond respectfully and effectively to people of all cultures, languages, classes, races, ethnic backgrounds, religions, spiritual traditions, immigration status, and other diversity factors in a manner that recognizes, affirms, and values the worth of individuals, families, and communities and protects and preserves the dignity of each.”
As a result, you must integrate cultural awareness into your practice. Cultural competence involves a deep understanding of one’s own cultural identity, an appreciation for the cultural backgrounds of others, and the skills to adapt interventions and communication styles accordingly.
Why Cultural Competence Is Crucial?
In social work, cultural competence is vital for several reasons:
Improved Client Outcomes:
When social workers are culturally competent, they can better understand their clients’ needs, leading to more effective interventions and improved outcomes.
Building Trust:
Clients are more likely to trust and engage with social workers who demonstrate respect for their cultural values and beliefs.
Ethical Practice:
Cultural competence aligns with the ethical principles of social work, including respect for the dignity and worth of individuals and the promotion of social justice.
Navigating Complex Issues:
Many social workers deal with complex issues such as immigration, racism, and systemic inequality. Cultural competence enables them to navigate these challenges effectively.
The Importance of CEUs in Enhancing Cultural Competence
Continuing Education Units (CEUs) are essential for social workers to stay updated on the latest research, best practices, and emerging trends in their field. When it comes to cultural competence, specialized CEUs offer targeted training that goes beyond general knowledge.
These courses provide in-depth insights into specific cultural groups, issues related to cultural diversity, and strategies for improving cultural competence in practice.
Here’s why specialized CEUs are crucial for mastering cultural competence in social work:
Continuous Learning:
Cultural norms and values are dynamic and can change over time. CEUs ensure that social workers are continually learning and adapting their practices to meet the needs of diverse populations.
Specialized Knowledge:
General training in cultural competence provides a foundation, but specialized CEUs dive deeper into specific cultural contexts, allowing social workers to gain expertise in working with particular groups.
Compliance and Certification:
Many states and professional organizations require social workers to complete a certain number of CEUs focused on cultural competence to maintain their licenses. These requirements emphasize the importance of cultural competence in ethical practice.
Enhanced Professional Development:
Specialized CEUs not only enhance cultural competence but also contribute to overall professional growth. They provide social workers with the skills and knowledge needed to excel in their careers and provide the highest level of care to their clients.
Key Areas Covered in Specialized Cultural Competence CEUs
Specialized CEUs in cultural competence cover a wide range of topics, each designed to equip social workers with the tools they need to work effectively with diverse populations. Below are some key areas typically covered in these courses:
Understanding Cultural Identity and Bias:
- CEUs often begin with a focus on self-awareness, helping social workers explore their own cultural identities and unconscious biases. This is a critical first step in developing cultural competence, as it allows practitioners to recognize how their own cultural background may influence their interactions with clients.
- Courses may include exercises and case studies that challenge social workers to identify and address their biases, fostering a more inclusive and empathetic approach to practice.
Cultural Humility:
- Cultural humility is an ongoing process of self-reflection and self-critique, acknowledging that understanding another’s culture is a lifelong journey. CEUs that focus on cultural humility teach social workers to approach each client with an openness to learn from them rather than assume expertise in their culture.
- This concept encourages social workers to build partnerships with clients based on mutual respect and learning, rather than imposing their own cultural norms.
Culturally Responsive Interventions:
- One of the most practical aspects of specialized CEUs is their training in culturally responsive interventions. Social workers learn to adapt their therapeutic techniques, communication styles, and intervention strategies to align with the cultural values and needs of their clients.
- This might include incorporating culturally specific practices, such as using spiritual or community-based approaches that resonate with the client’s cultural background.
Working with Specific Populations:
- Many CEUs offer focused training on working with specific cultural groups, such as African American, Latinx, Asian American, Indigenous communities, or immigrant populations. These courses provide in-depth knowledge of the cultural, historical, and social factors that influence the experiences of these groups.
- Social workers learn about common challenges faced by these populations, such as systemic racism, acculturation stress, and historical trauma, and how to address these issues in a culturally competent manner.
Addressing Cultural and Linguistic Barriers:
- Communication is a critical aspect of social work, and language barriers can significantly impact the effectiveness of interventions. CEUs often cover strategies for overcoming linguistic barriers, such as working with interpreters, learning key phrases in the client’s language, or using culturally relevant non-verbal communication.
- Additionally, social workers may learn about the importance of culturally appropriate body language, tone of voice, and other subtle communication cues that vary across cultures.
Cultural Competence in Policy and Advocacy:
- Cultural competence isn’t limited to direct practice. Social workers also need to understand how cultural factors influence social policies and advocacy efforts. CEUs in this area cover topics such as advocating for culturally inclusive policies, understanding the impact of laws on specific cultural groups, and working to dismantle systemic barriers to equity.
- This training empowers social workers to be effective advocates for social justice, ensuring that the needs of diverse communities are represented in policy decisions.
Ethical and Legal Considerations:
- Specialized CEUs also address the ethical and legal aspects of cultural competence. This includes understanding the implications of cultural competence for informed consent, confidentiality, and professional boundaries.
- Social workers learn how to navigate ethical dilemmas that may arise when cultural values conflict with professional standards, ensuring that they uphold the highest ethical standards in their practice.
Ramp Up Your Cultural Competence in Social Work

In a world increasingly interconnected, cultural competence is essential for effective social work. Our specialized CE courses equip you with the tools to bridge cultural divides, build trust, and provide effective care to diverse client populations. Don’t miss this opportunity to deepen your understanding and enhance your practice. Start your journey today and become a more culturally competent therapist.
Also, learn more about the latest suicide therapeutic interventions.
Benefits of Mastering Cultural Competence Through Specialized CEUs
The benefits of mastering cultural competence through specialized CEUs are far-reaching. They impact not only the social workers themselves but also their clients, colleagues, and the broader community. Some of the key advantages include:
Enhanced Client Relationships:
Clients are more likely to engage and participate in the therapeutic process when they feel understood and respected. Cultural competence fosters stronger, more trusting relationships between social workers and clients, leading to better therapeutic outcomes.
Increased Effectiveness of Interventions:
Culturally competent social workers can tailor their interventions to be more relevant and effective for each client. This personalized approach increases the likelihood of successful outcomes, as interventions are more closely aligned with the client’s cultural values and experiences.
Professional Growth and Competence:
Specialized CEUs contribute to ongoing professional development, ensuring that social workers remain competent and confident in their ability to serve diverse populations. This enhances their skills and makes them more competitive in the job market.
Contribution to Social Justice:
By mastering cultural competence, social workers play a crucial role in promoting social justice. They’re better equipped to advocate for marginalized communities, challenge systemic inequalities, and work towards a more inclusive society.
Ethical Practice:
Cultural competence is an ethical imperative in social work. By pursuing specialized CEUs, social workers can meet their ethical obligations to respect the dignity and worth of all individuals, regardless of their cultural background.
Choosing the Right CEUs for Cultural Competence
Selecting the right CEUs is crucial for effectively enhancing cultural competence. Practitioners should look for accredited courses from experts in the field tailored to their specific practice needs. Here are some tips for choosing the right CEUs:
Accreditation:
Ensure that the CEUs are accredited by a recognized professional organization or educational institution. This guarantees that the courses meet high standards of quality and relevance.
Instructor Expertise:
Look for courses taught by instructors with extensive experience in cultural competence and social work. Instructors with practical experience in diverse settings can provide valuable insights and real-world examples.
Relevance to Practice:
Choose CEUs that align with your specific practice area or the populations you work with. For example, if you work primarily with immigrant communities, pick courses that focus on the cultural and social issues relevant to these groups.
Interactive and Practical:
Courses that include interactive components, such as case studies, role-playing, and group discussions, are often more effective in building cultural competence. Practical exercises allow you to apply what you’ve learned in real-world scenarios.
Ongoing Learning:
Cultural competence is a lifelong journey. Consider choosing CEUs that offer opportunities for ongoing learning and development, such as advanced courses or a series of related training.

Improve Your Professional Practice by Understanding Cultural Competence
Mastering cultural competence is essential for social workers to provide effective, ethical, and compassionate care to all clients. Specialized CEUs offer a valuable opportunity to deepen your understanding of cultural diversity, enhance your practice skills, and contribute to social justice. You can advance your professional practice but also make a meaningful impact on the lives of the individuals and communities you serve by investing in your cultural competence.
Master Cultural Competence with Online CE
Unleash your potential as a culturally competent social worker. Our professional CE programs equip you with the tools to bridge cultural divides, build trust, and provide effective care to diverse client populations. Seize the opportunity to expand your horizons. Begin your learning experience today and become a more empathetic and effective therapist.

by Tim Cassidy | Aug 20, 2024 | Certificate
As a social worker in Michigan, staying current with your continuing education (CE) requirements is essential to maintaining your license and providing the best care to your clients. The social work landscape is ever-evolving, with new research, techniques, and ethical considerations continually emerging. As a result, Michigan’s requirements for Continuing Education Units (CEUs) enable practitioners to remain competent and up-to-date in their field.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about meeting your Michigan Social Work CEU requirements, from understanding the basics to finding the best courses to meet your needs.

Understanding Michigan Social Work CEU Requirements
What Are CEUs?
Continuing Education Units (CEUs) are a standardized measure used to quantify the time spent on professional development and learning activities. In Michigan, 1 CEU is equivalent to 10 contact hours of participation in an organized continuing education experience under responsible sponsorship, capable direction, and qualified instruction.
Michigan Social Work Licensure Levels
Michigan offers three levels of social work licensure:
CEU Requirements by License Type
LBSW and LMSW:
- Total CEUs Required: 45 CEUs every three years.
- Ethics Requirement: At least 5 of these hours must be in social work ethics.
- Pain and Symptom Management: At least 2 hours must focus on pain and symptom management.
- Human Trafficking: A one-time, one-hour training on human trafficking must be completed.
RSST:
- Total CEUs Required: 20 CEUs every three years.
- Ethics Requirement: At least 5 of these hours must be in social work ethics.
- Human Trafficking: A one-time, one-hour training on human trafficking must be completed.
Newly Licensed Social Workers
If you’re newly licensed, your CEU requirements are prorated based on when you received your license within three years. For example, if you’re licensed within the first year of the cycle, you would need to complete the full 45 CEUs (or 20 for RSST). If licensed in the second year, you would need 30 CEUs, and in the third year, 15 CEUs.
Meeting the Ethics Requirement
Ethical practice is the cornerstone of social work. Michigan mandates that all licensed social workers complete at least 5 hours of continuing education in ethics. This is crucial, as ethical dilemmas can arise in various aspects of social work, including confidentiality, dual relationships, and informed consent.
Recommended Topics for Ethics CEUs
- Boundaries in Social Work: Understanding the importance of boundaries to maintain professional relationships.
- Ethical Decision-Making Models: Learning different approaches to making ethical decisions.
- Cultural Competence and Ethics: Addressing ethical considerations in working with diverse populations.
- Technology and Ethics: Navigating ethical issues related to the use of technology and social media in social work.
Finding Ethics CEU Courses
Many organizations offer ethics-specific CEUs, both online and in-person. Make sure the content is relevant and applicable to your practice by looking for courses tailored to the unique challenges that social workers face.
Pain and Symptom Management CEUs
Michigan requires that all licensed social workers complete at least 2 hours of CEUs focused on pain and symptom management. The program teaches you how to help clients manage physical pain, which is especially relevant if you’re working in healthcare settings, hospice, or with populations experiencing chronic pain.
Topics Covered in Pain and Symptom Management CEUs
Understanding Pain:
Types of pain (acute vs. chronic) and their impacts on mental health.
Pain Assessment Tools:
Learning how to assess pain levels accurately.
Intervention Strategies:
Techniques for managing pain, including psychological approaches such as Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for pain management.
Multidisciplinary Approaches:
Collaborating with other healthcare providers to offer comprehensive pain management.
Future-Proof Your Social Work With Current CEUs
Need to ensure your license renewal and professional development are on track? Stay ahead of the curve with our comprehensive range of CE courses designed to develop your professional growth. Don’t let license renewal deadlines stress you out. Explore essential topics for social work professionals, including
The Human Trafficking Requirement
As a relatively new mandate, all social workers in Michigan must complete a one-time, one-hour training on human trafficking. This training aims to equip social workers with the knowledge to identify and intervene in cases of human trafficking.
What the Training Covers
- Understanding Human Trafficking: Definitions, types, and the scope of the problem
- Signs of Human Trafficking: How to Identify potential victims
- Intervention Strategies: What to do if you suspect someone is a victim of human trafficking
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: Understanding the laws surrounding human trafficking and your ethical obligations as a social worker
Where to Find Human Trafficking Training
The Michigan Department of Licensing and Regulatory Affairs (LARA) provides a list of approved human trafficking training programs. You can complete them online and usually fulfill the requirement in about an hour.
Choosing CEU Courses
When selecting CEU courses, it’s essential to consider the state’s requirements and your professional development goals. Here are some tips for selecting the best programs:
Accredited Providers
Always choose CEU courses from accredited providers. In Michigan, CEUs must be approved by the Michigan Social Work Continuing Education Collaborative. Courses from universities, professional associations, and recognized training organizations typically meet this standard.
Relevance to Your Practice
Pick courses relevant to your area of practice. For example, if you work primarily in clinical social work, courses on the latest therapeutic techniques or mental health trends would be beneficial. If you’re in a macro practice, policy development or organizational leadership certifications might be more applicable.
Course Format
Consider the format that works best for you—whether it’s in-person workshops, live webinars, or self-paced online courses. Online courses offer flexibility, allowing you to complete your CEUs at your convenience. On the other hand, in-person workshops can provide valuable networking opportunities and hands-on experience.
Cost and Time Investment
Compare the cost of courses and the time required to complete them. Some courses offer more CEUs for less time, but it’s essential to balance quantity with quality. Don’t just choose the cheapest option—make sure the course content is valuable and applicable to your work.

Record Keeping and Reporting
Maintaining accurate records of your CEUs is crucial. You must keep documentation of your completed CEUs for at least four years after the end of the renewal period in case of an audit by the Michigan Board of Social Work.
What to Keep:
- Certificates of Completion: These should include the course title, date, number of CEUs earned, and the provider’s accreditation information.
- Course Descriptions and Objectives: Keep a copy of the course syllabus or description to show the relevance of the course content.
- Transcripts: If you completed CEUs as part of an academic course, maintain transcript copies.
Reporting Your CEUs
When it’s time to renew your license, you’ll report your CEUs through the Michigan Online License Application/Renewal Service (MiPLUS). You must attest to completing the required number of CEUs, including the specific hours in ethics, pain management, and human trafficking.
Renewal Process and Deadlines
Social work licenses in Michigan are renewed every three years. It’s important to keep track of your renewal deadline and ensure all CEUs are completed well before this date to avoid any last-minute stress.
Late Renewals
If you miss the renewal deadline, your license will lapse, and you may not legally practice until it is reinstated. Late renewals require you to pay additional fees and submit proof of CEU completion.
Stay Abreast With Michigan Social Work Laws
Meeting the Michigan Social Work CEU requirements is a regulatory necessity and a commitment to your professional growth and the well-being of your clients. Your social work practice will continue to be high-quality if you select appropriate CEU courses and keep careful records.
Staying on top of your continuing education requirements is essential, regardless of when you started your career or how much experience you have. This will let you maintain your license, enhance your skills, expand your knowledge, and ultimately improve your patients’ lives.
Try Battle-Tested Online CE To Meet Licensure Requirements
Relax, and don’t worry about your license renewal. With expert-approved Online CE, you can easily fulfill your continuing education requirements while staying up-to-date on the latest trends and best practices. Enroll today and experience the convenience and flexibility of our online courses.

by Tim Cassidy | Oct 18, 2024 | Certificate
As a mental health professional, it’s natural to seek out training opportunities that enhance your skills without breaking the bank. Free resources are abundant, and they can be quite appealing when it comes to learning about various therapeutic approaches like Solution-Focused Therapy (SFT).
However, it’s essential to consider the benefits of investing in accredited courses, even when the free ones seem tempting.
The Appeal of Free Training and Its Limitations
Free online training can offer a quick overview and introduce key concepts, making them accessible to a wide audience. For practitioners just beginning their journey or those curious about different modalities, these resources might seem like a good starting point. However, they often lack depth, are not structured for professional development, and may not be created by experts in the field.

For practicing therapists, staying updated with evidence-based practices is not just about acquiring new knowledge. It’s about ensuring that your skills are in line with current standards, which ultimately affects the quality of care you provide to your clients. This is where accredited courses come in. They’re designed with a more rigorous approach, focusing on practical application, real-world scenarios, and feedback from experienced practitioners. For example, the SFT training program boasts instructors with decades of experience. Take a look at the course to ramp up your therapy skills.
Why Accreditation Matters?
Accredited courses are developed to meet the specific needs of professionals. They are often recognized by governing bodies, ensuring that the content is both relevant and up-to-date. Here’s why investing in these courses is beneficial:
Credibility and Recognition:
An accredited course provides a certificate that is recognized in the professional community. This credential is not just a piece of paper—it reflects a commitment to ongoing learning and adherence to professional standards. It can also be an essential requirement for renewing licenses or obtaining new ones in different states or countries.
Quality and Depth of Content:
Accredited training programs undergo a review process to ensure they meet certain standards. This typically means the content is more comprehensive, the instructors are qualified, and the material is based on the latest research. You’re not just learning what SFT is, but how to apply it effectively in various clinical settings.
Supervision and Feedback:
Many accredited programs offer opportunities for supervision or mentorship, something you won’t find in free courses. This one-on-one or group guidance can be invaluable in refining your approach, addressing challenges, and developing your unique therapeutic style.
Networking and Community:
Investing in a formal course often comes with the added benefit of connecting with other professionals in your field. This can lead to collaborative opportunities, professional support, and even friendships. The community aspect of learning should not be underestimated, as it provides a support system that can be crucial, especially in private practice settings.
The Practical Benefits for Your Practice
If you’re considering incorporating Solution-Focused Therapy into your practice, think about what kind of training will genuinely benefit your clients. Free resources might give you a brief overview, but they rarely equip you with the skills needed to handle the complexities of real client scenarios. On the other hand, accredited courses provide a structured pathway to mastery.
Here’s how they can make a tangible difference in your practice:
Increased Confidence:
With in-depth training, you’ll feel more confident in your ability to use SFT techniques effectively. This confidence translates into better client outcomes, as you’re more equipped to guide them through the therapeutic process with clarity and precision.
Better Client Outcomes:
When you’ve received training that’s grounded in evidence and best practices, it shows in your work. Clients benefit from techniques that have been tried and tested in clinical settings. You can help them navigate issues like complex trauma more efficiently, leading to quicker and more sustained results.
Professional Growth:
Accredited certifications often provide continuing education credits, which are necessary for maintaining your professional license. By doing so, you’re complying with regulatory requirements, growing as a therapist, keeping up with new developments, and continuously improving your skills.
Weighing the Costs
One of the biggest deterrents for many therapists when it comes to accredited courses is the cost. It’s understandable—these programs can be a significant financial investment. However, it’s essential to consider the long-term value of such an investment. It can also enhance your reputation, lead to more referrals, and increase your professional satisfaction and growth.

Also, many training organizations offer payment plans, scholarships, or sliding scale fees to make their courses more accessible. It’s worth reaching out to the providers to see what options are available. Remember, the goal is not just to add another certificate to your wall but to genuinely enhance your skills and effectiveness as a therapist.
Choosing from the Many Online Courses Available
The internet is flooded with online courses, and it can be overwhelming to choose the right one. Here are a few tips to help you make an informed decision:
Check the Instructor’s Credentials:
Look for courses taught by professionals who have extensive experience in Solution-Focused Therapy. It’s even better if they are still actively practicing, as they can provide relevant examples and up-to-date information.
Read Reviews and Testimonials:
See what other participants have to say about the course. Were they satisfied with the content? Did they feel it was worth the investment? Testimonials can give you a sense of what to expect.
Look for Interactive Elements:
Courses that include live sessions, Q&A opportunities, or peer discussions tend to be more engaging and effective. They allow you to clarify doubts and learn from others’ experiences, which can be invaluable.
Consider the Support Provided:
Good courses often offer additional resources like reading materials, case studies, and access to a community of learners. These extras can enhance your learning experience and provide ongoing support as you start implementing what you’ve learned.
Conclusion: Partner With Online CE Credits
While free Solution-Focused Therapy training resources can be a good introduction, they typically don’t offer the depth or quality needed for professional application. Accredited courses from Online CE Credits provide value that extends far beyond a single training session. They offer a structured path to mastering this therapeutic approach, ensuring that you’re equipped to deliver the best possible care to your clients. Investing in your education is, in essence, investing in your future practice and your client’s well-being.

by Tim Cassidy | Sep 10, 2024 | Certificate
EMDR (Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing) has long been a trusted approach in trauma therapy, known for its effectiveness in helping individuals process and heal from traumatic experiences. But as with all therapeutic techniques, EMDR has continued to develop, and EMDR 2.0 is the latest evolution, offering new methods that enhance its effectiveness.
EMDR 2.0 isn’t a total overhaul of the original method but rather an enrichment. It builds on the solid foundation of traditional EMDR while incorporating advancements in our understanding of trauma, memory, and neurobiology. For therapists, this presents an opportunity to provide even more nuanced and impactful care for clients dealing with trauma.
What Is EMDR 2.0?
EMDR 2.0 retains the core principles of standard EMDR but integrates additional elements designed to speed up and deepen the processing of traumatic memories. This enhanced version leverages recent research in neuropsychology and trauma to offer more effective interventions, particularly for clients with complex trauma.
One of the most notable aspects of EMDR 2.0 is its emphasis on maximizing the efficiency of bilateral stimulation (BLS). While traditional EMDR typically uses side-to-side eye movements, EMDR 2.0 encourages a more tailored approach, experimenting with variations in speed, intensity, and direction of the BLS. This fine-tuning aims to better match the client’s unique needs and how their brain processes information, potentially leading to a faster resolution of trauma.
Key Components of EMDR 2.0
EMDR 2.0 introduces several key enhancements that set it apart from its predecessor. Understanding these can help therapists make informed decisions about how to incorporate this method into their practice.
Enhanced Bilateral Stimulation:
Traditional EMDR relies heavily on side-to-side eye movements as the primary form of BLS. EMDR 2.0 expands on this by experimenting with the rhythm, direction, and speed of the eye movements or taps, adjusting them to better engage the brain’s processing systems. This customization can make the therapy more effective for individuals who may not have responded as well to the standard protocols.
Modified Target Planning:
EMDR 2.0 introduces more flexible approaches to selecting and processing target memories. Traditional EMDR often works through a hierarchy of traumatic events, starting with the most distressing. The new approach, however, allows for more adaptive sequencing, prioritizing targets based on the client’s current needs and readiness. This can be particularly beneficial for clients with multiple traumas or those who have difficulty accessing certain memories.
Somatic Integration:
Another enhancement in EMDR 2.0 is the greater integration of somatic experiences. The approach places more emphasis on connecting the mind and body, recognizing that trauma is often stored in the body as well as the mind. By incorporating body-based techniques and paying closer attention to physical sensations during sessions, therapists can help clients release trauma more fully.
Neurobiological Insights:
The latest research into how trauma affects the brain has informed the development of EMDR 2.0. This version places a stronger emphasis on the neurological underpinnings of trauma, helping therapists to target their interventions more precisely. This scientific grounding can make the therapy more understandable for clients, who may appreciate the clear explanations of how the process works.
Why EMDR 2.0 Matters in Trauma Therapy
Trauma is complex, and no two clients present with the exact same needs. EMDR 2.0’s ability to offer more personalized and adaptive interventions makes it a powerful tool for addressing a wide range of trauma-related issues.
For therapists, the ability to adjust the BLS to suit the individual’s processing style means that sessions can be more efficient. Clients may reach breakthroughs more quickly, and the therapy can be tailored to avoid overwhelming them with too much intensity or moving too slowly. This flexibility can be particularly helpful for clients with complex PTSD, where standard EMDR might struggle to produce results as quickly.

For example, one study showed significant improvement in PSTD treatment when Reprocessing EMDR 2.0 was combined with other therapy interventions.
The modified target planning is also a significant advantage. Trauma therapy can be unpredictable; memories and emotions can emerge in unexpected ways. EMDR 2.0’s flexible approach to target planning allows therapists to adjust on the fly, responding to the client’s needs in real-time. This adaptability can make sessions more effective and help prevent clients from feeling stuck or frustrated with the process.
Implementing EMDR 2.0 in Your Practice
If you’re already trained in EMDR, incorporating the principles of EMDR 2.0 might be a natural progression. The good news is that it doesn’t require abandoning the methods you already know. Instead, it’s about expanding your toolkit, refining your approach, and staying updated with the latest research.
Continuing education is essential here. Seek out training specifically designed for EMDR 2.0. These courses can provide you with hands-on experience and a deeper understanding of how to apply these techniques effectively. Additionally, consulting with peers who have already integrated EMDR 2.0 into their practice can be invaluable. They can offer practical advice, share their experiences, and help you navigate any challenges.
It’s also important to communicate these changes with your clients. Some may be apprehensive about new techniques, especially if they’ve had positive experiences with traditional EMDR. Take the time to explain how EMDR 2.0 works, why you’re adopting it, and how it could benefit their therapy. Clear communication can help build trust and encourage clients to engage with the process.
Level Up Your EMDR Therapy Skills Through Online Education
Want to stay ahead of the curve in your field? Our comprehensive EMDR courses are designed to equip you with the latest techniques and strategies. Master traditional EMDR methods and effectively address trauma in your clients. Our affordable online programs offer flexibility and convenience without compromising quality.

Invest in your professional growth and unlock the full potential of EMDR. Enroll today in the programs below and discover how our programs can enhance your therapeutic practice.
Potential Challenges and Considerations
As with any therapeutic approach, EMDR 2.0 isn’t without its challenges. Some clients may find the more intense BLS unsettling at first, especially if they’re used to the slower pace of traditional EMDR. It’s crucial to monitor their responses closely and be ready to adjust the intensity to ensure they remain comfortable and engaged.
Another consideration is the increased focus on somatic integration. Not all clients are comfortable with or ready for body-based work. It’s important to assess each client’s readiness and introduce these elements gradually, respecting their boundaries and comfort levels.
Lastly, staying up-to-date with the latest research and developments in EMDR 2.0 is vital. The field of trauma therapy is continually advancing, and what we know today may evolve further in the coming years. Regularly participating in training and staying connected with the broader EMDR community will help ensure that your practice remains effective and evidence-based.
The Future of Trauma Therapy with EMDR 2.0
The enhancements offered by EMDR 2.0 represent a significant step forward in trauma therapy. For therapists, this approach provides new tools to help clients process trauma more efficiently and effectively. For clients, it offers the promise of deeper healing and the potential to move past trauma more quickly.
Integrating EMDR 2.0 into your practice may require some adjustment, but the benefits it can bring to your clients make it a worthwhile endeavor. You can continue to provide the best care for those who turn to you for healing by staying informed, seeking out training, and being open to new techniques.
Integrate EMDR 2.0 Into Your Clinical Practice
The advancement of EMDR into its 2.0 iteration reflects a commitment to improving therapeutic outcomes in trauma care. You can help clients reclaim their lives from the grips of trauma by embracing these changes. Seize the opportunity to expand your horizons in EMDR via Online CE Credits.

by Tim Cassidy | Sep 3, 2024 | Certificate
Couples therapy is a cornerstone of relationship healing, offering a space where partners can work through challenges together. However, when traditional methods seem to stall, introducing Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) into couples therapy can unlock deeper levels of connection and understanding. This approach integrates the trauma-focused technique of EMDR into the relational dynamics of couples, helping partners address current conflicts and the underlying issues often rooted in past experiences.
For these reasons, Online CE Credits’ certification in EMDR covers the latest evidence-based therapies from seasoned practitioners with decades of experience. With this program, you can up your game in couples therapy to promote your clients’ healing.
Understanding EMDR’s Role in Couples Therapy
EMDR is often associated with treating trauma, but its applications extend beyond individual therapy. By focusing on how past traumas influence present behavior, EMDR provides a pathway for couples to explore how their personal histories impact their relationship. For many couples, unresolved trauma is an invisible barrier to intimacy, trust, and effective communication. EMDR helps by bringing these issues to the forefront in a way that feels safe and manageable, allowing both partners to address and process them together.
Imagine a couple where one partner has a history of abandonment. Even in a healthy relationship, this fear may manifest as PTSD, anxiety, distrust, or even sabotage. The partner might react disproportionately to perceived slights, creating tension that seems inexplicable. EMDR can help identify the root of these reactions, enabling the couple to see them not as personal failings but as remnants of past trauma. This understanding alone can transform how they relate to each other.
6 Signs of Couples Trauma (Infographic)

Creating a Safe Space for Healing
One of the most critical aspects of integrating EMDR into couples therapy is creating a safe space where both partners feel supported. This process often begins with individual sessions where each person works through their trauma separately. These sessions stabilize intense emotions and enable couples to approach each other from a place of empathy rather than defensiveness when they come together.
For example, during individual EMDR sessions, one partner might process memories related to childhood neglect. This processing could lead to a better understanding of why they struggle with vulnerability in their current relationship. Once both partners have had the opportunity to explore their histories, they come together in couples sessions, bringing a new level of awareness and readiness to connect.
Fostering Mutual Understanding and Empathy
In couples therapy, EMDR is not just about healing past wounds—it’s also about fostering mutual understanding and empathy. As partners share their experiences, they begin to see each other as the person standing before them and as individuals shaped by their pasts. This perspective shift can soften judgments, making it easier to approach conflicts with compassion.
Let’s consider a situation where one partner has experienced significant trauma that the other doesn’t fully understand. Without EMDR, the non-traumatized partner might struggle to empathize, leading to feelings of isolation and resentment. With EMDR, the process of sharing and understanding these experiences can create a bridge between them. They begin to see each other’s reactions not as random or irrational, but as understandable responses to deep-seated fears and hurts.
Enhancing Communication and Conflict Resolution
EMDR’s impact on communication in couples therapy is profound. Often, past traumas disrupt how individuals express themselves or listen to their partners. They might shut down, become overly defensive, or misinterpret their partner’s intentions. EMDR helps clear these emotional blockages, paving the way for more open and effective communication.
For instance, a partner who has always responded to conflict with anger might, through EMDR, uncover a history of feeling unheard or dismissed as a child. Understanding this link allows them to articulate their feelings more clearly and respond to their partner without the cloud of past pain. The other partner, in turn, can respond with greater empathy, knowing the deeper reasons behind the anger. This mutual understanding can significantly reduce the frequency and intensity of conflicts, allowing the couple to navigate disagreements in a more constructive manner.
Strengthening Emotional Bonds
EMDR doesn’t just help couples manage conflict; it can also deepen their emotional connection. When partners process their traumas together, they often experience a renewed sense of intimacy. They see each other’s vulnerabilities and strengths more clearly, leading to a deeper bond. This emotional intimacy is the bedrock of a strong relationship, providing resilience against future challenges.
Consider a couple who has been distant due to unaddressed trauma. As they go through EMDR together, they start to feel more connected. This is because they’re resolving past issues together. They begin to see their relationship as a safe haven, a place where they can heal and grow as a unit. This shift can turn a struggling relationship into a thriving one.
Advance Your Career in Couples Therapy With Trauma-Focused Courses
Wish you knew about our nationally approved certifications sooner? Our continuing education courses can help you achieve your professional goals faster than you ever thought possible. Enroll in the accredited CE courses below to enhance your trauma therapy for couples.
Real-Life Success Stories
Real-world examples highlight how transformative EMDR can be for couples.
One couple was on the brink of separation due to constant arguments and misunderstandings. However, they discovered through EMDR that they were reacting to unresolved trauma—one from a chaotic childhood and the other from a history of emotional neglect. By working through these issues in individual and joint sessions, they understood each other’s triggers and needs more clearly. This understanding led to fewer arguments and a stronger, more compassionate connection.
Another couple found that EMDR helped them break a cycle of mistrust. One partner’s past infidelity had shattered the trust in their relationship, and despite their best efforts, they couldn’t move past it. Through EMDR, the unfaithful partner processed the guilt and shame that fueled their destructive behavior, while the other partner worked through the betrayal trauma. Over time, they rebuilt trust on a foundation of honesty and mutual understanding, something they hadn’t thought possible before starting EMDR.
Integrating EMDR with Traditional Couples Therapy

EMDR doesn’t replace traditional couples therapy but enhances it. Therapists often blend EMDR with techniques like Emotionally Focused Therapy (EFT) or the Gottman Method, creating a comprehensive approach that addresses both the emotional and cognitive aspects of relationship challenges. By combining these methods, therapists can offer a more tailored experience that meets each couple’s unique needs.
For example, a therapist might use EMDR to help one partner process trauma that’s impacting their ability to engage in EFT’s emotional bonding exercises. Or, they might integrate EMDR with the Gottman Method’s focus on communication and conflict resolution. This ensures past traumas don’t derail the progress being made in therapy. The integration allows for a more personalized and effective therapy experience.
The Future of Relationship Healing
In the hands of a skilled therapist, EMDR couples therapy offers a powerful way to address the deeper issues that often underlie relationship struggles. It provides a pathway for managing conflict and fostering understanding, empathy, and connection. For couples willing to embark on this journey, EMDR can be a transformative experience. It can strengthen their relationship and lay the groundwork for a healthier, happier future together.
As more therapists integrate EMDR into their work with couples, the potential for this approach to revolutionize relationship therapy continues to grow. The benefits of EMDR go beyond helping couples cope with their challenges; they help them thrive. Begin your learning experience today.




















